An uninterruptible power supply is what you need. What is an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS). There are three types of UPS
To maintain the operability of devices in the event of network failures, an uninterruptible power supply unit is used. Depending on the type of consumers served and the parameters of electricity, you need to choose different models. These devices are in demand, therefore, it is not difficult to acquire the copy that is necessary according to the characteristics.
But before buying, you need to independently understand its features, and not entrust this issue to managers interested in sales.
In this material, we will consider the design and features of the UPS, and also talk about the rules for its use.
For household needs, devices for uninterruptible power supply are used, connected to a single-phase 220 V network, which can supply consumers that require the same voltage for some time in the absence of electricity.
There are also UPSs that are connected to the input to a three-phase network, and give either 380 V or 220 V to the output. However, they are expensive, they are used if necessary to receive autonomous power from 10 kVA, which is not required for domestic needs.
Household UPS AC according to the scheme of operation are divided into the following types:
- backup (offline);
- interactive (line-interactive);
- double conversion (online).
They differ in the quality of the output voltage and the price. The cheapest are backup, and the most expensive are double conversion.
A rectifier is used in the charger to convert alternating current to direct current. And the reverse transformation takes place using an inverter.
In uninterruptible power supplies, to switch the circuit from the network to the battery, as a rule, ordinary electromechanical relays are installed. If this part is of high quality, then its resource is enough for the entire operation time of the UPS. But most often, if a block breaks down, the problem lies precisely in this structural element.
The interactive circuit differs from the backup circuit by the presence of a voltage stabilizer. It is designed as a typical autotransformer with directly connected windings.
Voltage stabilization is also present in many household devices, so if the deviations are insignificant, then there is no point in purchasing a more expensive line-interactive model.
The presence of a transformer often forces the manufacturer to use forced cooling, so such UPSs are equipped with coolers. They emit a noise comparable in intensity to the operation of a computer system unit.
To measure the load of devices, you can either use an ammeter or calculate it using the readings of the meter installed in the apartment.

In the presence of a stabilizer, the voltage of the intra-house network will be brought to the standard indicators. This will also affect devices that are not connected to the UPS.
With a reduced voltage, the current flowing through the internal network increases. For example, suppose the total power of the consumers connected to the UPS is 1.5 kW and the supplied voltage is 190 V.
- I 1 \u003d 1500/190 \u003d 7.9 A - current in the circuit to the UPS without a stabilizer;
- I 2 \u003d 1500/220 \u003d 6.8 A - current in the circuit to the UPS with a stabilizer.
Thus, an internal network without a stabilizer will experience an increased load, which could not be taken into account when choosing a wiring cross-section.
Therefore, with a constant undervoltage, it is better to install a stabilizer. In this case, the load on the UPS autotransformer will be less, which will extend its service life. In addition, taking into account voltage equalization, you can purchase cheaper uninterruptible power supplies.
Uninterruptible power supply of DC consumers
For some devices, you need to provide uninterruptible power supply with direct current of 12, 24 or 48 V. UPS of this type is also on sale. They are labeled with the abbreviation “DC”. Blocks with a voltage supply of 60, 110 or 220 V also exist, but they are used in industry or energy.
The difference between DC uninterruptible power supplies in the internal device from classical models is the absence of an inverter. The batteries are connected directly to the output via a contactor with a current-limiting measuring shunt to prevent an impermissibly deep discharge of the batteries.
Sometimes a stabilizing converter can be installed at the output if the devices powered by the UPS are sensitive to small voltage fluctuations.
These redundant power supplies are used to protect the following household DC equipment:
- and protection;
- all kinds of sensors (leaks, smoke, fire, movement, etc.);
- lighting systems;
- telecommunication devices;
- communication systems;
- control system components.
Many DC UPSs have the option of connecting external batteries. In this case, the autonomous operation of the devices they serve can be very long.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Briefly about the main characteristics of household UPS:
The variety of UPS types and their characteristics is a consequence of the different conditions of their use: the power and type of connected devices, parameters and typical problems of a particular power grid. An uninterruptible power supply is usually not the most expensive element in the system, but the stability of its operation depends on it. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the operating conditions and carefully approach the choice of the model.
Still have questions on the topic of the article? Or can you supplement this material with interesting information about UPS? Please write your comments, ask questions, share your experience in the block below.

UPS stands for "uninterruptible power supply". English abbreviation - UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) , therefore, the names UPS, UPS, and upsnik are also common.
The main function of an uninterruptible power supply is to ensure the supply of electricity to the equipment connected to it during outages in the main network. But, depending on the type of equipment, the parameters of such an autonomous power supply may be required radically different. Accordingly, the UPS market offers different types of devices, which differ in a mass of parameters:
- operating principle: offline, line-interactive, online;
- type of automatic voltage regulation;
- the quality of filtering network noise;
- capacity (the number of ampere-hours, or in other words - how long it will last for battery life);
- time of switching to batteries in case of power outage;
- the ability to connect additional external batteries;
- various additional functions (filter sockets, sockets for telephone and network cables, LCD display, synchronization with a PC), etc.
How to choose a UPS with such a variety of models ? How to understand how they differ?In this article, we will look at the main types of uninterruptible power supplies, their differences, and what additional functions the manufacturers equip the UPS with. The next one is how to choose a UPS depending on the features of your equipment, how to calculate its required power, etc.
Three main types of UPS
Off-line (Back-UPS, standby) uninterruptible power supply

Backup UPS example: model .
The principle of operation of this type of UPS is very simple:
As long as the utility has power within the specified limits, the UPS supplies power to the connected devices directly from the utility while recharging the battery. The power supply passing through the UPS is not regulated at the same time, the filtering of impulses and interference occurs at the simplest level, using passive filters. The waveform corresponds to the mains signal, i.e. a sine wave.
As soon as the mains voltage is lost, the UPS transfers to battery power. The inverter, which converts DC current from the battery into AC at the output, is one of the simplest installed in this type of UPS, so the waveform does not correspond to the correct sinusoid. The maximum that manufacturers are doing is to bring it a little closer to a sinusoid, making it stepwise.
The UPS also switches to off-line autonomous power supply if the voltage level in the network drops below or rises above the threshold values, they may be different depending on the UPS brand.
The switching time to batteries in various models ranges from 5 to 20 ms. This is relatively high, and for some equipment such a long delay can adversely affect performance. ... Long-term operation of the relay is due to the fact that the device needs to match the phases of the mains and battery voltages at the moment of turning on the autonomous power supply, and since they are not synchronized, this takes some time.

Scheme of operation of a backup uninterruptible power supply.
Pros of Standby UPS:
- inexpensive price,
- high efficiency,
- silent work.
Disadvantages:
- long switch-over to battery operation (5 to 20 ms);
- the output waveform is not a sinusoid;
- filtering interference, noise and impulsesrather rough on the line;
- there is no regulation of voltage and frequency when operating from the network.
Line Interactive UPS

Line Interactive UPS Example: Model
Buyers choose this type of uninterruptible power supplies most often, as it optimally combines functionality and price.
The principle diagram of the operation of line-interactive UPS includes AVR - a module for automatic regulation of the incoming mains voltage. That is, unlike a standby UPS, it not only passes power through itself, but also stabilizes it, though not smoothly, but step by step.
When operating on mains power at normal voltage levels, the line-interactive uninterruptible power supply passes the incoming signal through passive interference and noise filters while charging the battery.

When the voltage in the network increases or decreases, the line-interactive UPS performs its stepwise correction. When the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the AVR will lower or lower it by a fixed amount (or percentage). There can be several such thresholds-steps in the AVR operation scheme; also, a different number of correction steps can be designed to work with a lowered and increased level (for example, 2 - for increasing, and 1 - for lowering).


If the mains voltage drops or rises to values \u200b\u200bthat lie outside the available input range of the UPS, the device switches to battery operation, as in the case of a complete power outage. These minimums and maximums may differ depending on the load on the UPS. For example, if the UPS is 70% loaded, and the voltmeter shows 160V in the network, the UPS switches to the batteries. And at a load of 30% and a voltage of 150V, it still adjusts using an AVR transformer.

Some of the line-interactive models do not differ in any way in the form of the output signal from the standby UPS: they have a step sine wave. Some manufacturers, especially with the growing demand for UPSs for boilers, equip their UPS with inverters that produce the correct sine wave.
The transfer times to battery operation are shorter in pure sinusoidal line-interactive UPSs than their standby counterparts. The reason is that in UPSs of this type, the voltage waveforms coincide (both from the network and from the battery it is a sinusoid), which speeds up the phase synchronization and, accordingly, the start of the autonomous power supply.
Pros of line-interactive UPS:
- reasonable price,
- silent work,
- automatic adjustment of the input voltage,
- in some models - a pure sine wave at the output,
- switching time is less than in standby ones (on average 4-8 ms, in some models 2-4 ms).
Disadvantages:
- there is no frequency adjustment,
- insufficient filtering of interferences, noises and network pulses,
- voltage regulation is not smooth, but stepwise,
- The efficiency is lower than in an off-line uninterruptible power supply.
Double conversion UPS (on-line)
Example of a double conversion UPS: model .
This is the most expensive but also the best type of UPS. It is ideal for expensive, capricious equipment, where not only DC voltage is important, but also frequency, as well as effective noise filtering, a signal in the form of a pure sine wave and no delays when switching to battery operation.
In fact, such an uninterruptible power supply works constantly, stabilizing, filtering the input signal, equalizing the frequency and shape of the output signal.
In mains mode, the incoming AC voltage is stabilized and converted into DC by the rectifier and distributed between the battery (for recharging, if necessary) and the inverter. The inverter converts direct current to alternating current, giving out a signal in the form of a pure sine wave, correct frequency, correct voltage. Interference and noise are completely absent - they simply do not remain after double conversion.
Such a constant "inclusion" of an uninterruptible power supply into the network gives one of its significant advantages: instantaneous switchover to battery operation... Actually, it is even difficult to call it "switching", since the power goes through the rectifier, battery (during charging) and inverter constantly. At the moment when the mains voltage drops below the threshold values \u200b\u200bor a complete power outage, the inverter simply begins to take some of the energy from the battery, and not from the rectifier. It happens instantly.

Double conversion UPSs usually have another mode of operation: bypass. This is a backup line that runs directly from the input to the output of the UPS, bypassing the rectifier, battery and inverter. It allows at critical moments for the UPS: overload (for example, starting currents), failure of the inverter, and others - to send electricity to the connected devices directly, avoiding the failure of the elements of the device.

Continuous operation of the UPS has a certain disadvantage: increased heat dissipation, which requires efficient cooling. Therefore, UPS online is most often equipped with fans, which makes their operation in residential premises not as comfortable as other types of silent UPS.
Pros of Online UPS:
- constant voltage stabilization,
- constant frequency stabilization,
- pure sine wave at the output,
- effective filtering of noise, impulses and interference,
- instant switch to batteries.
Disadvantages:
- high price,
- increased noise level,
- the lowest efficiency among all types of UPS.
When choosing an uninterruptible power supply, you need to take into account that there are exceptions. Some line-interactive UPSs can be more expensive than online models of another manufacturer, the transfer time to battery operation in a backup UPS may not be longer, or even less than in some line-interactive UPS, etc. in any case, it is necessary to read the characteristics of a particular model.
Additional UPS functionality
In addition to determining the type of uninterruptible power supply that you need, when choosing a UPS, you should also pay attention to what functionality is included in it. UPS can have various additional functions and design features:
Synchronization with PC... This function is present in not the cheapest models, but it is very convenient. With the help of special software, the UPS transmits data in real mode to the computer about the state of the power line, the level of battery charge. In addition to the purely informational component, there are also such opportunities as, for example, an autonomous shutdown of a computer while saving data in all applications in case of a power outage.
Cold start... An uninterruptible power supply equipped with this function can be turned on in the absence of power in the network. For example, the light went out, you saved the documents, turned off the computer and UPS, but after a while there was an urgent need to copy the document to a USB flash drive. A UPS with cold start support can be turned on even if there is still no utility power and the job can be done.
Previously, the connectors for connecting devices in an uninterruptible power supply looked like this:

This IEC 320 connector is ideal for connecting a variety of computer equipment. However, equipment with a regular power cord, the same WiFi router, cannot be connected to it. For these purposes, you can use a surge protector with a similar connector, which is connected to the UPS, and already include various equipment in it. But this is not always convenient.
Therefore, now many models began to simply be supplemented with Schuko-type sockets (in our country they are often called European sockets) so that the equipment can be turned on directly:

Interference filtering sockets.The UPS may be equipped with a receptacle or multiple outlet for sensitive equipment that does not provide power support during a power outage, but protects the connected equipment from mains noise.
Telephone line sockets, twisted pair... High-voltage pulses can be transmitted not only directly over an electric power cable, but also in the event of various accidents and breakdowns - both over a telephone cable and over a twisted pair. To protect telephone, network and computer equipment, some manufacturers provide special connectors (input / output) where you can connect a telephone or Internet line.
Continued in the next article.
website
Electric networks of Russian cities are difficult to classify as modern. The equipment is outdated, no repairs are carried out, voltage drops have become the norm. All defects and malfunctions have an extremely negative effect on the work of consumers. Poor-quality power supply especially hits computer and microprocessor devices, causing not only individual failures, but also a complete loss of performance. Unfortunately, electrical equipment is often not protected from such surges and the problem will be solved by an uninterruptible power supply. According to the configuration of the phases of the outputs and inputs, the UPS is divided into two types: single-phase input - output and three-phase input - output.
What is a UPS for?
Primarily, these devices prevent damage to equipment and prevent malfunctioning of electronic systems. They make it possible to correctly shut down in the event of an unexpected power outage.
The UPS successfully overcomes interruptions and electrical disturbances that occasionally occur in home and work networks. Among them, the following are most common:
- Voltage dips. In this state, the voltage suddenly drops by a significant amount. Its recovery requires different time intervals, in some cases tens of seconds. The reason for the failures is most often associated with the limited capacity of the substation, especially in winter, as well as with the launch and further operation of powerful equipment. Physically low voltage appears as flickering bulbs.
- Voltage pulse. In this case, the voltage changes sharply, with an amplitude of up to 2000 volts, and then reaches its normal level in a very short time. This requires no more than 10 milliseconds. The main reason is the operation of industrial equipment, air conditioners, elevators, the action of lightning discharges, etc.
- No voltage for a short time. This interval is no more than 20 milliseconds and is almost invisible. However, electronic equipment is negatively affected
- Lack of voltage for a long time. This period can range from 20 milliseconds to several hours. This is caused by overloads, adverse weather conditions and physical damage in substations that shut down power lines.
- Frequency changes over a short period of time when powerful equipment is connected to the network. Radio frequency noise from radio transmitters, loads, generators and industrial equipment also has a negative impact.
Electronics companies have conducted studies that have revealed that each personal computer is exposed to various negative influences at least 120 times in a month, one way or another related to voltage problems in electrical networks.
Main UPS functions
In accordance with the known problems that regularly arise in electrical networks, uninterruptible power supplies perform a number of important functions aimed at eliminating them and preventing negative consequences.

The purpose of an uninterruptible power supply is the following:
- They filter the supply voltage, reduce the noise level.
- They absorb short-term voltage surges, including minor ones.
- Protect against short circuits and overloads.
- In the absence of voltage in the network, the load is provided with a backup power supply for a specified period of time.
The most advanced UPS models can perform additional useful actions, thanks to specialized software designed to control these devices:
- The load is switched on and off by the commands of the internal timer at exactly the specified time.
- In the event of a prolonged power failure, the equipment is automatically serviced and restarted after the normal power supply is restored.
- Emergency situations are monitored, various warning signals are issued.
- The display of the device shows the voltage and frequency of the alternating current in this network, as well as the output supply voltage and power consumed by the load.
- Monitoring and recording data regarding the status of the UPS. This includes battery temperature, battery level, and other performance characteristics.
General scheme of operation of uninterruptible power supplies
Most UPSs are equipped with the following components according to their operating diagrams:
- An inverter with which a sine wave is formed.
- Batteries that store electricity.
- Electronic circuit to control all processes.
- Software.
- Battery charger.
If necessary, the device can be accessed remotely using a local network. The reliability and operability of the circuit is increased by its redundancy.

Uninterruptible power supplies can be in the following operating modes:
- Charging period. The sine wave circuit at the input and output is interrupted by an internal switch of the device. The battery connected to the rectifier is charged until it regains its optimum capacity.
- Ready period. When the battery is charged, the internal switch of the device is automatically closed. The battery goes into buffer mode and maintains a state of readiness for further operation.
- Discharge period. The battery is automatically transferred to power the load, which leads to its gradual discharge.
Specifications
All uninterruptible power supplies have a certain set of technical characteristics. They differ in individual parameters, depending on the design and modification of a particular device.
They each have their own input voltage ranges when the UPS is running on utility power and not using the internal batteries. Be aware that longer ranges will reduce battery life, thereby increasing battery life. In addition, they continue to supply power to the load from the mains, while at a lower range the UPS switches to the battery, quickly discharges it and de-energizes the load.

For all UPSs, the output voltage changes when the input voltage changes. That is, it must be maintained at such a level that the connected equipment can function normally. Undervoltage at the output often leads to malfunctions and loss of data. The excess gives the same results, and is complemented by the failure of the used load.
Of great importance is the quality of switching and transient processes to the battery and vice versa, which should not attract attention, be performed correctly, in a short period of time. The UPS frequency is correctly synchronized with the external mains frequency. In the event of an overload, a special signal is sent using light and sound indication. The device itself is disconnected during operation from the battery, and the user must reduce the load in a timely manner.

Many devices can be turned on in the so-called cold start mode, when there is no voltage in the main supply network. This function is useful when there is a prolonged power failure, when it is necessary to urgently perform any action on the electronic equipment.
Single phase input - output (1ph / 1ph or 1: 1)
Single-phase uninterruptible power supplies have been designed for single-phase networks. They reliably protect electrical equipment, which requires increased requirements for the quality of power supply, from any malfunctions in the network (for example, lack or distortion of voltage, suppression of high-frequency interference).

Such equipment maintains the quality of the output voltage if there are problems with the input voltage by using the energy of the batteries (nominal deviations, loss, shape distortion). Single-phase UPSs are used in many fields of information technology, communications.
Three-phase input - output (3ph / 3ph or 3: 3)
Three-phase types of uninterruptible power supplies are usually used for continuous 24/7 operation. The device is suitable for powering three-phase equipment, which is designed for 3x380 V and for single-phase energy consumers operating at 220 V. Three-phase UPS maintain the required quality of the output voltage. They are used in banks, computing centers, medical centers, transportation, etc.

Types of uninterruptible power supplies
The type of uninterruptible power supply is divided into three categories.
Interactive UPS (line-interactive)
This is the most ideal option for the home, namely where the voltage is unstable and often disappears. Compared to the rest of the species, there are two important aspects. First, their response is much faster, in 2-5 milliseconds. Second, before switching, they try to equalize the voltage, which works quite effectively with small surges. As a result, battery life is improved and a ton of money can be saved. It is ideal for home use.

These devices are distinguished by a more complex circuit, which includes a voltage stabilizer with an autotransformer that has a step regulation function. These devices only correct the output voltage, but cannot control the frequency of the signals. Full stabilization is impossible due to the small number of adjustment steps.
More expensive types of models are equipped with inverters with semiconductor switches. When switched to battery power, they are faster than other devices.
Offline uninterruptible power supply UPS (off-line)
The most inexpensive kind. The principle of operation is that in the event of a power failure or power surge, transfer the equipment to battery power. This type has significant disadvantages. The first is the response time, which is about 10 milliseconds. Second, if the voltage in your home is constantly jumping, such a UPS will often switch to battery power, this will significantly reduce its resource and you will have to change it after a few months.

Online UPS (on-line)
The most expensive and efficient uninterruptible power supply. In real time, it regulates the voltage, switching to the battery only in the most difficult situations. Often used for servers that require high quality power. The battery is permanently included in the circuit and does not require any additional commutation.

How to choose the right UPS
Before choosing a device, you need to decide which power supply problems will be the most urgent.
For residents of new districts located in large cities, the simplest offline devices will be quite enough. In these places, new networks are usually laid, providing a stable voltage. Therefore, in addition to the UPS, it is recommended to purchase a surge protector just in case. It cannot be connected to the output of the UPS, in order to avoid distortion of the current characteristics. When choosing uninterruptible power supplies for offices and large local area networks, you can choose any of the options discussed above, in accordance with the operating conditions.

When choosing an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), you should pay attention to the following parameters and specifications:
- Output power value
- The time required for switching to and from battery power.
- Battery life, depending on the capacity of the batteries and the power of the equipment connected to the UPS.
- The width of the mains input voltage range, at which it is possible to stabilize the power supply without switching to batteries.
- Battery life is on average 5 to 10 years.
The article discusses the types of UPS, the principles of UPS operation, and also provides real oscillograms of the output voltages.
To begin with, some general terminology. Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are also called UPS, from the English abbreviation Uninterruptable Power Supply (uninterrupted power supply). Therefore, they say both UPS and UPS, whoever is more convenient. In the article I will call it this way and that.
Why do you need a UPS (UPS)
The principle of operation of the UPS is revealed in the name - it is such a source, at the output of which there is always tension... But we have gathered here realist techies, and we understand that nothing is eternal, so below we will understand the principle of action.
UPSs are mainly used where power outages can cause negative consequences. For example, power supply of computers and servers, power supply of communication and signal distribution devices (routers), power supply of devices whose automatic reboot (restart) is impossible without human intervention.
How my reader modified a UPS for a strategically important system (2 servers, etc.). In addition, he improved the circuit, and added the ability to use a conventional car battery.
For household items, these are primarily computers and heating systems.
It should be understood that UPSs are selected for a load operating time of 10-15 minutes, rarely up to half an hour. It is assumed that during this time, power will appear, or a person (operator) will take the necessary actions (save the data, call the energy service of the enterprise, complete the technological process).
The UPS cannot be considered as a backup power supply. It is only an emergency source, and at best it is used very rarely, for a total of no more than 10 minutes a year (several times, for no more than a minute). If this time is longer, then you should think about improving the quality of power supply.
A backup power source can be considered such sources that can completely replace the main power supply for a long time, from several hours to several days. It may be another line (see article about), a wind generator. Theoretically, a UPS can serve for these purposes, but this requires batteries of enormous capacity, which will significantly affect the price of such a system.
Types of uninterruptible power supplies
The types (types) of UPS have many names, but there are still exactly three of them. Let's figure it out.
So, there are three main types of UPS:
Back UPS
Other equivalent names are Off-line UPS, Standby UPS, and standby UPS. The most common OOIs are used for most types of household and computer equipment.
Back simply switches the load to battery power when the input voltage goes out of range. The lower limit for different models is about 180V, the upper limit is about 250V. Transitions to the battery and vice versa - with hysteresis. That is, for example, when lowering, the transition to the battery will take place at 180 V or less, and vice versa - at 185 or more. The same principle applies to all types of UPS.
Something like that disconnects load, and Back UPS does not turn off, but switches on the battery, which allows her to work for some time.
Smart UPS
Other names - Line-Interactive, interactive type UPS. We are not far from Back.
Smart UPS are smarter, as the name suggests. They additionally switch the internal autotransformer, in a sense, stabilizing the input voltage. And only as a last resort they switch to the battery.
Thus, the output voltage is maintained at large input deviations (150 ... 300V). The autotransformer has several switching stages, so the Smart UPS switches the autotransformer outputs until the last moment, including the battery only at the last moment. This saves the battery by turning it on only when the power is completely lost.
This device resembles a stepwise switching of the autotransformer windings. The only difference is that when it goes beyond the operating limits, the stabilizer will be powerless, and our “clever girl” will put the battery into operation, and the power will not be lost.
Online UPS
Other names are online, double conversion uninterruptible power supply, inverter. A completely different principle of action, for lovers of pure sinus. The energy from the input is converted into DC voltage and fed to the inverter, which generates a pure sine wave. And at the same time it keeps the battery 100% ready. If necessary, the inverter continues to operate in the same way, only it receives power from the battery.
It is used for emergency power supply of equipment that is sensitive to the shape of the output voltage - for example, gas boilers, servers, professional audio-video equipment and other strategically important equipment.
There are two disadvantages of online UPS - price and efficiency. The efficiency is low, because such a UPS is always on, as the name implies. Unlike the other two types.
There are varieties of online UPS, which use the so-called "pass-through zero" for the correct operation of gas-fired electric boilers. This is due to the fact that such boilers are sensitive to the presence of a real zero, for correct ignition.
Examining the UPS with an Oscilloscope
And now the fun part.
Back UPS Output Voltage
Conducted a study using a Fluke 124 oscilloscope. Oscillograms (shape of pulses and oscillations at the output of ups) are presented and commented on below.
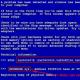
What does this timeline show? Period 20ms, frequency 50Hz, amplitude 315V. It is worth noting that the phase of the sine and the generated pulses are the same, which is good. When the mains voltage is lost, the UPS hesitates for 5-7 ms, and then there are pulses, which are called "quasi-sine". Here they are:

Back UPS. Output voltage when powered by batteries.
The oscilloscope has measured the RMS voltage (root mean square), it is correct. However, when I measured the same voltage with a multimeter, I got a reading of 155 V. Why is the UPS output low?
The fact is that the multimeter measures only the first harmonic with a frequency of 50 Hz. For the sine, everything is smooth. But if you measure the voltage of such pulses, you need to measure exactly RMS, rms, otherwise the following harmonics will not be taken into account - 100, 150, 200 Hz. And they make up a significant part of the energy, up to 30%. UPS manufacturers know this feature, and in order not to bother (and not to raise the price of their products), they issue such pulses to our devices with an amplitude of about 370V.
Read more about measuring the RMS non-sinusoidal voltage in the video:
Here is an enlarged graph, where you can see that the voltage after switching first rises for half a second to 400V, and then stabilizes:

Back UPS. Exit, duration 2 seconds
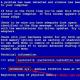
And here is how the voltage waveform at the Back-UPS output changes at the moment of switching from battery to mains supply:

Back UPS, - UPS output voltage when transferring from battery to utility. Pulse shape at the ups output
The phase does not change either, everything is fine. I connected the UPS to the output, switched power modes back and forth - the starter is pulled in securely, no problems.
The subject was an APC Back-500-RS UPS, the parameters are in the photo below:

Back UPS Options - Rear Panel
Smart UPS Output Voltage
Now I will give for completeness a picture of the voltage oscillogram at the output of Smart UPS. The UPS Ippon Smart Power Pro 1000 was tested.

Smart UPS_Grid-Battery
The switching time is also insignificant for all modern equipment - less than 7 ms.
I did not smoothly change the voltage at the input, since there was no such goal. I believe that in this case, the Smart UPS behaves exactly the same as a relay voltage stabilizer.
These studies were carried out as part of a project on an industrial refrigerator.
(UPS) for a computer is recommended to use when power surges are often observed or important information needs to be saved. There are different types of such devices. When choosing, take into account the main parameters, they are correlated with the characteristics of the PC. This ensures the reliability of the computer.
This is the name of a device that continues to supply voltage to the equipment connected to it. This is possible thanks to the built-in rechargeable battery, which turns on when the power supply fails.
When the network parameters change, interference occurs, the operation of the equipment that is connected to the UPS is disrupted: at best, the devices are turned off, at worst, structural elements burn out with strong voltage surges, short circuits.
The duration of the device's operation during a power outage depends on the parameters of the battery: capacity and type. However, the longer an uninterruptible power supply for a computer works, the larger its size, since this increases the capacity, and therefore the dimensions of the battery.
The device not only provides autonomous operation, but also maintains the voltage at a sufficient level, which allows the computer to continue working in a safe mode without the risk of losing information.
However, the UPS cannot run indefinitely. If the power supply is not restored, the device will shut down over time. As a result, information will be lost on the computer. For this reason, the battery level of the UPS is monitored during a power outage. The advantage of such a device is the presence of indication: light, sound.

Light indication of the device
When the operating parameters are changed (when going into offline mode or when the computer is connected to a mains voltage source, a critical decrease in the battery charge), the uninterruptible device emits different types of sound signals.
The lamps come on at the same time.
The color allows you to navigate what changes have occurred in the operation of the UPS. If a simple uninterruptible power supply is connected to the PC, then the minimum period of time during which the computer's autonomous operation is provided will be enough to dump the information on the USB flash drive.
UPS device
Main structural elements:
- battery;
- inverter;
- filter;
- rectifier;
- bypass.
The capacity of the uninterruptible battery can vary within 7-9 Ah. Often, the design of the UPS includes lead-acid batteries. They are sealed and therefore not subject to maintenance.
In simple models, 1 battery is provided, but there are models with a design of 2 or more batteries, which increases the battery life of the connected PC.

Lead Acid UPS
In terms of the device, uninterruptible power supplies differ, which is determined by the belonging of the device to one or another group of equipment. Connecting such devices is the way of connecting a PC - through a socket installed in the UPS case. Their number is different, which is also determined by the capabilities of the UPS.
There is a power button on the case.
The design of some models provides a display that displays information about the parameters of the connected voltage source.
How to choose
Having studied the design of the UPS, they pay attention to the main parameters before buying:
- UPS power (units of measurement - VA). It must be determined independently. For this, the power of the connected equipment is summed up. However, when turned on, the power increases several times, so the resulting value should be multiplied by the inrush current factor. Its indicator differs depending on the type of device connected to the UPS. To find out the value of the apparent power (VA), the net power is divided by 0.7.
- Battery life. This parameter is determined by the needs and financial capabilities of the user. If, after shutdown, it is enough to ensure the autonomous operation of the equipment for several minutes, you should purchase the simplest devices. They supply voltage to the computer for 4-15 minutes after the voltage disappears from the network. This is enough to save information and properly shut down the PC. If you need to ensure the autonomous operation of the computer for longer, choose more efficient uninterruptible power supplies.
- The number of sockets on the device. For home use is possible with minimal features. In offices, such devices are installed with a large number of outlets.

What is UPS used for
The main direction of application is to ensure the uninterrupted operation of equipment, you can learn about this from the name of such a device. If you are wondering what else a UPS is needed for, consider its other possibilities:
- maintaining the frequency of the mains voltage at the required level - 50 Hz, if the value of this parameter changes, the risk of failure of the connected equipment increases, at best the computer will be unstable;
- maintaining the voltage supplied to the PC at a sufficient level, which is necessary when the values \u200b\u200bof this parameter fluctuate;
- protection of the PC from breakage or shutdown during network overloads, which is possible when various household devices and a computer are turned on at the same time, including.
UPS operating principle
The mechanism of action of such devices is different, which is influenced by the type of construction. If you are interested in what a UPS is, you need to study the peculiarity of different types:
- backup (Offline);
- line-interactive;
- online appliances.
The principle of operation of the UPS of the first group is based on switching the computer to stand-alone mode (from an uninterruptible battery) when the mains power fails.
Under normal conditions, the PC is powered bypassing the uninterruptible power supply. These are the simplest devices.

Standby UPS Powercom SPD-1000u
The disadvantage is the low level of protection - efficiency 55-60%. This is because the signal is only partially filtered. The capabilities of such a device are sufficient for everyday use. At large enterprises, the quality of food is lower. For this reason, a reliable UPS is required under these conditions.
Line-interactive models are similar in structure and principle of operation to the previously considered option (backup type). However, they have the advantage of voltage stabilization.
For this, a switching device is provided. As a result, there is no voltage deviation at the UPS output.
An increase in the reliability of such devices is noted - the efficiency level is up to 85%. Uninterruptible devices of this type are divided into groups: models that produce a stepped or "pure" sinusoid at the output (without distortion).

Online UPS are highly reliable.
The principle of operation is based on double signal conversion. As a result, the level of reliability of devices reaches 100%, regardless of the type of power source: mains voltage or battery when disconnected from the power supply.
The current at the input of the uninterruptible power supply is converted into direct current, which is realized by means of a rectifier. Then the inverter converts it to AC. The result is a current with suitable parameters.
Online UPS are equipped with a bypass. This structural element ensures uninterrupted operation of the PC, even if one of the UPS components fails.

Why you need to use a UPS for your computer
The main purpose of connecting a PC via an uninterruptible power supply is to ensure the reliable operation of equipment. When the mains voltage drops, overloads, changes in the frequency indicator, the risk of computer failure increases. With a UPS, this is less likely. Such a device is the first to be hit when there is a power outage.
Another reason for installing it is the safety of information. If a UPS is present, it takes a few minutes to properly shutdown the computer.
An uninterruptible power supply allows you to increase the service life of the connected equipment. Thanks to the stabilization of the parameters, the need to repair the computer is eliminated. The PC works better: there are no crashes, slowdown in program execution.