How to create an internal page in a group or VKontakte community. How to make an internal page for the group menu in contact Building houses from a bar
Dmitry Skalubo
![]()
This article will be useful primarily for those who do not yet have a website. If you already have a website - perhaps you will find some ideas for improving the existing structure, or for creating new sections.
Here are my observations from my own experience with external and internal links. Just what worked for me personally badly or well on several dozen diverse projects:
- For a new project to wait for traffic from Google without links and clicks on them (from sites, social networks, forums, etc.) for the first 3-6 months there is almost no point. If your audience is Google users, you will have to learn to work with external links in one way or another.
- Internal linking is needed primarily in order to solve the user's problem, and not to be able to cram the desired request into the link anchor.
- A link that users regularly click on works much better than one that is just somewhere.
- All other things being equal (if two pages are very similar in content, site trust, behavioral factors, etc.), the page that is linked will be higher.
- Great content will not be left without attention - it will be linked to without you.
- Building rankings and traffic with internal links is sometimes faster than creating new content. Yandex and Google love links.
A site filter or its ban in search engines is also the fastest to come precisely because of the links. Including for the abuse of internal linking, since it is easier for the site owner to influence it.
The importance of internal linking
The importance of links has been declining over the past few years. No offense to patriots, but the Russian-speaking segment of the Internet is essentially copying the development of the English-speaking Internet with a delay of 3-5 years. In the MOZ data from three years ago, the first 2 places are occupied by links:
Here lies the most common mistake - in the West, the process of working with external links is called "link building", that is, creating links to a site, building links. Not a purchase, but primarily work with thematic sites, their authors, forums and others. Create better content to share.
And this is how it works in the West - if your target audience uses Google (for example, they are US residents), you need to understand that with a probability close to 100% you will NOT promote the project without working with external links. Not buying them, but doing “link building”, analyzing competitors, working with other sites and their audience.
For Russian-language projects aimed at residents of Russia, in the first year of the project's life, from 50 to 95 percent of visitors are brought by Yandex, and we still have a shortage of high-quality Russian-language content, that is, first of all, we have the factors that work in the study MOZ are in 3-5 places. These are factors related to the quality of a particular page on the site:
- How much the page content matches the user's request. The quality of the content on the page, the convenience of its consumption, how much it solves the visitor's problem.
- The volume of content, its readability (markup), uniqueness, page load speed, additional "features" like micro-markup, https-protocol, correct display on the user's device.
- User engagement, behavioral factors. This is the click-through rate of the page and the domain at different positions of the issue, the percentage of bounces, the depth of site viewing, the time on the site.
And with the help of internal linking, you can influence all 3 factors. Now let's look at examples. Here's a very well done:

What's good about this example:
- The block with an internal link is placed as it should be - this is useful additional information for the user.
- The link is contrasting and noticeable, the request of the promoted page is organically entered into the anchor.
- Good readability, it is clear what the user will see when they click on the link.
- You can enter from one to 10 words in the linking block, which does not stand out from the topic of the page, which will give additional traffic for low-frequency and low-competitive requests to the current page. The attentive reader will find in the first example several nonrandom matches with Yandex data:

In fact, such a block of internal linking does not contradict any of the 3 points that relate to the concept of a quality page. The linking block complements the content of the page, increases its volume and readability, increases the chance that the user will stay on the site to learn more about the insulation of the balcony.
What can be done better in my opinion - since this block already exists, it was possible to refer to other pages that invite the user closer to signing the contract - terms, guarantees, prices. Here's another example:

What's good about the second example:
- Prices are indicated.
- Links are divided into groups.
- A separate block of advantages of ordering in this particular company.
What is not very good is that it is a pass-through block, that is, it is the same on many other pages. Such a block copes with the SEO component (transfer of weights to important pages). And the disadvantage is that on the page about balconies there are 3 links exclusively about windows, they do not carry any added value and most likely are not needed by the user.
A few more reasons to set up competent linking
For large projects, linking blocks are one of the ways to quickly index site pages. The most understandable (although not entirely correct) example is news sites; it is critical for them that all news gets into search results as soon as possible. Specifically for news sites, it is also important to add the site to Yandex.News and Google News, since, first of all, the news is generated on the basis of RSS feeds. This is how it looks:

This issue is generated precisely by sending data to Yandex.News and Google News. And here's how linking is used on a news site:

Such blocks on any site will speed up the entry of new pages into search results. A small tip - new pages in niches with empty search results give the first visitors a few days after publication.
The main plus of internal linking is not SEO. The main advantage is the correct alignment of user paths through the site and, as a result, the increase in conversion. The fattest example from personal experience:
- A section with reference information was posted on the site.
- After 3-4 months, the attendance of the reference section from the search was several times higher than the attendance of the main selling pages of the site.
- Over the next 4 months, experiments were carried out to place links to selling pages on help pages.
- Selling pages in search grew by an average of 25-30% for basic queries (SEO-effect, which, however, could be the result of other work on the site).
- From 5 to 11 percent of those who went to the selling page using the links in the linking blocks ordered a product (on average, about 8% conversion). Despite the fact that the average conversion of selling pages for all traffic sources, including the search engine, was rarely higher than 3%.
That is, simply due to the fact that on all information pages of the site there were links of the form "You can see the price and buy here" - there were from 30 to 50 new hits per month.
I conducted similar experiments on different projects, on different topics. In financial terms, the linking gave clear and measurable financial results that are very easy to measure:
- In the linking block, a UTM tag was stitched into the link, indicating which page the click was from.
- In the analytics system, for the purity of statistics, data is taken, where the entry pages to the site are pages that have a link block.
- By tags, site visitors are counted who have become customers (for this, you need to set up goals in Yandex.Metrica or Google Analytics).
More clearly:

This method is available for any CMS, and even for a small site that uses HTML files. There is only one drawback of this method - you will not have quick access to transparent statistics for each link, if you have not configured the connection between the statistics systems and the application registration program.
More advanced level - set up a link module for your CMS, which allows you to:
- Insert the code on several pages at once (first, you place in the page code the places where the links will be located, and then in 1 click put the desired block on any number of pages).
- Automatically count the number of clicks on links (allows you to select the most clickable blocks).
- Conduct A / B tests automatically (if you are satisfied with the current click-through rate and conversion rates for option A, do not change all blocks, but show option B to a given percentage of visitors).
- Show linking blocks designed for the user's device (depending on the used OS and screen resolution, a block adapted for this device is shown).
If the site engine you are using does not have such modules, most likely you will have to master one of the TDS (Traffic Delivery System) systems. TDS - traffic distribution systems, allow you to replace the page code with a specified one, depending on dozens of parameters - by display resolution, by OS, by keyword, by geolocation, etc.
The introduction turned out to be quite voluminous, so once again, briefly about the important:
- Previously, the number of inbound links to a site and to a specific page was more important than the quality of content and behavioral factors. Now (at least for Yandex), even a site with zero links can receive visitors if the page is of high quality.
- It's hard to get traffic without inbound links on Google. Many commercial topics in the top 10 are old, awkward, but link-inflated sites.
- Yandex also considers links in commercial topics.
- For the purchase of links, you can get a filter in both Google and Yandex. A good purchase link is one that you yourself would not think was purchased.
- Internal linking works well for SEO, but it is more justified for large projects where there is where and where to put links.
- With the help of internal linking, you can improve the donor page on your site and get the desired anchor to another page.
- Internal linking allows you to "hook" the user and redirect him to the landing page.
- Internal links from the visited pages of the site to new ones accelerate their getting into the search results.
- Linking with an emphasis on marketing, not SEO, can be calculated very accurately - in the money earned.
- You need to deal with internal linking with a scientific approach - consider everything and everyone, experiment.
- Don't reinvent the wheel - most likely, there is already a module for the site engine for your needs, or one of the TDS systems will suit you.
Site structure. Why is power in SILO and where does the term come from?
For myself, I first discovered the term "SILO" by reading it (you can do this too, there is a volume of about 30–35 book pages). The basic idea is simple:
Grouping site pages into thematic sections allows search engines to more accurately determine the topics of pages in these groups and the topic of the site as a whole. The optimizer, on the other hand, can selectively "strengthen" some pages in groups using internal links.
The literal translation "SILO" (bunker) was not used by Russian-speaking SEO specialists. Commonly used terms are "cluster", "page group", "category".
Now there are 2 most common approaches when designing a site architecture. "Site architecture" sounds clever and it immediately seems that it is very difficult. To put it simply, this is what pages on the site to make and why, how to group them.
Site structure for SEO
The first approach is to collect as many user requests as possible and distribute them across the pages of the site according to the principle of semantic relevance. That is, queries are grouped by text match. It looks something like this:

With this approach:
- All possible requests in the site's niche are collected, non-target ones are removed (other cities / countries, not suitable for the type of goods or services, for the price, and so on).
- Requests are divided into groups by text (and partially) by logical coincidence. The quality of the breakdown depends on how well the performer understands the site's niche. If you don't understand well, you can see requests on the landing page for different target audiences, for example, "cheap" and "premium".
- The site structure is sketched from the list of pages. Very often - the main 10–20 pages have some kind of coherent structure, and the rest of the pages are simply published in the section "Information", "Useful materials" or similar.
- These pages are posted on the site, after which promotion is reduced to buying links and rarely adding new pages.
The first disadvantage of this approach is that most often new groups of requests are not collected. The site stops developing at the stage at which it was created.
The second drawback is that internal linking is done according to one of the schemes found on the Internet:

If the site does not have a clear logical structure, it is very difficult to do normal linking in it.
If on the site all pages are piled up in a heap, search engines cannot determine the topic of the site section or group of pages. Small (100-1000 pages) sites are bypassed in the search results of giants like "a site about everything", including due to the narrow specialization of the site or its section.
The third drawback of such a scheme is the quality of the pages itself, but this is a topic for a separate article. In short, in most cases it is impossible to take and create a page that will qualitatively answer 40-50 requests, especially if some of them are commercial, and some are informational.
How do search engines determine the structure of a site?
Search engines can determine the theme of a particular page on a site. And they can quickly and correctly determine the structure of the site, if the pages are divided into sections of the site physically or logically. Physical separation:

That is, in a browser, the URL structure looks something like this:
site-name / legkovie / diametr
site-name / legkovie / marka-avto
site-name / legkovie / brend
site-name / legkovie / sezon
site-name / legkovie / sezon / letnie
site-name / legkovie / sezon / zimnie
With such a site structure, search engines perfectly understand which pages more accurately respond to a user's request. And you will get more or less correct linking within one group of pages automatically. The most important pages will go to the main or additional menu, the nesting of the pages will be indicated by "bread crumbs" - navigation through the sections of the site and their hierarchy. Here's an example:

In this case, all pages of one group refer to parent pages, child pages, neighboring groups. It is easier for a search engine to understand what a section of a site is about. The site receives traffic:
- For narrow queries (for example, "buy an asus laptop model X") - to the product cards page;
- For broader inquiries ("buy an asus laptop") - to the category page;
- For competitive high-frequency requests ("buy a laptop") - to the "Laptops" page.
In this case, it is enough to simply "pump up" the necessary pages with internal links - for example, by placing in the category the block "top sales", "best rated" or similar ones with links to the necessary pages. This does not only apply to online shopping. Here's from another niche:

Together they form a cluster. For general queries, the search results show the entire catalog, for narrower queries - the corresponding cluster page. As you can imagine, the more niches a site unites, the more clusters it can accommodate.
The logical separation of the site structure differs only in that the URL structure is not specified by the site engine, and the search engines determine the connectivity of the pages by their linking. All site pages can have the same nesting level, for example:
site-name / page1 site-name / page2
site-name / pageN
…
site-name / pageN + 1000
In this case, search engines are more likely to identify the most significant pages by internal linking. These will be pages from the main menu (since it is present on all pages of the site), as well as pages with the maximum number of internal links.
Clusters will also be identified by internal links. For example, 100 pages of the site link to each other, and they all link to the 101st page, and the text on these pages has a common semantics (for example, "project", "house", "bar", "price"). The search engines will determine that these are pages of the same section. But organizing the correct structure of links on such a site is more difficult, and it will not be possible to do basic linking within clusters by 100% automatically; you will need to think over and write down the rules for each group of pages. What it looks like:

By the structure of the links, search engines understand that pages 2, 3, 4 and 10 are pages of the same group, and that 10 is the main page of the group (since everyone else links to it).
The main disadvantage of such a site scheme is the difficulty in building the site structure through interlinking. Here's what John Mueller, Google's Webmaster Specialist, has to say about this:

Changing the site structure can take time and not bear fruit. So if you don't have an obvious confusion with the structure, it's best to just keep going.
Site structure for people
When creating a site structure "for SEO", all possible user requests are found and page groups for these requests are created. When creating a website for people, the situation is reversed. A site structure is created that covers all possible queries from users, and when created, these pages are optimized, including for queries from search engine statistics.
The main advantages of this approach are:
- The site will have more pages, due to understanding the needs of the target audience.
- Pages will be linked to each other primarily not by semantic basis, but by user needs. This makes it possible to bring a visitor to the site at any stage from choosing a product / service to choosing where to buy.
- Due to the connectedness of the pages, the behavioral factors on the site are better - more depth of viewing, time on the site.
Let's take several different commercial niches and analyze clearly how the structure of a site for people will kill two birds with one stone - get the correct internal linking and excellent behavioral factors. Niches:
1. Construction of houses from a bar
As an example, let us take one narrow group of clients' interests - houses from a bar with an attic. In the best case, with an SEO approach, from 1 to 5 pages will be created on the site (projects, photos, reviews, finished objects).
But such a group of pages on the site can be made if you think about the needs of the user:

Here you can also add different foundations, roofing, quadrature, geometry (6 x 6, 8 x 8, 10 x 10), the presence of a terrace and another 30-50 options. With this approach, the number of relevant internal links between these pages will be tens or hundreds, there would be something to show on them. Such a group of pages will collect traffic for hundreds of requests - from low-frequency to high-frequency. And if for SEO purposes it is necessary to "transfer" the weight to some of the pages - you can do it, it will be enough to add linking blocks to the donor pages.
In addition to internal links, the conversion on these pages will be higher, tested in different niches.
And when you create such groups of pages, ideas for creating new content will snowball. For example:
- Differences between glued and profiled timber, advantages and disadvantages.
- What type of foundation can be used in the construction of a two-story house from a bar.
- What is included in the construction of a turnkey log house.
2. Online store of building products
If you take a step away from the catalog structure of almost any online store that sells materials for construction and repair, a lot of ideas will open up that have not yet been really implemented. In the best case, to help customers and to increase the average check, blocks “buy with this product” are used.
At the same time, GOSTs, SNIPs, regulatory documents are completely ignored. Everyone who has undertaken repairs will remember repeated trips and trips to “buy this or that”. This is an almost inevitable step, even with a well-made budget. And to get internal links you can use:
- Technological maps for work with a list of tools and materials. For example, from a work sheet for laying a laminate, you can get links to materials, to the tools used, to pages of laminate categories by class.
- Instructions for the selection and use of consumables - from paint to cutters.
- Photos of interiors from catalogs of suppliers - you can put internal links to the used articles of materials.
- Instructions like "How to do such and such work yourself."
And now the question is - have you seen this somewhere? I've only seen so far in directories like this:

And such pages fit perfectly into the structure of the site, they are useful to visitors, they provide internal links. You just need to think about people, not SEO.
3. City portal
Usually a city portal is a collection of news, a catalog of organizations, posters of various events and other things. It is easy to make the site more useful for users and get internal links to the necessary pages. It is enough to display the data in a format useful to the user:
- Not just a list of kindergartens or schools - but by district and bus stop.
- Any services like food delivery can be divided into round-the-clock and non-round-the-clock.
- Events are divided into free and paid. For children and adults. For preschool children, for elementary grades and so on.
Here's an example for Moscow:

And there will be many groups of requests like “where to go with a child 2/3/4 years old in Moscow”, “where to go with a girl at night in Moscow” and others.
How does a site structure for people find site ideas and improve conversions?
The site structure for people approach can be perfectly combined with a marketing approach. It works in niches with big checks, with a long journey from visitor to customer. Companies that are the first to learn how to build the structure of pages so as to direct the future client to the right stage before the sale will sooner or later overtake the competitors. Or they will not let competitors get around them.
What questions will interest me if I want to build a house, but I myself am not associated with construction?
- How many floors and rooms do you need?
- Should I order the project and construction separately or not? What's the best and why?
- What shape of the house to choose (if it is not limited by the shape and size of the plot)?
- Do you need a basement / ground floor?
- Do you need an attic or attic?
- Ceiling height?
- Which foundation is right?
- What are the walls made of?
- If there are several floors - what kind of floors to make?
- What is the roof from?
- How many chambers should there be in a glass unit?
This is only a part of the construction stages of the "box". Each of these items can be "expanded" to the same list.
And here a huge field of activity opens up for the development of the site and the creation of new materials. For example, in my region, wall materials can be called 7 or 8 offhand (brick, shell, aerated concrete, timber, sip-panels, cinder block, thermo, foam concrete). Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. If the company is only engaged in construction, you can safely create a cluster of pages, professionally comparing all these materials.
And this will be very useful material. And visitors readily follow the links between such pages. And the site rises to the top simply due to the fact that the time on the site and the number of page views are 2–2.5 times higher than those of competitors.
Such pages increase the credibility of the company and can lead to leads. A subscription form of the form "Specify your mail and phone number and get a comparative description of the top 10 wall materials in 3 minutes" will give applications from potential customers.
This approach will not let you miss out on pages that could have been missed when creating the site structure and collecting requests. And each of these pages will allow you to place internal links to the selling pages.
Also, on pages with a narrow focus, the conversion is higher. If you are reading this article, you probably have a website. Imagine that you are not satisfied with the current hoster (your online store on Bitrix began to slow down after adding 30,000 products) and you are looking for a new one - which offer will suit you:
- Great hosting for your website.
- Hosting for large online stores on Bitrix.
Most likely the second. And it works in any niche where the majority of customers are making choices rather than being driven by the wow effect.
Site structure and promotion
Site structure and linking greatly affect the position of the site. Of course, if the site meets the basic requirements:
- There are no technical errors on the site that hinder site promotion.
- The information is relevant and competitive (eg prices plus or minus market averages).
- The site loads quickly and is user-friendly.
How to more or less correctly compare the effectiveness of promoting a large site that tries to cover the topic completely, and a small narrowly focused project that compete in a group of requests? If you do not know the financial indicators, you can compare the number of visitors divided by the number of pages on the site. For example, here are the averages for two topics:

Data for all sites is taken from the same services, so the errors for all are approximately the same. Competition is the percentage of requests for which sites intersect in the top 10. It does not take into account domain trust, site age, links, and more - although by all of these indicators, large sites have an advantage.
I collected such data for absolutely different projects in different niches. And there is only one dependence - sites operating in a narrower niche (with rare exceptions, less than 5%) collect many times more visitors per page. For example, here are the sites that voluntarily shine their traffic. I selected sites with less than 1,000 pages in the index of Yandex and Google:

The other 30 are specialized sites. What does it mean:
- The site is not about all banking products in general and their comparison, but only about debit and credit cards. Or just about the mortgage and its terms.
- The portal is not about accounting from foreign economic activity to 1C, but only about everything for individual entrepreneurs.
- The site does not sell 100,500 construction products, but only doors. Or just wooden doors.
- The online store does not sell everything for needlework, but only everything for knitting.
Why are sites with a narrower subject area the number of visitors per page hundreds of times higher than that of larger competitors?
The less content, the easier it is to make it of high quality.... Backlinko.com, a foreign SEO specialist's website, can be considered an excellent example. Hundreds of thousands of clicks from the search every month, despite the fact that the site has 71 pages. Internal linking there is also done perfectly - I want to click on every link in the text.
The pages on these sites are usually linked and provide more information.... Where there will be 1 page on a large project, on a small one there will be several linked together in a cluster or group. Moreover, most often each of the group pages on a small project will be more complete than a page on a large one.
Due to the previous point, visitors spend more time on the site, look at several pages... Follow internal links. That is, internal linking works many times better if the site has a cycle of materials that is conveniently linked to each other than if it is just links to pump the page weight.
Many topics have their own slang or specialized terms... Small thematic sites are many times superior in semantic coverage to large ones. More or less like this:

So it turns out that small sites with well-designed pages, with cool content, with a good logical structure (visitors "hang" on the site and look at 5-10 pages) collect traffic comparable to mastodons, at incomparable costs.
How to build a logical site structure?
If you have a commercial resource that makes money selling a product or service, the correct logical structure can be described in one sentence:
A potential client on each of the pages of the site should see a simple and understandable next step that brings him closer to closing the deal.
In some cases, this is very easy to do. For example, online stores almost always follow this pattern.

The goal is to place an order. To do this, the visitor must add the product to the cart. You can add a product to the cart either from the product card, sometimes from the category. This means that all the paths of the user through the site must be built in such a way that he falls into either a category or a product card. In the example above, a popular article can be referenced by 10 categories, an article (or several), neighboring articles.
And the rest of the pages that do not directly sell a product or service link to selling pages. This can be a Q&A section, background information, comparison pages, blog articles, news.
On small sites (10-100 pages) everything is simple, the most basic pages are located in the menu, which means they receive links from all other pages. In addition to menus from other pages, internal links can also be placed for marketing or SEO purposes.
On medium sites (up to 10,000 pages) usually implemented either a catalog structure (if it is an online store) or headings. Pages are arranged by groups (headings, categories), each page of the group links to other pages of the same heading. For SEO, the most important headings and pages are linked from other relevant headings.
On large portals (with hundreds of thousands and millions of pages) either an approach with categories is implemented (only adjusted for the number of categories), or simply all pages link to more or less suitable pages according to the Wikipedia principle. Some kind of systematic linking work on such projects is unrealistic for the following reasons:
- Lots of UGC content - users create site content.
- The site receives traffic from hundreds of thousands of requests. It is possible to “pump” pages with internal links only selectively if there are some pages that give the main result (selling something).
- Often the traffic is event-driven, or generally one-time. This is especially true for news resources - you just need to post more news and do it faster.
Site URL structure
Today it makes no difference whether the structure of the site is organized by nesting levels (sometimes it reaches 4 or more levels) as in large projects:

Sometimes it also happens - Main page / category / sub-category / sub-sub-category / sub-sub-sub-category / page / page-option
This option is convenient because automatically all pages in the chain link to each other. The disadvantage is that you need to think over the structure of the site in advance, otherwise transferring pages from one section of the site to another will require setting up redirects. What kind of hard labor it is - you won't understand until you need to spread several thousand pages into several hundred different sections.
The second approach - all pages of the site can be nested at 2-4 levels:

In fact, the product is at the second level, and the / p block displays either the current category or some other parameter of the store.
The advantage of this approach is that all main pages can generally be in the same category, and the rest of the pages just display lists for the convenience of users. For example, all products are located at site / tovarN100500, and categories of the form:
Home / notebook-asus /
Home / notebook-asus / 8gb-ram
Home / notebook-asus / core-i3
They are simply listings of goods according to specified characteristics. The main advantage of this approach for internal linking is that from such categories you can get dozens of internal links to promoted products.
The disadvantage is a lot of work with the head or hands. The products themselves will not appear in the category, you will need to include them by hand, or think over output templates.
I cite examples for online stores as the most accessible to understanding, but the same principle can be applied to projects of a wide variety of topics. For example, for a site about dogs, information about the breed can be kept in one category, for example, "Home page / poroda / haski", and links to it can be displayed on dozens of other project pages:
Home / srednie-sobaki /
Home / krasivie-sobaki /
Home / sobaki-dlya-semei-s-detmi /
Which internal linking option should you choose?
If you know for sure that you will not have the time or opportunity to do point-by-point linking, choose one of the automatic schemes tied to the URL structure. The following options are obtained ...
First, all pages link to each other:

In such a situation, all pages are more or less equivalent, all pages are linked to each other.

The third option - the weight is transferred to the final pages of the site. The scheme would be similar, only the arrows would go in the opposite direction (to the page blocks).
Any of these schemes are usually hardwired into the logic of the site's engine. If you want to go to advanced internal linking, then the scheme will be something like this:

How this will be implemented in the URL structure and in the physical structure of the site depends on the technical solution used.
In my opinion, this option (or adapting it to your business) provides maximum flexibility. In the example above, a specific model was left from production and sale - it was replaced with a similar one. And in more conservative topics for a year or two, tens and hundreds of internal links can be put on the main selling pages.
How to organize data storage on the site?
If it seems to you that the diagram from the previous picture is my hypothesis about content marketing "like in the West" and this will either never happen here, or will come sometime in 5 years, go to any of the articles on request:

More than 1,000 materials, which perfectly fit the internal linking with the intention to invite the visitor to walk closer to the checkout and unbutton the wallet:

Each link leads to the corresponding section of Yandex.Market. Of course, 1000+ articles on the Internet are a drop in the ocean. But this is Yandex. Which can display "Yandex.Market" for its entire audience for any commercial request.
And big companies do the same:

Think big companies can't count money? Experience tells me that the production of one page for these sites can cost tens (if not hundreds) of times more than the owner of an online store or a thematic site. And 2,000 articles for the example on the right almost certainly cost several million rubles (or rather a sum with 7 zeros).
There are many niches in Runet where large companies will reach only in a few years. And all these years, it is you who can receive visitors and sell them your goods. You just need to start early, this is almost always enough.
To successfully implement internal linking that combines SEO and marketing, take note of the following tips:
Characteristics of goods or services... Everything that can be considered a characteristic should be stored in a format that will allow you to get complete information automatically. For example, if you sell wallpaper, all characteristics like "plain", "with a large pattern", "white wallpaper", "with a black pattern" and other options should be assigned to the corresponding articles. So that you can create a category "white wallpaper with black pattern" in a couple of clicks by simply adding the characteristics.
Better to see once than read several times... Classic links also work well if they are in place. But in information materials it is better to provide for a beautiful linking output. At least with banners, if appropriate:

Here's another good example:

Think broadly - the more possible target audience groups you can reach, the more visitors and sales you will get.
Content marketing works best in the long run... Search algorithms change from year to year, every month a new wow-technology comes out that "should break the market and take a significant share of sales." And projects that systematically work on the production of high-quality content simply grow every year. In attendance, in recognition, in money.
And this is not only in conservative niches, where nothing new has appeared in the last 20 years and will not appear for another 20 years (for example, many construction niches). See how many tech projects are attracting visitors. The technique becomes obsolete every year, but leading portals and many newbies are quietly gathering their share of the audience.
Think about how to create new pages with existing content that address the needs of your potential customers.
When designing a new site functionality (content section, filters, blog, question-answer, etc.), think about how you can quickly put useful and convenient links to the goods and services sold from this section.
Consider efficiency immediately. Analyze your competitors, make predictions.
What if you have a small project?
Many of the techniques mentioned earlier can be easily implemented in online stores or catalog sites. But what if you have a small project with a narrow topic? A universal option is a section with questions and answers.
- Don't make everything one page. A separate issue is a separate page.
- Provide helpful answers. Pages "for SEO" with answers like "and you can find out by calling by phone" if they go to the TOP - they won't stay there for a long time. In addition, it is more difficult to link to other pages of the site on uninformative pages.
- Make the section convenient. No 11 size light gray fonts. If you yourself are uncomfortable reading such pages, visitors will also be uncomfortable and will leave.
- If there are a lot of questions, make the navigation easy. Subsections, headings.
- Strange advice, but proven on my own projects. If you have an online consultant, don't let visitors add questions. They will often be short, stupid and illiterate. And the same or the same type. Which is bad for both convenience and SEO.
- On the question pages, give the opportunity to contact you from the same pages - phone numbers, instant messengers, social networks.
In addition to questions and answers, you can use references, comparisons, instructions, standards. If you have few ideas for such sections, check out the most trafficked sites in your niche in big cities. If old projects can still go out due to reference, domain age, site trust and other things, young sites have to create awesome content.
Why does it generate sales?
If you are looking for a "black women's long down jacket with a hood" - you will linger on this page:

And it is in the top 3 for many targeted queries. Including because of the linking - on other pages there are links with a direct entry of the request.
The next time you walk around the city, pay attention to the colors of the PVC window profile, except for white and wood-like. And then look in your city for something like "pvc windows% color%% city% price". And look at SERPs in a very competitive niche. Yes, at least in Moscow:

Even the screenshot shows that the price of windows with a colored profile is 40% higher. Such a request can be perfectly worked out in the "question-answer" section, you can create a separate page with standard sizes and prices. And the buyer will call if everything suits him. And such pages can pump other pages with links. Solid benefit, in general.
As always, there is a little catch. In order for such pages to appear on the site, you first need to think, and then work.
How to make the correct site linking - checklist
If you already have a site with a large number of pages, I can only advise the obvious - count the page weight and link to the most important pages from the rest. This is the easiest and most painless way to transfer weight. Finally, a small checklist.
- You must have a semantic core for the site - user requests distributed across the pages of the site. Information requests should be placed in the information section, commercial - on the selling pages.
- If possible, there should be no cannibalization within the same project. That is, one group of requests on the site should be represented by one page. If there are several pages, the site will compete with itself in the search results, this is bad. If there is such a thing, combine it into one page, set up redirection from a remote page.
- When working with internal links, the ratio from paragraph 4 can be disregarded, there is only one rule - do not bend with anchors. It is better to write an incomplete request naturally than it is unnatural to write a full one.
- Avoid broken links on the site, if you have a lot of them - you "overflow" the page weight to nowhere.
- On the donor page, 1 link to the acceptor page is enough, if there are several of them, the transferred weight will not increase from this. If you need to put several links, you can close unnecessary links in scripts.
- Links that are followed carry more weight than just links.
- The link should look like a link (for example, different color, underline, hover effect) if it is text.
- The acceptor page can be downgraded for too unnatural internal linking environment. Therefore, it is better to use constructions of 2-3-4 words, while not often repeated within the site.
- If an image is used as a link, the “alt” tag for this image will be taken into account as an anchor.
- Search engines are smarter than you think, so don't try to "pump" important pages with js-scripts with different ways of hiding links.
- Bother less. Any excessive manipulation by the site is a signal that the site is trying to somehow outwit the search engine algorithms. I have yet to see a site that gets significant pessimization for working with internal links if the links there simply provided easy navigation (and still promoted landing pages).
- Use such linking blocks in which you yourself would like to click on the link.
- For a visited project, you can quickly promote new pages for non-competitive requests simply by placing links and getting transitions within the site. This technique also speeds up the pages to get into the main search engine index.
- When you work with a reference, consider the result. In SEO metrics or money. If you are using internal links for marketing purposes - test, choose the best option.
- If you do not have interlinking, implement it, you increase the time on the site, the number of page views.
- If your site structure is not based on URLs, but on links, try to link within the thematic sections of the site.
- If you don't know where to get links from, start a blog or content section.
A little practice
Two simple rules:
- Correct or remove broken links.
- Make sure important pages get the most internal links.
Search for broken links on the site. How to check and quickly fix broken links for free?
The free Xenu program (you can download it from the official site) allows you to scan a small site in a few minutes and find broken links. Download, run. After installation:


To do this, use the Ctrl + R combination. A repeated error check is needed, because the program might have made a mistake - at the time of the check, the link might not be available, although in fact everything is in order. This can happen due to a second failure of the site, due to a too long server response. If after re-checking the errors remain, check what is wrong. In order to open a page with a broken link you need:

Decoding:
- Go to the URL properties with the "not found" status.
- There is a broken link in the "Page URL" section.
- The "N pages linking to this one" section lists the page (or pages) where this link is located.
All you have to do is fix the broken links.
How to find out the link weight of pages for internal linking?
For small sites (up to 2,000 pages), the free version of the Page Weight Lite program is enough, you can download it on the official website.


For small projects, 2 passes are enough to determine the most cited pages of the site. It makes sense to set a higher value only if after two iterations the difference in weights differs slightly, and you cannot understand which pages receive the most weight. It's best to ignore external links to calculate internal weight. Today they are there, tomorrow they are not --– so we disable this option.

Administering a community or a VKontakte group, page managers most often have enough of the usual post format, which assumes solid text, video or photo in the form of a gallery with an attached link leading to a third-party site, etc. But sometimes there comes a time when you need to create a more formalized material in the social. networks, using headers, lists, and other design features that are usually inherent in standard pages on information sites. It should also be borne in mind that many VK users will be happy to read material on social media. networks, but will be reluctant to go to another site, in addition, wiki pages can be indexed by search engines, which will attract visitors to the community who can subscribe.
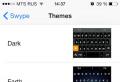
In order to create a VKontakte wiki page, copy the following URL into the address bar:
http://vk.com/pages?oid\u003d-XXX&p\u003dHeader_Example
change "XXX" to the id of your public or group, change "Title_Example" to the title of your future article and press Enter. Now the page is created, and you can start filling it by clicking on the button "Fill with content".
Once the page is ready, you can publish it to a community or group post by specifying the URL of the material without the ending "? Act \u003d edit". When the page is pinned to the post, erase the url, the link will still be active and will not disappear. If you simultaneously attach a wiki page and a photo to a post, then when you click on the photo, your material will open.


IMPORTANT POINTS:
1) Page access
In the lower right corner of the page you have created there is a button "Access to the page", where you can specify who will be available to the page for viewing and editing. By default, editing is available only to administrators, which is not advised to change, since your guests, most likely, will not miss the opportunity to contribute to the material, sometimes not entirely useful.

2) Save the url of the wiki page you created
After making the wiki page, do not forget to copy the address of the material, this information is not saved anywhere in the community. If you create materials in a group, then they can be seen when editing the section "Latest news" by highlighting the title and clicking "Add link".
3) After creating the page, the title of the material can no longer be changed
When creating a wiki page, indicate the correct title of the material in the URL "Title_Example", it will be the title of your page, which cannot be changed.
The windows and doors in the bath are made smaller than in ordinary living quarters: this makes it easier to keep heat. Doors are usually single-leaf and open outward.
Bath doors can be made in different ways. One of the options is a door made of boards, upholstered on the outside with some kind of insulation, and on the inside covered with linseed oil, thin waterproof plywood or fiberboard.
Another option for a sauna is comfortable and warm panel doors made of two different sized wooden frames (the inner frame should easily fit into the outer one). For a snug fit, the outer frame must strictly match the dimensions of the doorframe, and the edges must be slightly chamfered. Both frames are sheathed with fiberboard on both sides and filled with heat-insulating material. Then the inner frame is inserted into the outer one and fixed to it with screws.
In the washing room, you can install a vapor and moisture resistant door from one frame, attaching fiberglass sheets to it with screws on both sides. The space formed between the sheets is filled with a light heat-insulating material.
Locks on the doors are usually done from above and below. At the bottom, for this purpose, you can use any metal hook, and at the top, the lock should be wooden, so as not to burn yourself.
Door handles are also made of wood. For their manufacture, you can use any available material, up to knots and bizarre roots found in the forest. Before installation, the door handles are covered with linseed oil and dried well.
The windows in the bath should have the form of horizontally elongated rectangles, since it is this shape that makes it possible to better retain heat in the room. Windows can be made both in walls and in doors. The area of \u200b\u200bthe bath window may vary depending on the view that opens, but, as a rule, it does not exceed 5-7% of the floor area. The window is positioned so that you can look into it while sitting or lying in the steam room or standing in the washing room.
Both with double and single frames, the windows in the bath must have double sealed glazing (on a single frame, glass is attached on both sides). It is difficult to make a window in such a window, but it greatly facilitates the ventilation of the bath.
In brick baths, it is advisable to make windows from glass blocks. They provide soft diffused light, do not require curtains, and are more hygienic and durable than conventional ones.
For artificial lighting of the baths, sealed fog lamps of yellow and milky colors are usually used.
To ensure good ventilation, an outlet is made over the upper shelf - a small rectangular or round hole in the wall. It is closed with a removable cover made of a lump upholstered in soft material with a handle or a sliding wooden flap.
For the same purpose, an inlet ventilation hole is made at the bottom of the door or near the stove-heater at a height of 25-50 cm from the floor. It should also be closed with a flap or latch.
The next stage of the internal equipment of the bath is the manufacture of shelves in the steam room. If the bath is spacious, there can be 2 or 3 shelves.
The widest is the upper one, on which they are usually soared lying down, the lower ones should be a little narrower. The shelves are placed one above the other or with the letter "G" (the latter option is appropriate in saunas with a combined steam room and washing room).
To make it convenient to sit on the upper shelf, the distance from it to the ceiling should be 115-120 cm, and between the upper and middle shelves - 40 cm. The lower shelf is usually made at a height of 20-25 cm from the floor. In addition, it must be taken into account that the upper shelf must be at least 50-100 cm higher than the upper stones of the stove.
The best shelves are made from linden, aspen or poplar planks: they are pleasant on the body, dry quickly and do not contain tar.
Shelves are made on the frames of beams, placing the boards across the frame so that a small gap is obtained. In this case, the boards are fastened with stainless screws from the side of the beams so that their caps do not burn the body.
For greater convenience, the upper and middle shelves can be made removable on stationary supports, and the lower one - in the form of a portable bench.
However, do not forget that all elements of this equipment, even the smallest ones, must have a bulge or a slight slope so that water can drain freely.
It is also necessary to take care of the little things that will help to create maximum comfort in the bath: wooden grilles on the floor, shelves for bath accessories, footrests.
Do not paint or varnish wooden surfaces in the bath, as the wood will immediately lose its warmth and its pleasant natural appearance.
Ceiling
The ceiling in the bath should also be insulated, in addition, you should take care of the impregnation of the rafters and beams, as they will constantly be exposed to high temperatures and humidity. Heaters can be very different (glass wool, mineral wool, polystyrene, foam rubber). The main thing is that they are fire safe and sufficiently resistant to decay.
Before hemming the ceiling, which is usually made from planed boards in a bathhouse, the space between the roof and the ceiling should be covered with a vapor barrier. It can be a special material or just plastic wrap. But now the bathhouse is built, and you can't wait to check how much it retains heat. Such a test furnace will allow you to identify all the shortcomings of your work, and, since the construction is not yet completed, quickly fix them.
Bath with your own hands. Interior decoration (video):
The internal sewerage system in its structure is practically no different from. Even at some points it is easier to do it.
Firstly, most pipes are not 110, but 50 sizes (inner diameter in millimeters). Secondly, these pipes are much easier to dock yourself without the help of another person. Thirdly, they are cut faster and easier. By the way, we cut both wide and thin pipes with an ordinary hacksaw with hot teeth made in Germany.
The main meaning in the internal sewage system is the same as in the external one. Horizontal sections must be laid with a certain slope. Only in pipes with a diameter of 50 mm it is necessary to make a slope 1 cm more. For every meter of pipe - 4 centimeters of slope (in pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, this slope was 3 centimeters).
Why do we need such a specific slope, why can't we make 10 or 15 centimeters per 1 meter, because the greater the slope, the better the water will leave? That's right, the water will drain better, but if we only poured water into the sewer. The fact is that with a large slope of the horizontal section of the sewage system, the water will leave too quickly and it will turn out that the water will drain, and small solid particles of debris may remain in the pipe. This is especially important for the sewer pipes through which the waste from the toilet bowls passes. In this case, if there is a very large slope, then the water leaves and the turd))) remains in the pipe.
But I want to note right away that deviations from the slope norms can be allowed, but only for areas not more than 1.5 meters. If you need to change the slope on a small area up to 1.5 meters long, then you can safely do it upwards. As I was told, these are the norms.
Just like when laying large pipes, it is better to replace all 90-degree elbows with two 45-degree elbows. This is 2 times more expensive per knee, but your sewage system will be much better protected from blockages.
It is also very important to install so-called revisions when laying sewers on long horizontal sections. What it is? I'll tell you an example. From the sink and dishwasher from the kitchen there is a pipe with a diameter of 50 mm, the length of this section is 7 meters. So, approximately in the middle of this section, I brought the pipe up to floor level. This pin will be at the level of the finished floor with a plug. I made it in the corridor near the wall itself. Then there will be, or a wardrobe, or a mirror. But if the sewage system gets clogged, then the 7 meter section is very difficult to break through. And with such revisions, everything will be much easier. I hope it won't come in handy, but it's better to let it be. It is recommended to do exactly the same for.
All pipes of the internal sewage system were laid in a dug trench and covered with sand. Then you need to spill it with water, tamp this sand under the pipes with your hands, and then add it with sand, pour more water and preferably walk around.
That's all. Now the photo report:


Left: black, thinnest pipe - water supply; the thickest pipe - outlet to the floor level of the revision for cleaning the sewer; middle pipe - outlet for washing machine just above floor level. Right: outlet for toilet and riser to the second floor. Right corner: outlet for the washbasin in the toilet. Note: this is a furnace and a toilet on the ground floor. There will be a partition between them in the future.

Conclusion in the kitchen for sink and dishwasher just above floor level. In the future, there will still be branching in two directions.
Hello friends. Today I want to talk with you about competent internal linking of sites, and not just any sites, but specifically online stores. Once upon a time, when I was engaged only in my information sites, I would begin to talk about content creators, but now the guys and I in the studio are engaged only in commercial sites, and 80% of them are online stores.
All stores are unique in their own way: different topics, engine, structure, different vision of a “convenient” site from the side of the owner. And for each site you have to implement solutions that are most often repeated from site to site. Today we will consider the most common linking options., among which you will definitely find something new and useful for your online store. In addition, I have stored up examples of bad practices, how to avoid it.
I have described each linking option in detail, why it is important and how to implement it correctly. In the meantime, a little general theory.
What is the correct linking and what is it for
Formally, a link from one page to another is already a linking. But today we look at interlinking in the following vein: interlinking is links or blocks of links that help website visitors find the desired product or service faster and easier, and get to the desired page. Site linking helps search robots to index and re-index pages faster, to correctly distribute static weight between them.
User interests prioritize interlinking, because it is impossible for buyers in the block of similar products to show dissimilar goods or in the block of related products when buying a refrigerator, to show other refrigerators, or, for example, car tires. Everything should be smart: first of all, conversion and sales, and seo is only one of the channels for attracting traffic. In practice, the benefits for seo and for human beings go well together.
So, linking should ideally solve the following tasks:
- Navigation assistance for visitors;
- Acceleration and improvement of indexing;
- Passing static link weight to the desired pages;
- Surely something else, but never comes to mind.
General rules for linking sites
Try to adhere to the following rules when linking (regardless of the type of site):
- Internal links should not contain the rel \u003d "nofollow" attribute. Otherwise, the weight from the donor page will flow away, but it will not be added to the acceptor page, that is, it will simply evaporate.
- The rel \u003d ”nofollow” attribute should be used when the link leads to a non-indexed page, but this link is required. Accordingly, there is no need to force the robot to follow the link and waste time and crawling budget in vain. An example of such a case can be seen on my blog: at the bottom of the post there is a block "What's new on the forum:", links from there come with a redirect to the url pointing to the last post in the forum topic, which is not indexed. Ideally, you should get rid of such links using JS, as I already wrote, the method still works.
- Links should always lead to the indexed pages of the site, otherwise the story described in paragraph 1 above will be repeated.
- Even when setting internal links, you should use unique anchors when linking. Most likely, this rule applies in online stores only for the info section, if it exists, and for manual links. Other links from menus, blocks, filters, tags, etc. are not dynamically modifiable, and there is no need to, because their purpose is simply to be a link passing static weight.
- There are no restrictions and recommendations on the number of internal links on site pages. I am often asked, they say, I heard somewhere that more than 150 internal links on a page is very bad, what should I do? Who said this, where this information came from - I do not know. But I know for sure that everything depends on the specific site and the specific situation. The most important thing from which to proceed is the convenience of the user, there should be exactly as many links as the visitor of your site needs. If you have any doubts, just look at the sites of your main competitors, most likely, they are all similar in structure, navigation and other basic elements, you can learn from their successful experience.
- Internal links should always be direct and go strictly to the landing pages. This means that clicking on the link should return a 200 OK response. I’m not saying that broken links are unacceptable, this is obvious, but I’m saying that links should go without (and if there is not a 301, but a 302 redirect, then it’s quite a disaster). It is not uncommon when the structure is changed, or through the fault of the layout designer (forgot the slash at the end of the link, for example) internal links go through a redirect, it is very difficult to trace it by eye. Everyone should definitely run their site at least once with a crawler, for example, or any other tool.
I would be grateful if you could tell me something else for this section from your practice in the comments. Well, I'm going to describe the schemes and methods for linking online stores.
Linking schemes for online stores
Navigation menu
The first thing I will start with is an element that no online store can do without, and indeed no site at all, is the navigation menu. Navigation can be horizontal, vertical, drop-down, whatever, its purpose is access to all key sections of the site from any page, wherever the user is.
What to do with the menu, how to link from it, how to get rid of unnecessary links, etc.? Personally, I think that the cross-cutting elements of the site, in particular the menu, are not taken into account by search engines, or are taken into account very poorly, because are present on every page and little changes from their absence / presence.
Nevertheless, there are various options. You don't have to go far, I will open 4 large online stores that first came to mind: www.dns-shop.ru, www.mvideo.ru, www.eldorado.ru and www.tehnosila.ru. Let's consider each in more detail:
On the Technosila website, the menu is like a menu, they decided not to do anything with it.
On the M.Video website, absolutely the entire navigation menu with categories and subcategories is closed in the noindex tag. A similar picture is on the Eldorado website. Close menu in noindex it only makes sense not to take into account its textual component, so that the menu does not get into the snippet on the search results, so as not to interfere with the identification of the relevant page (although this does not happen often). In this regard, I fully support the use of the noindex tag, but I do not like that this tag is taken into account only in Yandex, and Google ignores it, but in Google it is much more often the description content is taken as a snippet and problems with a low-quality snippet rarely arise.
On the DNS site, only the deepest categories in the menu are closed in noindex (we also note that in addition to noindex, rel \u003d ”nofollow” is also used for links - I don’t know why), and global and parent categories are indexed. Interestingly, the DNS site uses tags and... These tags are not related to global network search, but are intended to manage indexing for corporate solutions, such as intranet. Apparently insane seo specialists working on this site misinterpreted the meaning and application of these tags.
Footer menu. You can do nothing with the menu in the footer, not close it in any way and not be afraid of the weight leaking onto the technical pages. In terms of content, I like the way it is implemented in the examples above. The menu contains contact information, social networks, as well as links to important information pages: payment, delivery, about the company, etc. It makes sense to duplicate the navigation through the product sections in the footer only if there are no more than 5-7 of these sections (that is, as you do NOT need to do on the vcedetyam.ru website.)
The number of links in the menu. Many people worry about the number of internal links on each page of the site, and with such menus as in Eldorado and M.Video it is not at all surprising. What can and should be done about this? Alternatively: display an incomplete list of categories, subcategories, subcategories, etc. in the menu. And confine ourselves to displaying only parent sections. To make it clear, I will show by example: take the Eldorado website, the "Electronics" menu item, it now contains about 100 links, but it was possible to display only 6 (TVs, Computers, Phones, Software, Photo and Video and Automotive), that is, exclude child elements. But there is also a downside - the lack of detail will confuse visitors, so you, for example, can immediately determine where to look for faxes, memory cards or headphones? Me not. So this option of "losing weight" of the menu is not always applicable, first of all, you should try to look through the eyes of your visitor (and consider him dull, no matter how strange it sounds :), and it is advisable to check hypotheses with some A / B test.
Based on practice, I can say that link manipulation does not give any tangible result for seo. I tried to remove and add links, I tried to close links in JS - this had absolutely no effect on positions and traffic.
Bread crumbs as a linking element
The next integral element of any site, and especially an online store, is bread crumbs. The usefulness of this element is difficult to overestimate, the crumbs carry information and navigation meaning: by looking at them, the visitor understands which section he is in and can always go to the parent category if he is interested in the brand or product category.
Crumbs are difficult to consider as an important element for linking, because 95% of the time crumbs use the same categories and sections as the navigation menu. In other cases, the crumbs may contain links to seo filters from a certain category, which are generated by a bundle of a product category with some property or characteristic. In this case, the crumbs link allows such filter pages to be indexed.
With bread crumbs, there are both unambiguous solutions and not so:
Indexing. I am quite sure that there is no need to hide crumbs from indexing using noindex and / or rel \u003d ”nofollow”. Having opened a dozen well-known store sites, I also did not see a single case of prohibition of indexing.
Schema.org markup. It is worth marking bread crumbs. This will reflect on the beauty of the snippet in Google, although functionally, unfortunately, it will not work. (If you remember, earlier the navigation chain in Google contained clickable links, but once they became just text.) The markup does not affect the formation and naming of the navigation chain in Yandex, but the crumbs themselves do.
The presence of the current page in the navigation. A common question is whether or not to display the title / title of the current page the user is on in the breadcrumbs. I believe that the title of the current page should be displayed as a header in large font below the crumbs, and in the breadcrumbs themselves, only parent categories should be displayed without the title of the current page.
My opinion is subjective, and you yourself decide what you like best. By the way, on the websites of Technosila and MVideo there are crumbs without a product name, while DNS and Eldorado have a product name.
Drop-down menu in items. Another controversial solution is a drop-down list of categories located at the same logical level. In a way, it is very similar to the navigation menu. Here is an example for you, which I took from the site http://ru.biksiko.com:
Or here's another example https://004.ru/catalog/kholodilniki/
I don't know how useful and convenient this is, but such a solution is quite rare.
Another element that is commonly used is related products and recommendations. This block of links, no matter how it is called and what functionality it has - similar products, recommended products, related accessories, other products of this brand, etc. - intended primarily for the user. And it has a marketing goal: a second joystick for a set-top box, a bracket for a TV, a mouse pad - all this to sell additional goods, not for SEO.
 |  |
This is only formally linking. If we talk about seo, then we need a more technical / algorithmic approach to linking, one of such algorithms is ring linking.
Ring linking
I don't know who came up with the logic of work and the name of this algorithm. Although I thought that I came up with when I used this algorithm for my sites, and then released two modules for DLE. But it turned out that everything was invented before us: there are references on the Internet earlier than my posts about linking and modules. But this is absolutely not important now.
The main task of circular linking is to evenly distribute the weight between pages of the same level. The main marker in this case is the page id in the database. That is, there is a sequential selection and substitution of links to products that come before or after the current product. For example, each page links to the previous 10 pages, and at the end, the chain closes, linking the very first to the very last product in the chain. With this algorithm, each page will accurately receive the same number of inbound and outbound links, as well as the same internal weight. Dropping pages from the chain from the index does not break the algorithm, because we link to 10 pages at once. I think you understand the principle of work.
I made modules for circular linking for my information and entertainment sites and tested only there, but theoretically this should work for any site with a large number of pages. According to my experiments, this gave an amazing result: thanks to such interlinking, I achieved 100% (and not approximately, but exactly, page to page) indexing of absolutely all pages for sites where I used the module.
It is logical that we cannot talk about at least some similarity of pages or products, if the selection is simply by id from the database. To do this, in the module, I came up with restrictions that somehow solved this problem - to make a selection by id, but within a certain category or subsection. Thanks to this, it was possible to achieve the output of the same type and similar links without violating the technical requirements - not one huge ring was formed for the entire site, but many rings within the categories.
If we talk about online stores, then in my entire life I have seen only one single store where ring linking is used - www.haldi.ru. You can see an example by going to the page of any product and scrolling down to the "Other products" block.
To preserve the similarity of products, there was a restriction on the withdrawal of products from the common parent category. As you can see, there is no need to talk about similarity anyway. In general, the site is quite interesting in terms of SEO, many different teams have been promoting it (including my team), so I recommend to study it.
To summarize, I will say that this is a very dubious linking option for an online store and I am unlikely to recommend it.
Random linking
An even more ridiculous version of linking, which I called "random linking". Several types of linking can be combined under this name. The first option is purely random linking, when there is a certain block in which links to N random pages are displayed. Links can be both dynamic, that is, each time the page is visited, the set of links changes, or static, that is, a random set of links is cached in the database on the first visit to the page and is displayed in this form on subsequent visits.
Another option is to link pages by search terms of transitions. If you remember, about 6 years ago there was such a script HTracer, which pulled the page address and search query from the referrer, if the transition was made from the search engine and saved to the database, then a block with links was formed on the site pages, which contained the keyword in the anchor there was a transition from the search. There was also a module for DLE, it seems, it was called "Transitions" and had similar functionality. Soon, search engines filtered out sites using a similar linking scheme, quite rightly considering it as search spam. I wanted to find a live example or take a screenshot for you, but I have not found a single site with such a scheme, even among the warez sites, not to mention online stores.
You can come up with a lot of dubious schemes if you want: a block with links to non-indexed pages to speed up their indexing, a block with links to pages that have maximum / minimum visits in order to pump their static weight.
Re-linking from category / product descriptions
Another useless, in my opinion, occupation is placing links from seo-texts in categories or product descriptions to other categories or products.
At first, seo descriptions in categories online stores are not made for reading by people, it is stupid to hide it, realizing that only a SEO specialist could go to the site on the request "buy 4k TV" and be interested in the text, not the goods :) Isn't that so? Therefore, there is no benefit for visitors in the links from the description, and I don’t see the seo benefit from the link from the description on the scale of a large site. I talk about seo-benefits because I had to put down such links in my work and I can say that the effect from them has never been observed.
Have you ever seen yourself linking from product descriptions in an online store? Not from the characteristics, but from the description text. I don’t remember such stores, but my colleagues helped me find an interesting copy - the Labyrinth bookstore.
An example from the pages http://www.labirint.ru/books/409187/ and http://www.labirint.ru/books/320735/
 |  |
Anchors "book", "because", "time"! It's crazy, they just search for words from the description that match the title of the books and link. They also link to the main and key sections. You can go around the site and look at it.
This is complete nonsense. Clicking on such links will be only by chance, the "ala Wikipedia" effect does not work - the links are not contextual and it is not clear where they lead. By the way, the same functionality was in the HTracer script, which I already mentioned, it looked for suitable words, taking into account the morphology and linked articles with each other within the site. I've tried it on my info sites, but to no avail, although I'm firmly convinced that if it could ever work, it would be in those days (6 years ago), not today.
Stop writing about useless tricks, in the end, I have to write about what will bring a positive effect, and not vice versa.
Re-linking from the publications of the info section
In almost any commercial topic, there are many information requests that cannot be covered by either categories, products or other pages. And it happens that for general queries, info articles are shown instead of product pages. A striking example from my practice is the theme of adult stores (sex shop, it so happened that we work a lot with them), for interest, enter "vibrator" in Yandex and see the results. Sometimes the only way to get into the top is to create a high-quality info article on the site.
We followed one of the clients in this way. The entire catalog, categories and subcategories, filters and tags, product pages - everything was polished and brought to perfection, even unique texts were written on each page. There was simply no more elaborate site in my practice, I'm serious. But the traffic stubbornly refused to go to commercial pages. When I was collecting SN, I did not delete information requests, but clustered and put them into a separate group, as a result I got about 50 topics for future publications. Since the site already had an article section, we immediately began to slowly fill it. To my surprise, information requests began to shoot in the top1-top3 of Yandex and Google. As a result, the traffic on the site was brought to 700-900 visitors per day, and only 15-20% of the traffic went to commercial pages. Of course, we have linked articles to the corresponding product categories and filters (no more than 3-4 links per publication).
But there was also a better decision that we made - to create contextual product informers. That is, the blocks where the most popular products from the corresponding category of the catalog were displayed. With price, name, rating, the ability to add to the basket, etc. It turned out very organic and cool.
Despite all the coolness, the client's business never became successful. But this is beyond the scope of this post, and certainly the failure has nothing to do with the interlinking we are talking about :)
There is another example in our practice, this time a positive one. For certain categories of products, next to the characteristics and descriptions, links to instructions for installation and care of the product are displayed. Judging by their behavior, these pages are useful to customers, they read them, save them in pdf. They even recorded videos for the most popular pages. Instructions rank well in the search and generate conversions, knowing this, we have placed product informers on them. As a result, there are several dozen completed orders per month from such pages.
With this example, I would like to remind you that linking is done not for the sake of linking, but for the sake of a certain result - sales. So I advise you to jerk off not to anchors and the number of internal links, but to something more pleasant :) Well, you get the idea ...
Another good example of an information page with product informers and multiple linking on Yandex.Market. I understand that it is very strange to be guided by Yandex in terms of seo, but it is worth navigating in terms of conversion and sales.
Online store tagging / seo filters
I'm sure each of you has heard about tagging, burning out or expanding semantics, seo filters, etc. All of this is about the same thing - creating additional landing pages for search queries (usually low-frequency queries). Trend of the year 3-4, no more. On this wave, they rose and flourished (the post about clusterizers was written for a long time, you can imagine how many of them have appeared since then).
For online stores, large portals, catalogs, tagging is the most effective and understandable way to generate traffic from search engines. Even before it became a trend and people began to talk about it publicly and often, I already practiced this approach. As one of the most striking examples, I published and clearly showed how this affects traffic.
For several years, advanced agencies and studios have been practicing seo filters and the network has already accumulated a lot of sites with a deep study of semantics. In Moscow and other large cities in competitive topics, everything is licked, there the use of tagging is no longer an innovation that puts you ahead of competitors, but on the contrary an attempt to keep up. It's easier in the regions, thoughtful seo endures competitors, but this will come to an end.
Six months ago, there were rumors that Yandex was going to punish for senseless and unjustified generation of such seo filters as for low-quality and useless pages (remember the times of the AGS). But the matter calmed down, and I did not observe a single case of punishment. Yandex's motives are clear - no one needs categories with only a few products, or if the products do not meet expectations. Wait and see.
As I said, SEO filters are usually obtained from a combination of product categories and some properties. The most common example of a filter is brands. The easiest way to imagine this is using the example of household appliances, for example, TVs, where linkages with brands are more frequent than a general query without a brand. Next are the properties inherent in a certain category of goods, in the case of TV sets, these are: matrix type (LED, OLED, LCD, plasma), resolution (Full HD, 4K, 8K), technologies (3D, Smart TV, Android), view (curved , backlit), etc. It is very easy to extract such filters from product specifications, or to extract "popular filters" from wordstat. Cross filters often work as well - for example, linking properties with brands - 4K Samsung TV, Philips TV with Ambilight.
Such filters are made for seo, accordingly, pages should be prepared and optimized for them - titles, meta tags, descriptions. Links to such pages go directly from the filter block, or they are created as separate subcategories, it all depends on the complexity of the technical implementation:
 |  |
The Technopark online store is generally fierce filter nerds. All filters in the sidebar are clickable and go to the corresponding heavily shaded pages. There is no other way, competition is tough!
There are less elegant solutions, just a random set of links to filters according to search queries. Like on Wikimart. Very ugly:
Another ugly example. I found this page in the top10 in Moscow on the request "buy a TV". For some reason, it is not the general category of TVs that is ranked, but the tag "cheap", which is generally with an empty page:
So, we found out about tagging, talked about links from the filter block in categories. Implementation examples are not difficult to find - take any site from the top in Moscow by general request.
Personally, I think we need to go further and do what no one else does. I stubbornly scrolled through the TOP50 of Moscow for electronics and did not find a single example of what I wanted to show you - links to SEO tags from product characteristics. Except for our clients, only one site came to my mind where I saw a decent implementation, this is SotMarket, which has slipped into complete shit, turning into a doorway. Nevertheless, the remnants of the former glory are still in place:
Pay attention to the underlined text - these are links to the corresponding seo filters. I dare to assume that sometimes it can be useful for live visitors.
The benefits for promotion and search engine robots are obvious - a large number of internal links gives a large static weight to the pages and will keep them in the index. In short, a cool solution, but not easy to implement, at least our clients pay a lot of money for such implementations to their programmers or contractors. Trust me, it's worth it!
Verdict: linking is good!
You have read a great post with tips and live examples, and I wanted to end with this, but I decided that it would be wrong to take and leave you alone with your thoughts, questions and, possibly, doubts. So let's put together some kind of summary + short answers to questions that were not discussed:
It is absolutely possible to state improved indexing due to linking - often pages are not indexed or dropped out of the index as of insufficient quality, in fact, they simply lack weight, and this weight will be given to them by internal links.
Number of links for linking does not matter - there is no definite number of links from a page that would be considered normal. There should be exactly as many links as there will be enough live site visitors for comfortable navigation through the site. Go to the metrics webviewer and view dozens of visitor behavior records. You will be surprised at the results!
How does internal linking affect positions? Not directly. But thanks to interlinking, the pages are confidently kept in the index, and due to the higher static weight, the page should rank better for all target queries, but not separately for any query. Please note that we are still talking about online stores and automatic linking from menus, filters, blocks and everything else that we talked about above.
How to choose the right scheme - linking from product cards to categories, from categories to product cards or from products to products? Previously, there were a lot of conversations on this topic and, it seemed, they came to a logical conclusion: if the pages of product cards have the greatest traffic potential, then we should try to distribute all the weight to them, if categories, then try to link to categories as much as possible from product cards. Let me give you an example: when buying a laptop or a phone, most people ask for a specific model of a laptop or phone, respectively, the product cards have the greatest potential. If a person is looking for wallpaper, for example, he is unfamiliar with the SKUs or names of specific wallpaper collections, he is looking for “buy wallpaper”, adding a maximum of color or property to the request (vinyl, non-woven, paintable). In this example, categories, subcategories and seo filters have potential. What types of pages need to be promoted is absolutely clear, while I deny the need to purposefully place more links somewhere, and to deprive some pages of these links. In my work, I adhere to the schemes described by me, without changing them in any way depending on the type of promoted pages.
Manual linking inappropriate for online stores. The only place where manual labor can be useful is the information section, where it will be wisely necessary to put contextual links to the relevant sections and or product cards, introduce product informers. In other places, this type of slave labor should not be used :)
Finally, I'm done. If I find interesting questions in the comments, I will add the answers to them to my list. Until then, thanks for your attention!