Instructions for setting up and connecting Wi-Fi on Xiaomi routers. Instructions for setting up and connecting Wi-Fi on Xiaomi routers Xiaomi wireless smart wifi 3 router
The Xiaomi brand is primarily famous for its mobile devices. They have long won the hearts of customers thanks to their excellent combination of price and technical capabilities. However, Xiaomi's product line is much wider than it seems at first glance. In the company's assortment you can find various products, everyone will find what they need. Today we’ll look at the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router. This model has a low price and attractive characteristics, which can interest the residents of our country. Today we’ll tell you how to set up a Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router. We’ll also get acquainted with its features.
The device is equipped with an MT7620 processor with a frequency of 580 MHz. The Xiaomi router has 128 MB of RAM and 128 MB of internal memory. There are two wireless radio units. The first is at 2.4 GHz and speeds up to 300 Mb/s, and the second is at 5 GHz with connectivity up to 867 Mb/s. The cables to the router are connected to the WAN port and two LAN inputs, the speed of each reaches 100 Mb/s. In addition, there is a USB 2.0 connector.
The strength of the model is that it belongs to a very affordable price range. At the same time, the device can be safely called balanced, which cannot but attract attention. Also a plus was the radio unit operating at a frequency of 5 GHz. Of course, speeds up to 867 Mb/s are not always needed. But it’s nice to have a device with such capabilities.
Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router in action
The processor resource allows the router to work without problems. The device maintains stable communication, no drawdowns were noticed. If the optimal firmware is installed, then the performance will not cause any complaints. You also need to properly configure the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router, but more on that later. The tests showed that the router, when operating in IPoE and PPPoE modes, reached 90 Mb/s. This is if we talk about one-way transmission, but even in full-duplex modes the device behaves quite decently. Impressive performance was a result of the use of a good hardware accelerator embedded in the chip.

The Xiaomi router has difficulties using the L2TP and PPTP modes; the speed level is significantly reduced. It can be seen that they are poorly optimized, but this is not particularly upsetting, because these modes are not so common. For full operation, what the PPPoE and IPoE modes offer is enough. Using a VPN, data is downloaded from the World Wide Web and the local network from your provider. In this case, the speed does not decrease, it even increases in certain scenarios. As you can see, the parameters of the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi Router 3 router are quite good; we’ll talk about how to configure it further.

Setting up a Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router
The main difficulty in connecting and setting up the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router is the inscriptions in Chinese. However, this cannot be called an obstacle to connecting the device for further use. For those who do not understand how to configure the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router in Russian, we can recommend various services, for example, Google Translate. After all, the setup is done online. Thus, entering the necessary settings will not be difficult, because everything is clear. In addition, you can immediately update the firmware to the latest version, if one is offered, this is an additional benefit of online configuration. However, not all users know how to connect a Xiaomi router to the Internet. To do this, you need to make a considerable effort to become familiar with the interface that the device is equipped with. It is important to follow the correct sequence of actions. Then you won’t need much time to set up the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi 3 router; step-by-step instructions can help you in this matter.

We go to the resource http://miwifi.com/, it will act as an interface. The setup of the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi router has begun. We enter the necessary data in the appropriate fields, which includes the passwords of the admin panel, as well as your Wi-Fi. After these steps, the automatic configuration of the router will start. It will reboot, after which it will display that the installation is complete.
But before you configure Xiaomi Router 3 completely, you need to connect again. The same passwords are used this time. We gain access to the control panel, now we see four tabs - memory, routing status, general and additional settings. First we need the general settings section; all available fields are filled in here. This will allow the router to connect to the Internet.

It would also be a good idea to familiarize yourself with the remaining tabs. With their help, software is updated, VPN is turned on and off, backups are made, and much more. Here is the answer to the question: how to configure the Xiaomi 3 router. But if you have not encountered all this before, at first you should not touch tabs that are not related to general settings. It’s better to understand everything well; the connected options can lead to a significant reduction in speed limits.
What is alternative firmware?
It is recommended to use standard software, but many are interested in how to configure a Xiaomi router using alternative firmware. For example, you can use the developer version, which opens the built-in operating system to the user. Due to this, functionality is expanded, performance and stability are increased, as well as the level of speed. Alas, such firmware cannot be found in finished form. However, you can use available open source sources for your own purposes to create a prototype firmware that will be customized to your preferences. You need to work hard to get the treasured advantages, such as support for PPTP and L2TP modes, Russian and English interface languages, an increase in the number of connected USB devices, and so on.

However, it is better to contact a specialist, since independent actions can lead to a complete stop of the router. Also, unskilled intervention in the settings can lead to loss of remote control of services, and options related to mobile devices may also become unavailable.
Work together with Mi Wi-Fi+
Many have heard about such a device as Mi Wi-Fi+. It essentially duplicates the operation of the main device, that is, the router. Although there are different opinions about this gadget. Some consider it a repeater, while others consider it a Wi-Fi signal booster. If you use it in conjunction with a router, the coverage area will expand significantly. The price of Mi Wi-Fi+ is approximately $8, it is extremely convenient to use due to its compact size. To understand how to connect the Xiaomi Router 3 router with this gadget to the Internet, you don’t need any special knowledge, everything is quite simple. When two devices operate simultaneously, the signal will become more stable or appear where there was none at all. But you shouldn’t get too carried away with the operation of the router together with Mi Wi-Fi+, although this gives some positive results. This may negatively impact your overall connection speed.

Conclusion
This device from a well-known Chinese manufacturer rightfully takes its place among the best routers in the mid-price category. And it’s not at all difficult to figure out how to configure the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi router; the router turned out to be simple and effective in operation. And the tempting price tag, good technical components, along with reliability make it very interesting in the eyes of the buyer. Xiaomi manages to do well not only smartphones; other products are also worthy of attention.
For initial setup, it is most convenient to use the MiWiFi mobile application; you can download it by reading the QR code from the original packaging.



On Xiaomi smartphones with the proprietary MIUI shell, to call the scanner, just swipe from top to bottom to call the information panel. In the right corner of the search field there is an icon for calling the scanner.
In principle, the application can be found manually on Google Play, it is called MiWiFi Router.


When you first launch the application, you will be prompted to create a new Mi account, or log into an existing one. On Xiaomi smartphones, you can log into your existing account with just one click, the system will automatically detect all login parameters.

You need to connect to the router's wireless network in advance. On Mi smartphones, “native” routers are marked in the list of networks with a proprietary logo. After connecting to a wireless network, the application searches for devices on the network.

The setup process is extremely simple and resembles setting up a Zyxel Keenetic router using the appropriate mobile application. A special step-by-step wizard is used in which only the most important parameters are configured.

After changing the wireless network settings, the application will automatically switch the smartphone to the new network. Everything is as automated as possible and does not require user participation. Just right for beginners and inexperienced users.
By the time this publication was completed, the application had been updated with minor interface changes. The menu is divided into 4 categories: Mi Router, Storage, Plug-ins, Settings.


In the Mi Router section, you can switch between several routers (if there are several of them), as well as view statistics on traffic and connected devices.
The Storage section is aimed at using an external hard drive. On Xiaomi routers, you can deploy a small cloud, which can be configured to upload files from your smartphone when it is connected to your home network. The function is aimed at owners of Xiaomi smartphones. However, there is a desktop client for PC and Mac, which will allow you to use the functionality of the device as a regular network drive.

The plugins section contains router settings regarding its direct functions. But such settings as password, time zone, etc. moved to a separate settings section.




You get used to the application very quickly, after which you unmistakably find yourself in the required section. For experienced users, the list of available options will be clearly insufficient, for example, there are no IPTV settings, no support for 3G modems, and in general, all options and settings are greatly simplified and optimized for inexperienced users.
Xiaomi routers are greatly simplified in terms of settings and make them an ideal option for inexperienced users who require a simple and reliable solution.
A little more settings are available through the web interface, which is accessible via the domain name miwifi.com, or IP 192.168.31.1 (sometimes 192.168.28.1).
By the way, if you use Kaspersky Anti-Virus, for unknown reasons, sometimes it blocks access to IP 192.168.31.1 and 192.168.28.1 via the HTTP protocol, which makes access to the web interface impossible. It helps to disable the antivirus and change the home subnet in the router settings to the more familiar 192.168.0.0/24, 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24. There shouldn't be any problems in the future.
If you are setting up your router for the first time without using the mobile app, you will also be greeted with a setup wizard when you first launch it.
Below you can see all the available options that can be configured using the web interface.








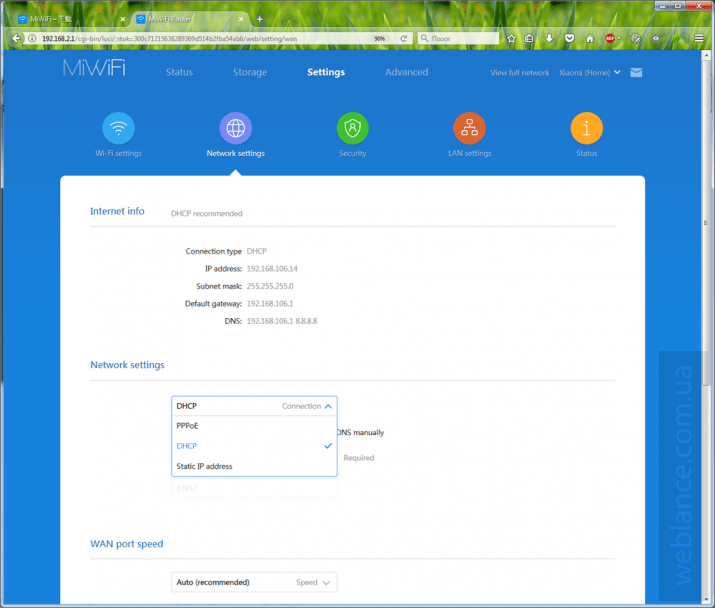













The list of available options is much wider than in the mobile application.
There are a couple of notes on the settings and use of the interface. Firstly, the QoS option should not be enabled if necessary. The fact is that by default, all traffic passes using HW_NAT (hardware NAT), without creating a load on the central processor. To be more precise, when processing 94 Mbit/s? CPU usage will be only 2-4%. When QoS is activated, the use of HW_NAT will become impossible and all traffic will go through the processor. The more devices there are on the network and the faster the connection speed, the higher the processor load will be, up to 100%.
WiFi performance and quality
Both routers have an excellent processor that provides good performance.
Please note that MiWiFi devices are designed primarily for the domestic market of China, which is why support for L2TP and PPTP is implemented here in a basic form.
When using native firmware, in conjunction with L2TP/PPTP, you can only count on 50-60 Mbit. For those who like to work with files, we inform you that on alternative firmware both routers can easily provide up to 100 Mbit when working with VPN and much more.
Regarding the most common types of connection via DHCP/Static IP/PPPoE/IPoE, there are no complaints at all about routers with stock firmware; you are guaranteed up to 95 Mbit.
Regarding Wi-Fi, to be honest, both routers were a very pleasant surprise. When setting the maximum power level to “Block” (on some versions of the firmware “Wall penetration”), both routers “pierce” solid load-bearing walls without any problems.




Quite expectedly, Mi WiFi Mini is slightly inferior to Mi WiFi Router 3 in signal level, which is clearly visible in the broadcast scans.


The older model provides a higher signal level in both the 2.4 and 5 GHz range. Sometimes this difference can reach 10 dBm, but most often the difference does not exceed 2-4 dBm.
Many users have a question: why do we need 5 GHz support in a router that is equipped with 100 Mbit ports?
In “spherical vacuum” conditions, 802.11n in the 2.4 GHz range using MIMO 2x2 and 40 MHz channels pumps 94-95 Mbit without problems. In actual operating conditions, especially in apartment buildings, the 2.4 band is loaded to such an extent that even 50 Mbit will be an excellent result.
The 5 GHz band provides more non-overlapping channels and higher speeds.
Let's look at a real example. I have a laptop that supports the 5 GHz band, but does not support 802.11ac (802.11n only). We placed the laptop at a distance of 8 meters from the MiWiFi Router 3, between the devices there is 1 load-bearing solid brick wall (~55 cm) and 2 half-brick walls.

In 802.11n + MIMO 2x2 + 5 GHz mode, we received an average of 90 Mbps over the air. This is an excellent result.
Now let's see what will happen in real conditions for 2.4 GHz.

Less than 20 Mbit, just, no comments here. As you can see, there are benefits from 5 GHz even on older devices.

Let's see if a proprietary extender can correct the situation. Just for fun, we tried placing the Mi WiFi Amplifier in the middle. As a result, the speed became more stable and rose to 21-22 Mbit.
To be honest, I didn’t expect any special results from WiFi Amplifier. The problem is that, wanting to make the device cheap, the company greatly overdid it. The extender only supports legacy 802.11b/g/n standards, SISO (MIMO 1x1) configuration and internal antenna. As a result, ideally 150 Mbit of channel speed is available, which must be divided between clients and the uplink. In noisy air conditions we get the same 20-40 Mbit.
Mi WiFi Amplifier is capable of increasing the coverage radius, but you shouldn’t expect great speed from it. The expander is more suitable for “smart home” and “Internet of things”, when the network does not have high speed demands.
Finally
After two weeks of using both routers (daisy-chain connections), I did not have any problems in terms of network speed and stability.
There are still some comments, but they relate to the features of the software. There is no usual Russian language, there is Chinese and English. When you try to update from the official website, you may receive a device entirely in Chinese. To switch to English, you need to set the “Europe” region in the Wi-Fi settings, after which English will become available. There are also special English firmwares, which is what we recommend using, or alternative ones if you have the necessary knowledge to install them.
If you're looking for a router that's inexpensive yet powerful and easy to set up, both models are a great buy, especially if you own a Xiaomi smartphone.
One of the minuses should also be noted is the limited list of available settings on official firmware.
Online course on network technologies
I recommend Dmitry Skoromnov's course "". The course is not tied to the equipment of any manufacturer. It provides fundamental knowledge that every system administrator should have. Unfortunately, many administrators, even with 5 years of experience, often do not have even half of this knowledge. The course covers many different topics in simple language. For example: OSI model, encapsulation, collision and broadcast domains, loopback, QoS, VPN, NAT, DNS, Wi-Fi and many other topics.
I will separately note the topic of IP addressing. It describes in simple language how to make conversions from the decimal number system to the binary system and vice versa, calculations by IP address and mask: network addresses, broadcast addresses, number of network hosts, subnetting and other topics related to IP addressing.
The course has two versions: paid and free.
In comments to almost any material about “hardware” there are often statements in the spirit of: “Well, why is it needed? There is almost the same thing, but N times cheaper in Chinese online stores.” Xiaomi products were also mentioned in discussions of other routers. Well, let's see how good Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 is for Russian users. Fortunately, he is a purebred Chinese, and he came to us from the Chinese store GearBest. At the time of writing, the average price of this model was in the region of 2-2.5 thousand rubles, which, in general, is not much for what at first glance is a very decent hardware filling. However, as always, during testing various nuances emerged, which we will talk about.
Equipment and appearance
It's no secret that Xiaomi is trying to save as much as possible on the hardware of devices and a number of other aspects of doing business. At the same time, she manages to maintain a balance between accessibility and quality of the final product. Mi WiFi 3 is no exception. The router comes in simple but attractive packaging - a white box made of thick cardboard. True, this density did not in any way affect the fact that the box reached the editorial office in a very deplorable condition - dented in the middle and with damaged corners. Fortunately, the router itself was not damaged, although it only had a small bag for protection, which would hardly have saved the device if it got wet or had a little more pressure from above.
Let me immediately note that this is not an attempt to denigrate the device out of hand. Not at all, the developers also saved a little on packaging. As well as the rejection of the “garland” of indicators on the front panel. There's only one of them - it's hidden in a small recess on the front end, but it's three-colored and can be turned off in the settings. Exactly the same savings are seen in the refusal from removable antennas, from installing the so familiar five network ports - there are only three of them, and those are only 100 Mbit/s, because the SoC supports exactly this speed, and installing a gigabit switch is not free. All of them are equipped with their own non-switchable activity indicators. For the same reason, the router doesn’t even have a power button - all these are not very necessary components, on each of which you can save from a few cents to tens of cents.
In addition to the opportunity to reduce costs, thanks to the elimination of some elements, the printed circuit board will be smaller (it actually takes up less than half of the device body), and the wiring on it will be simpler. There isn't even a patch cord included. There is only a small power supply - in this case with an American plug, but designed for a 110-240 V network. Well, and also a small paper instruction. In Chinese. By the way, all information on the packaging is also presented in Chinese. And even the firmware based on OpenWRT (also saving money) has a web interface exclusively in Chinese. On previous router models, some sellers pre-installed a modified version of the firmware with English localization, but in our case there was nothing like that.
At the same time, the device itself looks nice: matte, non-marking white plastic, thin body, small dimensions. All ports are traditionally located on the rear panel. The bottom of the case is dotted with ventilation holes; there are no rubber feet or holes for attaching the router to the wall. During operation, the device heats up moderately.
Specifications
At first glance, the hardware is quite good: the MediaTek MT7620A SoC and the MT7612E ac radio module have long been familiar to us. Both chips are inexpensive and popular solutions. The main complaint about this particular configuration is that the manufacturer did not want to supplement this pair with a gigabit switch. And the dual-channel Wi-Fi 802.11ac module could also be abandoned. But the developers did not skimp on memory - the volume of main and RAM is 128 MB, which is very rare for devices of this class. The description even emphasizes that SLC NAND is used. In general, the calculation of the creators is clear - attractiveness for the user can be ensured not only by powerful hardware, but also by good firmware. In addition, Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 has a USB 2.0 port designed for connecting external drives.
Possibilities
Perhaps, for the first time, we will consider in detail not the web interface of the router, but the mobile application for managing the device. Why? Because the router's web interface, as well as desktop applications, is only available in Chinese. Of course, for the “web face” you can use some online translation plugin in the browser. The same Google Translate tolerably translates most of the controls into English. In Russian too, but again not without problems. However, for this you need to have an already configured Internet connection on the WAN interface of the router.

Mi Router app for Android
However, it is much easier to use a mobile application for Android or iOS. When you turn it on for the first time, the router creates an open wireless network to which you need to connect your smartphone. First of all, the application will offer to configure Internet access via IPoE (direct connection) or PPPoE, as well as set the parameters of both Wi-Fi networks and the administrator password, which by default is the same as for the networks. Please note that without Internet access to both the router and the application at the same time, the latter will not actually work after the initial setup! After this, the application will offer to link the router to your Xiaomi account in order to manage the router remotely via the Internet and save a backup copy of the settings. You can also add other administrators.
|
|
|
|
|
It will be easier for owners of Mi smartphones - Xiaomi routers are marked in their list of wireless networks, and an account has already been created. And by the way, it will also be needed to activate some additional functions. If your Internet connection uses PPTP/L2TP, then the initial setup will still have to be done using the web interface. Both of these protocols, although supported by the router, are - as in almost the whole world - considered as a means of accessing the corporate network or for protecting information. In the settings, you can even choose what kind of traffic will be sent to the VPN tunnel. And yes, some parameters are available only through the web interface: advanced Wi-Fi and LAN/WAN settings, DDNS, port forwarding/forwarding, router load graphs. The other part is only available in the application.
|
|
|
|
|
Immediately after setting up access to the Network, the router does one very “smart” thing - it measures the connection speed and immediately records the obtained indicators as the maximum available in the settings of the shaper enabled by default (indicated as QoS). And since it obviously communicates with Chinese servers, all this amateur activity must be immediately stopped, either by disabling the shaper altogether, or by manually setting the real speed values. Even if you have a gigabit channel, and the router measured the speed and received, for example, 30 Mbit/s, then clients will not receive anything higher than this “thirty”. If you still decide to use this function, then there are three options for the shaper: automatic selection of Network access priority for each client, manual selection of one of the three available priorities, manual setting of the maximum values of incoming and outgoing speeds.
|
|
|
|
|
The router independently tries to determine the type and manufacturer of each client device. Apparently, he does this using the MAC address, and therefore is often confused in the readings. Yes, yes, this is a small thing, but there are a lot of such little things in the application. The annoying reminder about changing the time zone alone is worth it - you simply cannot select Moscow time, although it is present in the list of zones. Or, for example, it is impossible to disable a video plugin once enabled, which will also remind you of itself with notifications. Or a built-in reference book available only in Chinese. Or... Oh, it doesn’t matter, the shortcomings will be discussed separately during the text.
|
|
|
|
|
So, the first tab of the application shows a list of clients and current data transfer rates. Clients that consume too much of the Internet channel are flagged separately. For each client you can see the amount of traffic consumed. In the client settings, you can rename it (taking into account the above, this function is incredibly useful) and select a short description (for example, “friend’s smartphone”). There you can also reconfigure the shaper, select the mode of operation with a USB drive, enable notification of the client connecting to the local network or completely block access to it, and also configure Internet access settings. The last function is the simplest implementation of parental control, as it offers to block access to the Internet completely or set up an access schedule, and at the same time enable a white or black list of URLs.
|
|
|
|
|
To work with a USB drive, the application has a good file manager with which you can receive and send files, manage folders, backup data (folders and files) from your phone to the drive, and also view images. In MIUI 7, the standard file manager, when connected to Wi-Fi, recognizes the router and gives access to the drive. In addition, the application settings have a useful function for automatically copying recent images and videos from your smartphone to a USB drive. Mi TV owners can stream multimedia files from their smartphone to their TV. For all other clients, working with the drive is only possible via SMB, for which you will have to install a separate plugin. There is no distribution of access rights - for each client you can choose full access either to shared folders or to the entire disk at once.
Working with the drive
Theoretically, you can upload and download files remotely via the Internet without being connected to the router’s Wi-Fi network, but in fact you can only view pictures, and even then with very long delays. Apparently, all remote work with the router is “proxyed” through the manufacturer’s servers. In addition, the application has a somewhat controversial “optimization” - when you open any image, not only it is loaded, but also the previous and next images. So it takes a minute to open a half-megabyte photo, and an attempt to download an MP3 file to a smartphone ends in failure. China probably doesn't have this problem.|
|
|
|
|
Chinese users should not have problems with the function of accessing video services - they are all presented on the next tab of the application. They are designed only for users from the Middle Kingdom, and they are directly pushed towards piracy. The search section displays the most frequently requested films, TV series and TV shows - for many of them you can select the episode and video quality. Surprisingly, you can even try asking a query in Russian in the search bar and get corresponding videos in the search results. Alas, they will almost certainly still have Chinese voice acting, and they will be downloaded at a meager speed, if the download starts at all. In fact, video search is carried out on the eDonkey network.
|
|
|
|
|
Additional functions
Finally, the last tab is reserved for various additional options and plugins. Some of them are quite strange. For example, in the Optimization section there are mysterious functions that, judging by the names, offer some kind of improvements to web surfing and apparently interfere with traffic. In fact, they do not work, since they are probably designed for Sinet. The function of allegedly optimizing the operation of a smartphone, which looks for junk files, looks no less strange. Why anti-virus databases and offline maps, in particular, are considered garbage is not very clear. And how their removal will affect the speed of work - too. The list also includes one plugin for China Unicom users (according to Google Translate).|
|
|
|
|
In addition, in additional settings you can enable two schedules. The first, relatively useful one, allows you to set the Wi-Fi operating time. The second gives rise to some bad feelings, as it controls the periodic reboot of the router. However, among all the additions there are some really useful ones. Firstly, the ad blocking module, which, of the banner networks common in Russia, seems to know only about Google. Secondly, the “Wi-Fi acceleration” module. If the application considers that the signal from the router is too weak, it will offer to correct this situation by switching to another band or changing the settings of the radio modules.
|
|
|
|
|
The implementation of a kind of task manager is also interesting. It shows the current memory and processor load, as well as data transfer rates - both overall and for individual modules. Moreover, the work of these modules can be completed manually or completely disabled. Another unusual feature is the way you organize access to the guest network. In addition to the usual password, you can also somehow let your friends from the WeChat messenger into it (could not be verified). There is also another strange item for launching the Diangping geoservice, which shows the nearest points of interest (POI) on the map. In this case, it displays a list of nearby establishments with free Wi-Fi.
|
|
|
|
|
Finally, the last important module is a firewall and antivirus in one bottle. Yes, that’s right, the application has a built-in antivirus. The whole thing works on the basis of Baidu Security cloud services, which, judging by the description, are potentially useful. They protect against dangerous sites, malware and data leaks. This plugin also evaluates how secure the settings of the router itself are. True, by default all this protection is not enabled, and, in addition, in the plugin itself it was not possible to add at least one device to the list of blocked devices. It is difficult to judge the effectiveness of this module. For example, he several times allowed the download of Android malware, which has been spreading through a large advertising network for several weeks now and which almost all known antiviruses know about.
Baidu Security Firewall and Antivirus
In general, the Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 firmware is very unusual and unusual. Frankly, I liked this approach, when there are separately plug-in extensions and a mobile application for managing functions. I would like to see something similar from other manufacturers. Perhaps the closest analogue is the new ZyXEL Keenetic. However, they cannot be compared directly. The main drawback of the Mi WiFi 3 firmware is that it was created for Chinese users. Therefore, VPN connections are not basic here, there is not even basic support for IPTV, and some of the functions are meaningless. And this is not to mention the complete absence of Russian localization and too strong dependence on Internet access. However, if you have a lot of Xiaomi products in your home, then the router integrates perfectly with them. And those who like to tinker with hardware can install alternative firmware and manually bring it to fruition.Mi WiFi 3 web interface
Testing
Standard stands were used to test Wi-Fi. Configuration of the first: Intel Core i7-2600K, 12 GB RAM, ASUS PCE-AC68 (indicated as A in the table), Windows 7 SP1 x64. The second configuration: Intel Core i7-4700HQ, 12 GB RAM, Windows 10 x64, Realtek RTL8168 (designated as R) and ASUS USB-AC56 (designated as U). In the router settings, WPA2 encryption was enabled and the channel and its width were manually selected. When automatically selecting a channel number, you cannot specify its width. LAN ↔ WLAN speeds are obviously limited by the network port. However, duplex in this case could be faster. Purely wireless connections are quite fast.
| Router Xiaomi Mi WiFi Router 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Streams | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 |
| Average Wi-Fi speed 802.11ac 5 GHz, Mbit/s | |||||
| A → U | 128 | 123 | 134 | 138 | 141 |
| U → A | 143 | 169 | 185 | 192 | 189 |
| A ↔ U | 156 | 157 | 176 | 171 | 161 |
| A ↔ R | 146 | 134 | 126 | 124 | 116 |
| Average speed of Wi-Fi 802.11n 2.4 GHz, Mbit/s | |||||
| A ↔ U | 70 | 73 | 73 | 77 | 61 |
| A (5 GHz) ↔ U (2.4 GHz) | 97 | 98 | 104 | 100 | 75 |
| A ↔ R | 140 | 130 | 124 | 119 | 118 |
To test network operation with drives, we used a LanShuo INIC-3609 box and a Kingston SSDNow V+200 SSD with one NTFS volume. The read and write speed was around 9-11 MB/s. Surprisingly, when connecting wirelessly to the router, the speeds turned out to be the same, although theoretically they should be higher. In addition, it should be noted that a couple of tests in NASTester 1.7 ended with the benchmark freezing on 4 GB files. However, no such problems were noticed in everyday work.
The router works best with direct and PPPoE Internet connections. In both cases, forward and reverse speeds are at the level of 93-94 Mbit/s. Duplex is a little worse - about 155 Mbit/s. VPN connections were expectedly slower. The L2TP connection averaged about 64 Mbit/s, and the PPTP connection averaged 29 Mbit/s. The speed of two-way exchange in both cases was almost the same as that of one-way exchange. In general, this router is not very suitable for owners of the last two types of Internet connections. There is no support for IPv6 in the firmware, although given the low prevalence of this protocol, this is not such a big loss.
Conclusion
Let's summarize. The advantages of Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 include: nice design, support for dual-channel Wi-Fi 802.11ac, a solid amount of memory, control using a mobile application, a set of interesting functions (for example, a built-in ad blocker and a universal download manager) and, of course, a relatively small price. But there are many more disadvantages. Firstly, there is a complete lack of support for the Russian language, both in the application and in the web interface. Even if you are not embarrassed by the presence of only English in the mobile application, then you should not delude yourself too much - this is not the first time that Xiaomi “rolls back” to supporting only the Chinese language for its programs during a major update. Secondly, it’s a pity that the developers saved money on a gigabit switch, which is why it’s impossible to fully exploit all the capabilities of the radio modules. Yes, and working with a USB drive could be faster.
In addition, the router firmware lacks a number of familiar functions. There is no support for IPTV (or IPv6, if anyone cares), and PPTP/L2TP VPN connections are optional and not entirely suitable for constant connection to the Internet. In addition, full operation of the router is only possible if the Internet is available. And these are, perhaps, only the most noticeable among other shortcomings or errors in the firmware. It’s hard to blame him for the fact that the router is designed for Chinese users - no one promised anything else.
It can only be recommended to those with direct or PPPoE Internet connections who are interested in trying something new or who already have many Xiaomi products, as well as those for whom IPTV support is not that important. Please note that this model has not been officially certified in Russia, and you should not count on warranty service.
As you know, Xiaomi knows how to surprise with its innovative solutions. The most successful example is smartphones, which captivate with their amazing technical characteristics and relative cheapness. At the same time, Xiaomi does not stop there, so it is actively expanding the list of devices produced under this brand. Among such devices, one cannot fail to highlight routers that may be of interest to our compatriots.
First of all, the routers are very cheap, but their characteristics, in accordance with the best traditions of the company, are very tempting. One of these Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 or 3c routers, ac1200 class, can be purchased for just a few thousand rubles, taking advantage of a promotional offer from the well-known Internet resource AliExpress. Before agreeing to purchase, please note that instructions and usage guides are offered exclusively in the native language, that is, Chinese. If this doesn’t bother you at all, then you should definitely take a closer look at this high-tech product.
Features of the router from Xiaomi
Let's move on to the key characteristics of this router.

- Processor MT7620A with a frequency of 580 MHz.
- 128 MB RAM.
- 128 MB flash memory.
- Wireless radio units - one with a frequency of 2.4 GHz and providing connection speeds of up to 300 MB per second, and the other - 5 GHz and speed capacities of up to 867 MB per second.
- Two LAN ports and one WAN, each providing a speed of 100 Mb/s.
- USB 2.0 port.
 It is worth noting that the listed characteristics are almost identical to those offered by the Mi WiFi Mini router. However, judging by external data, there will be differences. The body of Mi WiFi 3 has become noticeably larger, and the number of external antennas has increased to four.
It is worth noting that the listed characteristics are almost identical to those offered by the Mi WiFi Mini router. However, judging by external data, there will be differences. The body of Mi WiFi 3 has become noticeably larger, and the number of external antennas has increased to four.
A pleasant surprise for interested citizens will be the price category in which the Xiaomi Mi Wi-Fi Router 3 finds itself. Only $30, which is not so much for such a balanced device. Among its obvious advantages is the operation of one of the radio units, which is capable of operating at a frequency of 5 GHz. On the one hand, speeds of up to 867 Mb/s will only occasionally be fully realized. This is all due to the limits for the LAN and WAN ports, which can only provide 100 MB per second. On the other hand, it is better to purchase a router with such an opportunity, even situational, than to be content with its complete absence. 
What Xiaomi Mi Router 3 is capable of
Of course, with port capacities in the region of 1 Gb/s, the value of this router has increased noticeably, but at the same time it is possible that the cost would also be revised. Based on the current parameters, the functionality of the processor used ensures stable operation with virtually no incidents. By adding the optimal firmware version here, overall performance will only benefit.
During a series of tests, it was found that in IPoE and PPPoE modes the router is capable of providing a router speed of 90 MB per second. This is true for one-way speed transfer. Speaking of full-duplex modes, you can get even more impressive results. The hardware accelerator installed in the chip played an important role in this.
 But if you switch to using L2TP and PPTP, you will have to be content with modest speed capabilities. The good news is that it was not possible to achieve such wide distribution for these modes, so they were deprived of even basic optimization. Thus, for full operation it is enough to use IPoE and PPPoE.
But if you switch to using L2TP and PPTP, you will have to be content with modest speed capabilities. The good news is that it was not possible to achieve such wide distribution for these modes, so they were deprived of even basic optimization. Thus, for full operation it is enough to use IPoE and PPPoE.
When connected via a VPN, you can equally use downloading data from the Internet and the local network provided by the provider. At the same time, the speed not only does not decrease, but also in some moments demonstrates its growth. Given the presence of USB ports, you can connect a printer without any problems.
 While testing the capabilities of the radio units, we were able to discover several interesting details. Firstly, at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, the speed varies at around 60-65 MB per second, which is valid under single-thread conditions. By increasing the number of threads to 8, the speed limits will expand to 70 MB per second, and sometimes this mark can reach 90. Secondly, at a frequency of 5 GHz it will be possible to get no more than 90 MB/s when one stream is loaded. For simultaneous operation of eight threads, the total speed will reach 160 Mb/s. All this suggests that a radio unit with an increased frequency reduces speed due to the presence of restrictions.
While testing the capabilities of the radio units, we were able to discover several interesting details. Firstly, at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, the speed varies at around 60-65 MB per second, which is valid under single-thread conditions. By increasing the number of threads to 8, the speed limits will expand to 70 MB per second, and sometimes this mark can reach 90. Secondly, at a frequency of 5 GHz it will be possible to get no more than 90 MB/s when one stream is loaded. For simultaneous operation of eight threads, the total speed will reach 160 Mb/s. All this suggests that a radio unit with an increased frequency reduces speed due to the presence of restrictions.
Setting up the Xiaomi Mi WiFi 3 router
Let's return to one remarkable detail related to language. Taking into account the ability to connect the Xiaomi Mi router online and configure it, you can quite easily and quickly translate Chinese inscriptions using various services, such as Google Translate. If you don't know how to connect your router to the Internet, you'll have to work hard to familiarize yourself with the router's interface and follow the next steps in the correct order. Another advantage of using an Internet connection is that you can update the firmware to the latest version.
 So, setting up Xiaomi Mi WiFi is as follows. First of all, we need the site miwifi.com, which will act as the online interface of the router. After entering all the necessary data, including passwords for Wi-Fi and the admin panel, the router will begin automatic configuration. Once this installation is complete, a message will appear on the screen indicating that the router will reboot.
So, setting up Xiaomi Mi WiFi is as follows. First of all, we need the site miwifi.com, which will act as the online interface of the router. After entering all the necessary data, including passwords for Wi-Fi and the admin panel, the router will begin automatic configuration. Once this installation is complete, a message will appear on the screen indicating that the router will reboot.
The next step is to connect again using the previously set passwords. Once you enter the control panel, you will see several tabs: routing status, memory status, general settings and advanced settings. First of all, you need to go to the third tab, filling out all existing fields. These steps will help you automatically connect your Xiaomi WiFi router to the network in the future.
 As you explore the other tabs, you'll be able to add and edit whitelists and blacklists, set ranges for valid IP addresses, update firmware and backups, and activate or deactivate VPN services. Separately, you should look at the “Advanced Settings” tab, where you can find QoS - smart speed.
As you explore the other tabs, you'll be able to add and edit whitelists and blacklists, set ranges for valid IP addresses, update firmware and backups, and activate or deactivate VPN services. Separately, you should look at the “Advanced Settings” tab, where you can find QoS - smart speed.
It is highly not recommended to make any changes here if this is your first time seeing the router settings. Otherwise, the connected options will lead to a sharp decrease in speed limits.
Features of alternative firmware
Despite the fact that it is advisable to use the standard version of the firmware, which is in the stable branch, it is possible to switch to another one. This is a special version for developers, thanks to which they will be able to use the console for the embedded OS. The main advantages are stability, high performance, maximum speed characteristics and wide functionality for subsequent changes.
 Unfortunately, it is impossible to find a ready-made version of such firmware. Therefore, you will have to use open source sources to recreate the firmware prototype and use the customized device for your needs. And who said that setting up a router would be easy? It turns out that this will take a considerable amount of time and effort. But the end result of such work will certainly bear fruit!
Unfortunately, it is impossible to find a ready-made version of such firmware. Therefore, you will have to use open source sources to recreate the firmware prototype and use the customized device for your needs. And who said that setting up a router would be easy? It turns out that this will take a considerable amount of time and effort. But the end result of such work will certainly bear fruit!
In the future, you will be able to be content with the following: get a choice of one of the proposed interfaces - Russian and English, support for PPTP/L2TP, greater opportunities for setting up and working with many USB devices, as well as editing user scripts to create key events.
 A specialist who configured the router using non-standard firmware notes that independently changing certain settings may not only not lead to the desired results, but also to situations in which the operation of the router will be completely stopped. And in such cases, it is no longer possible to do without the efforts of qualified specialists who will have to recover data from flash memory. In addition, rash actions when setting up the device yourself can deprive you of managing services remotely and working with special options for mobile gadgets. The latter factors play rather a formal role, but they will still negatively affect the comfortable work with the router.
A specialist who configured the router using non-standard firmware notes that independently changing certain settings may not only not lead to the desired results, but also to situations in which the operation of the router will be completely stopped. And in such cases, it is no longer possible to do without the efforts of qualified specialists who will have to recover data from flash memory. In addition, rash actions when setting up the device yourself can deprive you of managing services remotely and working with special options for mobile gadgets. The latter factors play rather a formal role, but they will still negatively affect the comfortable work with the router.
Collaboration with Mi WiFi+
Surely, many are familiar with the Mi WiFi+ device, which repeats the actions of the main router. If some call it a repeater, others call it a Wi-Fi signal amplifier, which will not be entirely appropriate, based on its features. To expand the coverage area, the Mi WiFi 3 router should be used together with Mi WiFi+. The latest gadget is interesting because it costs only 7-8 dollars, and its compact size will not cause any difficulties with subsequent operation.
 Once the two devices start working simultaneously, the signal that was previously intermittent or non-existent will now be stable. In what cases is this important? In city apartments, when you have to deal with a huge number of other networks. By expanding your wireless network range, you get a nice bonus when using mobile devices. It is not recommended to use such a duet on an ongoing basis, because it can negatively affect overall speed performance.
Once the two devices start working simultaneously, the signal that was previously intermittent or non-existent will now be stable. In what cases is this important? In city apartments, when you have to deal with a huge number of other networks. By expanding your wireless network range, you get a nice bonus when using mobile devices. It is not recommended to use such a duet on an ongoing basis, because it can negatively affect overall speed performance.
Thus, Mi WiFi 3 is a worthy representative of mid-class routers. Excellent technical data, a reasonable price, reliability and practicality in use, as well as decent speed parameters with additional capabilities from Mi WiFi+ - all this suggests that the Xiaomi company knows how to make not only smartphones and tablets.
A few months ago I ordered the third version of the router from Xiaomi. And only now is it time to make a full review of the Xiaomi Mi Router 3. I’ll say right away that I really liked the device. Easy installation and configuration, decent functionality, its own bells and whistles. And most importantly, it’s inexpensive.
Equipment
From the photographs it seems that the device is quite miniature. However, the box in which it came to me surprised me. Upon unpacking, it turned out that the router’s antennas were not removable, and therefore the box had grown to a very impressive size.

Inside there is a short instruction for initial setup (in Chinese), the router itself and the power supply for it. The length of the latter wire is about a meter and this, admittedly, is not enough. I want to say right away that the device was created by the Chinese and for the Chinese, accordingly, take care in advance of an adapter from a flat plug to ours. Or ask the seller to include the required adapter in the package.

Appearance
The main feature of this device is its four antennas, which are designed to improve the signal quality and bring the Internet to the most remote areas of the apartment. I’ll say right away that I compared it in terms of range with my 2012 Apple AirPort Express and, I must admit, I didn’t feel the difference. In the most remote room of the apartment (there are three medium-thick walls along the way and about 5 meters away) the signal is below average. The Apple device reached the same place with exactly the same signal strength.
The antennas can be tilted in almost all directions, thereby correcting the signal propagation. Again, I didn't notice any difference.


The body of the device is entirely plastic, matte and white. The latter is rather a plus, because the color itself is neutral, but most importantly, dust is not visible on the surface.


There is an LED on the front that lights up blue if the router is operating normally. The LED indication, if necessary, can be disabled via the application or web interface. But we will return to this later.
On the back side there are connection ports:
- full USB port for flash drives and hard drives
- two LAN ports
- one Ethernet connector for connecting the Internet itself to our hero (blue frame)



The connectors have their own LEDs to indicate their operation (a normal phenomenon), and in addition, there is a tiny hole right there for a forced reset. I’ll say right away that it has never been useful to me.
The bottom has perforations for air circulation and a sticker with various information about the product. Everything here is also in Chinese, so we won’t focus on that.

It is impossible to mount the gadget on the wall. No special holes were provided for this. Exactly like the rubberized legs.
In other words, the gadget may slip on some surfaces.
Before studying the operation of the router, it will be useful to familiarize yourself with what it can actually do. To do this, look at the “specs” below:
- MediaTek MT7620A processor with operating frequency up to 580 GHz
- RAM 128 MB DDR2
- 128 MB flash memory (SLC Nand type)
- Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11 n (speed up to 300 Mbps)
- Wi-Fi 5 GHz IEEE 802.11 ac (speed up to 867 Mbps)
- maximum speed up to 1167 Mbit/s (simultaneous, parallel operation of two bands)
- protocols: 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, 802.3/3u
- signal transmission power up to 6 dBi at 5 GHz frequency
- passive cooling
- ports: 2x LAN (up to 100 Mbit/s), USB 2.0, Ethernet or WAN, power connector 12V, 1A
- encryption: WPA-PSK / WPA2-PSK
- OS support: Windows, Mac OS X, iOS, Android
- languages: Chinese (mainly) and English
- dimensions: 195 x 177.3 (antenna height) x 131 x 23.5 (height of the device itself) mm
- weight 220 grams

Additionally, I note that connecting the printer via USB will not work.
This functionality is not provided. Only flash drives and hard drives will do.
Settings
Connecting to the Internet and setting up is almost completely automatic. However, something still needs to be done.

To begin with, you should download the Mi Router or MiWiFi Router application from the Google Play Store. There is a client for iOS. Moreover, there are applications for both Windows and Mac OS X.

I installed the latest one, but it's all in Chinese, so it's impossible to use.

There is another alternative way to manage the parameters of our hero - through the web interface. To do this, you need to type miwifi.com or 192.168.31.1 into the address bar of your browser (I used Chrome).

Everything on the main screen will be in Chinese, but it doesn’t matter. Just use the built-in translator and everything will immediately become clear.
To go to the settings, the first thing you will need to do is create a mi account. There are plenty of instructions on how to do this on the Internet, so I won’t give a specific link.
After logging into your account, you will need to add a router (link it to your account) and only then will the initial setup become available. It looks complicated, but in fact, everything is as simple as shelling pears. Especially if you already have an account from Xiaomi.

Overall, I didn't configure anything special. The router independently determined the network settings and connected to the Internet
The interface will ask for a username and password where necessary, and if anything goes wrong, there's a built-in error correction system that works great.

In general, despite the fact that the gadget is entirely Chinese, it is great friends with our providers. Everything starts with half a turn, and this is the most important thing.
Control
I preferred to delve into the settings through the proprietary MiWiFi Router application for Android. At the moment, the latest version is 2.2.30, and the current software of the device itself is 2.14.6.



The most important thing is the presence of English on the menu. 90% of the interface has been translated, and places where hieroglyphs are present are, as a rule, associated with purely “local” services and are of no interest to us.



The welcome screen displays devices that are currently or were previously connected to the router. There can be up to 126 of them in total. This is really a lot and is enough even for a large family and the smartest apartment.



Interestingly, the router can create a separate, guest network at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, and provide access to it either in normal mode (using a password, etc.) or through the WeChat or Dianping application. These services are, of course, not very popular here, but the functionality itself is quite interesting.


For each device you can see all the statistics, and in the form of a graph.

Various useful tools were also found in the parameters. For example, you can audit the operation of the router and find out how you can speed up its operation and signal transmission speed. Of course, the tool is not the smartest, but third-party Chinese services can be disabled through it.



In addition, it has a built-in firewall, a black list of connected devices, anti-hacking, and so on. Also, from the menu you can artificially limit the speed of signal transmission via Wi-Fi if, for example, different devices use the same Internet channel, including via wire.



For some reason, they put a cleaner and an anti-virus for the smartphone itself here. It turns out that Kaspersky is not needed. On the other hand, I would not trust such third-party clients. 
Of course, the following standard options for any similar gadget are supported:
- installation of two networks (2.4 and 5 GHz)
- Data transmission security (WPA / WPA2)
- setting up a VPN connection
- built-in file manager
- backup all settings to file
- remote control via smartphone app



Regarding the latter. You can set up a home server by connecting some kind of flash drive or hard drive to Mi Router 3, and have access to it via the Internet or Wi-Fi network from different devices. The feature is useful, but it’s all configured through a desktop client, which... is in Chinese. At least for Mac OS X.


However, simple operations with files can also be performed through an application on a smartphone. It's not a problem.

Bottom line
I bought a Xiaomi Mi Router 3 to replace my AirPort Express. The latter didn’t suit me too much with its range; I wanted something more interesting. And since Xiaomi products are quite close to me (especially in price!), the choice was clear. It turned out that Mi Router 3 beats the Wi-Fi signal about the same. No, everything works well and within the average apartment and even higher (up to 150 m2) the signal will be good. If not, then you should blame the receiver device.
I'm talking about something else. You won't be able to buy anything like this for your money (about $30). You can take something like a USB access point, but nothing serious. And our router has a flexible nature, a convenient application for managing it, high-quality implementation and very extensive functionality.
The official price in China is 149 yuan or $22. It is clear that this is only true for holders of a real Chinese address and a card issued by a bank from the Middle Kingdom. We have neither one nor the other, so we should look towards resellers. I ordered my device from here. It cost me $32, now they sell it for a little cheaper. I think this is a good offer for those who want to change their old access point and switch to the modern 802.11 ac standard.