What does fat32 mean on a USB flash drive. Difference between FAT32 and NTFS. FAT file system
Surely when formatting a flash drive, many users got lost when choosing a new file system for it. Indeed, the average person hardly knows how NTFS differs from FAT32. But the differences are quite significant. In this article, we'll cover the main differences between these three formats. Of course, there are an order of magnitude more of them, but others, such as ext4 and HFS, are irrelevant within the Windows operating system, since they are used to work in distributions based on the Linux kernel and in Mac OS.
What are NTFS and FAT32?
To understand the difference between NTFS and FAT32, let's try to give them a definition, because not every user understands all the intricacies of a computer system.
So FAT32 and NTFS are file systems. In turn, the file system is a way of organizing all information coming to the drive. Without it, the operating system simply will not be able to interact with all the data on a flash drive or hard drive. The presented file systems, as already noted, are not unique, but are considered relevant, that is, often used in Windows.
Now let's outline the criteria by which it will be possible to compare the described file systems with each other. This is necessary in order to understand how NTFS differs from FAT32. So, there are three main aspects in this question:
- Compatibility and system requirements.
- Impact on wear of drive chips.
- Limitations on the size and amount of recorded data.
Well, now you can proceed directly to the analysis of the question of how the FAT32 system differs from NTFS.
Criterion one: compatibility and system requirements

If you plan to use a flash drive not only for a computer, but also for other multimedia devices, then compatibility is one of the most important criteria for choosing a file system. Let's see what it is in terms of compatibility and system requirements.
- FAT32
FAT32 is the oldest file system presented in this article. Its data organization has been used since the days of the popularity of the MS-DOS operating system. Of these systems, it is also the most optimized for all types of devices. That is, you can easily use it on newfangled devices like the latest Android smartphones or play music on old audio players. As for the system requirements, everything is loyal here too. FAT32 does not consume a lot of computer resources and practically does not load the processor.
When the Windows operating system received a new NT architecture by those standards, then the NTFS file system was born. Now it is considered standard for all Windows operating systems. However, despite this, you can view it on computers running Mac OS and Linux. But do not even try to play music from such a flash drive on car radios or second-tier players: with almost one hundred percent probability, you will not succeed. Also smartphones based on Android and iOS systems will refuse to detect the connected drive via the OTG cable. Also note that the system requirements have also increased.
Criterion two: impact on drive wear

We have found out how the FAT32 file system differs from NTFS in terms of compatibility, but now let's look at the second criterion - the impact on the wear and tear of the drive. The fact is that the Flash memory, which any flash drive is equipped with, has its own limit, upon the exhaustion of which it simply ceases to function. It is expressed in the number of permissible overwrites of data cells, that is, the less frequently data is overwritten, the longer the flash drive will last.
- FAT32
If you value the durability of your flash drive, then you better refuse this file system. It works great with small to medium sized files, but it still fragments them quite a lot. Accordingly, the number of overwrites of the same memory cells increases, while the durability of the drive, on the contrary, decreases.
As for NTFS, then with this file system the flash drive will last an order of magnitude longer than with FAT32. The developers have achieved this by introducing a technology for indexing all data, as a result of which the number of overwrites of the same memory cells is reduced. But there is also a significant drawback - this system is noticeably slower to work with data.
Criterion three: limitations

Two criteria have already been analyzed, now let's go directly to the last one and see how NTFS differs from FAT32 in terms of restrictions imposed when using them.
- FAT32
If we talk about the main disadvantages of the FAT32 file system, then these are undoubtedly its limitations on data recording. Due to the peculiarities of data organization, the maximum size of the recorded file should not exceed 4 GB. Of course, earlier this figure seemed transcendental, but now this size is more related to average than to large. There is also an unpleasant moment: the root directory of such a system cannot contain more than 512 files. However, it is leveled by a little trick - if the files are placed in directories, then the limitation disappears.
If we talk about NTFS, then, closing our eyes to all the technical issues, we can say that there are no restrictions on data recording. Of course, they exist, but it is simply unrealistic to achieve them in our time. This also applies to the size of the recorded file and the number of files in the root directory.

So we figured out what is the difference between the NTFS and FAT32 file systems, now we can give some recommendations on their choice.
- If you plan to use a USB flash drive to play media files in old-style players, then it is better to use FAT32.
- If you need to write large files to the drive, then be sure to format the flash drive to NTFS.
- If you need a high data write speed, we recommend using FAT32.
- To prolong the life of your Flash drive, format it to NTFS.
Conclusion
Above, all the nuances of using the NTFS and FAT32 file systems were analyzed. We hope this article was useful for you and you were able to understand what are the differences between these seemingly two similar systems.
Today, Flash drives have practically replaced all other portable storage media such as CDs, DVDs, and magnetic floppy disks. On the side of flash drives, there is undeniable convenience in the form of a small size and large amounts of information that they can accommodate. The latter, however, depends on the file system in which the drive is formatted.
What is a file system? Roughly speaking, this is a method of organizing information that a particular OS understands, with division into documents and directories familiar to users. There are 3 main types of file systems today: FAT32, NTFS and exFAT. We will not consider ext4 and HFS systems (options for Linux and Mac OS, respectively) due to their low compatibility.
According to the importance of the characteristics of a particular file system, it can be divided into the following criteria: system requirements, the impact on the wear of memory chips and restrictions on the size of files and directories. Let's consider each criterion for all 3 systems.
Compatibility and system requirements
Perhaps the most important of the criteria, especially if the USB flash drive is planned to be used to connect to a large number of devices on different systems.

FAT32
FAT32 is the oldest document and folder organization system still in use, originally developed for MS-DOS. It has the highest compatibility of all - if the flash drive is formatted in FAT32, then most likely it will be recognized by most devices, regardless of the operating system. Besides, working with FAT32 does not require a lot of RAM and processing power.
NTFS
The default Windows file system since the transition of this operating system to the NT architecture. Tools for working with this system are present both in Windows and Linux, Mac OS. However, there are certain difficulties with connecting drives formatted in NTFS to car radios or players, especially from second-tier brands, as well as to Android and iOS via OTG. In addition, the amount of RAM and CPU frequency required for operation have increased in comparison with FAT32.
exFAT
The official name stands for "Extended FAT", which corresponds to the essence - exFAT and there is a more extended and improved FAT32. Developed by Microsoft specifically for flash drives, this system is the least compatible: such flash drives can only be connected to computers running Windows (at least XP SP2), as well as to Android and iOS smartphones. Accordingly, the amount of RAM required by the system and the processor speed have increased.
As you can see, FAT32 is the undisputed leader in terms of compatibility and system requirements.
Impact on wear of memory chips
Technically, flash memory has a limited lifespan, which depends on the number of sector rewriting cycles, which in turn depends on the quality of the chip itself installed in the flash drive. The file system, depending on its own characteristics, can either extend the life of the memory, or reduce it.

FAT32
According to the criterion of influence on wear and tear, this system loses to everyone else: due to the peculiarities of the organization, it works well with small and medium files, but it significantly fragments the recorded data. This leads to more frequent calls of the operating system to different sectors and, as a consequence, an increase in the number of Read-Write cycles. Therefore, a USB flash drive formatted in FAT32 will last less.
NTFS
The situation is better with this system. NTFS is less dependent on file fragmentation and, in addition, it already has more flexible content indexing, which has a positive effect on the longevity of the drive. However, the relative slowness of this file system partially negates the obtained advantage, and the peculiarities of data journaling make it necessary to frequently access the same memory areas and use caching, which also negatively affects the durability.
exFAT
Since exFAT was developed specifically for use on flash drives, the developers paid the most attention to reducing the number of rewriting cycles. Due to the peculiarities of organizing and storing data, it significantly reduces the number of rewriting cycles, especially when compared to FAT32 - a bitmap of available space has been added to exFAT, which reduces fragmentation, which is the main factor in reducing the lifespan of a flash drive.
As a result of the above, we can conclude that exFAT has the least effect on memory wear.
File and directory size limits
This parameter is becoming more and more important every year: the volume of stored information, as well as the storage capacity, is steadily growing.

FAT32
So we have come to the main disadvantage of this file system - in it the maximum volume occupied by one file is limited to 4 GB. In the days of MS-DOS, this would probably have been considered an astronomical value, but today this limitation is inconvenient. In addition, there is a limit on the number of files in the root directory - no more than 512. On the other hand, there can be as many files as you want in non-root folders.
NTFS
The main difference between NTFS and the previously used FAT32 is the practically unlimited volume that this or that file can occupy. Of course, there is a technical limitation, but in the foreseeable future it will not be possible to reach it soon. In the same way, the amount of data in a directory is practically unlimited, although exceeding a certain threshold is fraught with a severe drop in performance (a feature of NTFS). It is also worth noting that this file system has a character limit per directory name.
The choice of a file system for the average user becomes relevant when formatting a hard disk, flash drive or other storage medium. The system offers several options: FAT16, FAT32, exFAT, NTFS. Almost nothing is known about the advantages and disadvantages of each, so they often choose what they hear - as a rule, it is NTFS. For the sake of fairness, it is worth clarifying that FAT16 today is more of a memory, and formatting a medium into it is performed only as an experiment. The exFAT system, due to its still insignificant distribution, can also be considered, if not an exclusive, then not a universal solution - not all operating systems support it. So the choice is between two abbreviations - FAT32 and NTFS.
FAT32 - a file system based on FAT16. Basically, this file system is a file allocation spreadsheet using 32-bit records. By the way, the acronym stands for File Allocation Table.
NTFS - a file system, which is a certain structure: at the beginning of the disk, a summary table (or directory) of all files, then - the actual data. The abbreviation stands for New Technology File System.
In practice, today the FAT32 file system is more often used on small removable media, NTFS - on system drives and for storing large files. FAT32 clusters are larger, therefore, disk space is used irrationally when storing a large number of small files. A large number of programs that require the presence, for example, many libraries, font files and others, in the FAT32 system will respond to slow operation. NTFS provides quick access to a small file or part of a file.
In general, NTFS is noticeably slower than FAT32, but NTFS is more efficient when accessing large files. Fragmentation does not affect NTFS in any way, while FAT32 will noticeably decrease performance (especially when working with medium-sized directories).
If we talk about the hardware operation of hard drives, then FAT32 will provide a gentle mode for them: when reading, the head makes fewer movements, respectively, the degree of mechanical wear will be less. However, the relevance of this property is lost in light of the minor use of the FAT32 file system on hard drives in systems. The design of flash drives and memory cards does not imply mechanical wear.
The NTFS file system requires a significant amount of RAM, so weak systems with less than 64 MB of RAM are not designed for it. Although at present, such assemblies can only be found in museums or created for the sake of experiments. However, remember that the FAT32 system does not impose requirements on the amount of RAM - it's worth it, especially if you take into account the option of expanding the standard memory of mobile devices. The phone simply will not be able to work with a memory card formatted in NTFS, even if it can be accessed from the operating system.
The maximum file size in FAT32 is 4 GB. NTFS theoretically supports files of about 16 TB. The theoretical maximum disk size for FAT32 is 8 TB, while for NTFS it is about 16 exabytes. However, technologies have not yet reached the use of these properties in practice.
Another undoubted plus for NTFS is the ability to compress a file at the file system level. We can also talk about a higher level of system reliability, and, in addition, the ability to save the file structure in NTFS in case of a failure.
Conclusions site
- NTFS uses disk space more efficiently.
- FAT32 is faster.
- NTFS provides high performance when working with large files.
- FAT32 supports files up to 4 GB in size.
- FAT32 does not require a lot of RAM.
- NTFS provides high system reliability.
How can I change ntfs to fat32? What is the correct format for a FAT32 or NTFS stick? All this will be discussed below.
By and large, both formats can be used with FAT32 and NTFS. It all depends on how you are going to use the flash drive.
When buying a new flash drive, as a rule, they have a FAT32 file system and this is not surprising, since this file system is readable from many devices, something like a universal format. Well, there are opinions that this format is more productive than NTFS.
Difficulties you may have, will arise only when you need to upload a file with a size exceeding 4GB to a USB flash drive. There may be other errors that, but these are usually special cases.
For example, you go to install windows from a USB flash drive. If your flash drive is in FAT32 format, then when you try to write a large file (more than 4GB) to it, windows itself will give you an error that the file is too large.
Well, when recording an image, you will be prompted to format the USB flash drive or you will also receive an error.
Therefore, before recording a windows image or before moving a large file to a USB flash drive, first format your USB flash drive into NTFS format.
And, of course, you have a reasonable question, which file system to choose for a FAT32 or NTFS flash drive.
Today, flash drives already come with a large volume of 32 GB and 64 and more. Accordingly, if you buy a flash drive with such volumes, you probably plan to throw both films and large files on it.
For such purposes, format the flash drive in NTFS and use it as you please.
If you do not plan to put large files on a USB flash drive, but plan to use them for documents, photos or small files, for example, music files, then formatting is not necessary.
When choosing a file system for a flash drive, first think about how you will use it, from here and choose the format.
In addition:
How to change fat32 to ntfs or ntfs to fat32 on a USB flash drive
If for some reason, you have previously formatted the flash drive from fat32 to ntfs and now you need to return everything back from fat32 to translate ntfs or vice versa, then to change the fat32 or ntfs file system you need, follow these steps:
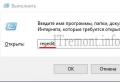
1. Insert the USB stick into your computer / laptop.
2. When your computer detects your device, select the USB flash drive and right-click, in the menu that opens, click Format, then select the desired file system format and click Start.
After the completion of the operation, your flash drive will be in the file system you need.
Attention! Before formatting a USB flash drive to another format, if there is data on it, first transfer (copy) the files to another location. When formatting, all data from the flash drive is deleted!