How to find out which pages are indexed in Yandex. The number of indexed pages in Yandex: how to see why you need it. How to quickly check indexing in Yandex and Google
Good day, dear friends. Many novice webmasters who independently promote their sites do not pay enough attention to indexing their resource. This leads to a loss of time and money spent on creating an ineffective Internet site, which is not liked by search engines, and, accordingly, users and advertisers.
Therefore, today, continuing the series of articles on site building, we will talk about how to check whether the site is indexed in general and its individual pages in particular, and also discuss how and for what to speed up the indexing process.
We have already talked more than once about what is possible only if a high level of traffic is achieved, which is interesting for potential advertisers.
The majority of users go to a certain resource from search engines by entering queries that interest them. Search robots check these queries against their database and display optimal search results. In order for a site to be included in this database, it must be indexed by a search engine. Otherwise, visitors simply won't be able to find it.
At the same time, it is very important that not just a resource, but each of its new pages, be taken into account by the search engine as quickly as possible. It is optimal if it contains an internal linking, which allows not only adding new material to the database, but also updating the old one using the specified links.
Why should indexing be fast?
In addition to increasing visitor traffic, the indexing speed affects many other indicators of the resource.
Every day, new sites appear on the network, the subject of which competes with your website. All of them are filled with similar content, which, as the number of competitors grows, loses its uniqueness. This is because most sites publish multiple rewrites. In simple terms, if you wrote a unique article and did not immediately take care of taking it into account by the search engine, it is not a fact that at the time of such a material will remain unique.
In addition, content that is not indexed becomes a tasty target for scammers. Nothing prevents an unscrupulous webmaster from simply copying the material to his resource, quickly indexing it and getting the right to authorship from the search robots. And search engines will consider your article not unique in the future, which can lead to the ban of the Internet site. Therefore, it is especially important to control and speed up the indexing process for young resources making their way.
Another point that depends on quickly indexing each page is the ability to get paid for paid links. After all, until the article with the link is indexed by search engines, you will not receive your reward.
How to check if the whole site is indexed?
First, you need to make sure that your site gets into the search engine base. To do this, you need to find out the total number of its pages. If you have a modern web resource management system, you can see this figure in the administrative part. This takes into account the total number of pages and records.

If for any reason this information is not available, you can use the Xml-sitemaps.com service. Please note that it is free only when working with sites that have up to half a thousand pages in their arsenal.
Having found out the required number, you can start checking the site indexing in the main search engines - Yandex and Google. There are several ways to do this:
- Using dedicated webmaster tools: webmaster.yandex.ru and google.com/webmasters ... By registering in them and adding your resource to the system, you will be able to access not only data on the number of indexed pages, but also statistics of other "puzomerok".
- Manual verification by entering special commands into the search bar. In this case, in Yandex, you need to enter the construction host: site name + domain or host: www + site name + domain, for example, host: abc.ru. The system will return all indexed pages for this. To check in Google, you need to enter the query: site: site name + domain, i.e. site: abc.ru.
- Use of automatic services that check indexing in both search engines at once. These include, for example, Site-auditor.ru, Pr-cy.ru or Seolib.ru... You can also add the RDS Bar plugin to your browser, which will show information about the resource, including the indexing of the pages you are on.
Using any of these methods, you can find out whether the site as a whole is indexed, and determine the number of resource pages entered in the search engine database.
What to do with the information received?

Ideally, the number of pages on the site should match the number of indexed pages. Unfortunately, this is not always the case. Much more often there are two options for the development of events:
- The indexed number of items is less. Accordingly, you lose a lot in traffic, because for many user requests your site remains inaccessible to them.
- The number of indexed pages exceeds the actual number of those. If you have a similar option, you should not rejoice. Most likely there is duplication of pages, which dilutes their weight, increases the number of repetitive material and interferes with the promotion of the resource.
Both problems need to be resolved as quickly as possible. Otherwise, you run the risk of getting an ineffective web site, where you can only make money in your dreams. And to do this, you will have to check the indexing of all pages separately to find out which of them "stratified".
How to check indexing of individual or all pages
Checking a separate page is needed when you need to make sure that new published content has been successfully "noticed" by search engines. Or when you purchased a paid link on someone else's resource and are now looking forward to indexing it. This can be done via:
- Entering the page URL into the Yandex or Google search bar. If there are no problems with the perception of the page by search engines, it will be displayed first in the search results.
- The already mentioned RDS Bar plugin.
To check the indexing of all pages on the site, you need a list of their addresses (URL). To do this, you can use any web resource map generator, for example, Sitemap Generator. To collect only the URLs of the pages, do not forget to add a mask of unnecessary addresses, for example, for comments, in the "Exclude Patterns" window. At the end of the process, go to the Yahoo Map / Text tab, from where you can copy the generated list of all addresses.
Having it on hand, it will not be difficult to check the indexing of all pages using the program YCCY.ru... Just add the data to the list of source URLs and select one of the suggested search engines: Google, Yandex or Rambler. Click the "Start Check" button and get comforting or not very good results.
How to improve and speed up the indexing process?
 Having learned the list of non-indexed pages, you need to understand the reasons for this. First of all, it is worth checking the quality of the hosting and the web site itself and make sure that the materials posted are unique. Next, monitor the resource for content that is too short (up to 2,000 characters without spaces), containing more than 2-3 links to third-party resources, or a lot of Java and Flash links. All these factors can primarily affect the fact that your material remains "invisible" to search engines.
Having learned the list of non-indexed pages, you need to understand the reasons for this. First of all, it is worth checking the quality of the hosting and the web site itself and make sure that the materials posted are unique. Next, monitor the resource for content that is too short (up to 2,000 characters without spaces), containing more than 2-3 links to third-party resources, or a lot of Java and Flash links. All these factors can primarily affect the fact that your material remains "invisible" to search engines.
You can speed up the site indexing process using:
- frequent updating of unique material, which is very much appreciated by search engines;
- competent internal linking of pages, allowing search engines to see new and update content already contained in the database;
- publication of links to articles in all social networks and thematic forums;
- purchasing links from a pumped account.
I hope you understood that fast indexing of resource pages is the basis of its promotion in search engines, on which your potential income directly depends.
Logical reasoning on the topic: "How to check how many pages are in the index of search engines."
And numerical calculations that show how I was balancing, studying what is indexed and what is not and why.
I decided to deal with this more closely and put everything on the shelves.
Let's look at the example of Yandex and Google.
Indexing problem, or what are indexes.
The problem of indexing constantly worries the owner of any site. When a site's pages are indexed by search engines, it provides stable and, most importantly, free traffic. Pages participate in search results, and visitors themselves search for information and get to your site. This is great!
Well, finally, the site starts indexing stably.
Now the owners are worried that each new article gets into the search as quickly as possible, and they dream that the site is visited by the so-called "fast robot".
To do this, it is advised to add information to your site regularly and post links to new articles on social networks, especially and.
This can be easily done using.
But life goes on, algorithms change. If a website has been visited by a quickbot before, and the article got into Yandex search for several hours, recently (November 2014) many webmasters have been complaining that it takes several days.
I also noticed that after I began to add information to the page in the Yandex webmasters service before publishing (which I was strongly advised to do by the specialists of this search engine), the new article gets into the search only with the next Yandex search results. Just a few days pass.
It turns out something like that: your text is already in our pocket, you will not get away from us anyway, and we don't have to rush.
How, then, can you determine that an article has already been indexed?
I do this using the Google Chrome browser extension.
The same extension is installed on my Opera browser. It allows you to determine for any open page whether it is indexed or not.
How to add a page to the Google index yourself.
Google is more responsive in this matter. It allows everyone to force a new page to be added to the index. It can be done . There you need to first select the "View like Googlebot" tab, where then it becomes possible to independently add a page to the index, if you specify its Url.

As the saying goes: both you feel good, and we are not bad.
In this way, you can add up to 500 pages per month.
And what about the quantitative indexing indicators for the site?
How many pages are in the search engine index?
The easiest way to see this is in services for webmasters of search engines.
Let's say I have 106 articles and 10 pages on my site (this can be seen in the administrative panel of the site) plus the Home page, or news feed. It is easy to calculate further (106 + 10 + 1 \u003d 117). This means there will be 117 Url on the sitemap in total.
By the way, there you can also see the indicators of the additional and main Google index for his site. He had them much closer to each other.
Alas, there is a lot of snot on my WordPress blog.
Eh, we need to learn how to create websites at a more professional level. Instead of using ready-made templates ...
It turns out that the sites need to be built so that there is no duplicate content on them and all the links to the pages there immediately go into action, i.e. to the main index.
Maybe WordPress will grow to that point someday.
In the meantime, it turns out that if you use short links to pages, it does not contribute to SEO (optimization). And if you use CNC links, you get duplicate content.
I look forward to your comments.
What thoughts did you get on this?
For the promoted pages to be displayed in search, they must be in the index of search engines. Let's figure out how to check which website pages are in the index of Yandex or Google, find out the number of documents in the search engine database. What tools exist to track page indexing. But first, a little educational program.
What is a Search Engine Index?
Search engine index Is a database that contains information about all documents (pages from sites, files) that can participate in the search.
Not all pages are included in the index. For example, if a page on your site is considered low quality by a search engine spider, it may not be included in the index and may not participate in searches. A similar fate often awaits duplicate pages or documents containing texts copied from other sites.
Google has a main index and a supplemental index.
The secondary index includes documents that are of lower quality than documents from the main index. They do not participate in the main search, they are rarely visited by the Google robot, they practically do not bring traffic to the site.
The Google supplemental index usually includes:
- pages with non-unique content,
- pages with virtually no content and pages with text less than 500 characters,
- duplicates,
- sometimes low weight pages may be included in the secondary index.
Why is it important to check the number of pages in the index?
It is very important to track the indexing of pages, because traffic from search engines depends on it. If the page is not indexed, it will not be able to appear in the search results for any request.
How to find out how many pages are in the Yandex or Google index?
There are several ways to check the number of pages in the search engine index:
1. Enter in the search box the query: site: site.com (where site.com is the URL or the address of the main page of the site), as in the screenshot below:

Below the search bar, you will see the approximate number of pages in the search engine index. The example above shows the number of pages in the Google index. This method allows you to find out the number of pages in the search engine base for any site, including a competitor.
2. You can check the number of pages in the Google index in the service Google for webmasters ... A similar service in Yandex is Yandex.Webmaster. It shows the number of pages in the index of a given search engine. To view the data, you will need to confirm the rights to the site in the services. Therefore, this method is not suitable for analyzing competitors' sites.
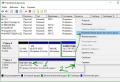
If you have access to Yandex.Webmaster, go to the "Indexing" -\u003e "Pages in search" tab and select the "History" display above the graph. Here you can see not only the number of pages in the index, but also the site's indexing history.
3. With the help of online services, for example, many free services for auditing sites display information about the number of pages in the index.
How to check a page in the Yandex or Google index?
Often a webmaster needs to find out whether a specific page of a site is in the index or not. The easiest way to find out is to enter a search term consisting of the page address. If you see the page you are looking for in the search results, then it is in the index:

Yandex.Webmaster has a function that allows you not only to check whether a page is in the index or not, but also to make sure that important pages do not fall out of search. To add a page to the tracked list, go to the "Indexing" -\u003e "Important pages" section and add the required pages in the form that opens:

You can set up tracking up to 100 pages, which is enough for many projects. If you need to track more documents on the site, then you can use the Topvisor service. It allows you to check whether a site page is indexed or not, without limiting the number of documents. In addition to checking the indexing of the site, the service allows you to remove positions by queries, group queries and much more.
How do I return or add a page to the index?
In the panels for webmasters there are special services that allow you to send a page for reindexing or add a new page from the site to the search engine:
The second way to send a page for reindexing is to add links to the page in social networks, news resources and other Internet resources that search engine robots often visit.
If you sent a page for indexing, but it did not appear in the search, most likely, the robot found the document of little use. The page needs to be improved to be indexed.
How to speed up website indexing?
Site indexing can be accelerated at different stages of site promotion:
- Add your website to your webmaster panel. This will speed up the entry of the new site into the index.
- Update your content often. Then search robots will visit the site more often and new pages will be added to the index faster.
- Monitor the quality of your content. Robots may visit sites with low quality content less often or completely stop indexing such projects.
- Periodically conduct a technical audit of the site to exclude technical reasons for missing pages from the index. For example, sometimes when editing a robots.txt file, webmasters mistakenly close some documents from indexing.
- If you applied to remove a page from the index through the webmaster panels, but then changed your mind and decided to include the page in search again, then there may be problems with its indexing. It will not be added to the index no matter what you do. Sometimes only contacting the search engine support service helps to solve the problem.
- If the pages began to fly out of the index, check the site for filters, uniqueness of texts and the technical side of the site.
- If the site is too large, you can reach the limit on the number of documents in the search engine index (there is such a limit for each site). In this case, you can close secondary pages from indexing so that the main ones are present in the search.
In this article, we looked at how to check the index of a site in Yandex or Google, find out the number of pages in the search engine base, set up automatic tracking of project indexing. If you still have questions, add them in the comments below the article.

Most online services for checking indexing provide an opportunity to check a small number of pages - from 10 to 100. But what if you need to check for indexing a large online store or portal of 100,000 or several million pages? For tasks of this scale, Rush Analytics launched a module for checking indexation in Yandex and Google. The main advantages and capabilities of this module:
a) Using a list of URLs

Search engine index
- duplicates,

Check site indexing in search engines. Site indexing in Yandex and Google.
You can check the number of pages in the Google index in the Google Webmaster Service. A similar service in Yandex is Yandex.Webmaster. It shows the number of pages in the index of a given search engine. To view the data, you will need to confirm the rights to the site in the services. Therefore, this method is not suitable for analyzing competitors' sites.
If you have access to Yandex.Webmaster, go to the "Indexing" -\u003e "Pages in search" tab and select the "History" display above the graph. Here you can see not only the number of pages in the index, but also the site's indexing history.

Yandex.Webmaster has a function that allows you not only to check whether a page is in the index or not, but also to make sure that important pages do not fall out of search. To add a page to the tracked list, go to the "Indexing" section -\u003e

How to correctly check a site for indexing in Yandex and Google?
Most SEOs use browser bars like RDS-bar and others to check the site for indexing.
All bars take this data from search engine results using various operators and simply "pull" it into their interface.

But it should be borne in mind that the data obtained in this way is not accurate, since search engines do not give correct indexing data for large sites. From the pictures above, you can see discrepancies in the data even for a small site. For large sites (starting from 10,000 pages), indexing data can be very distorted!
How to correctly check the site for indexing so that the data is accurate?
Unlike the entire site, search engines provide accurate data on the indexing of each specific page. Therefore, it is necessary to take all the necessary pages of the site and check the indexing of each of them separately, and then bring all the data together to get a complete picture of the indexing of the entire site. This is true for both Yandex and Google.
Bulk check of site pages for indexing in Yandex and Google by Rush Analytics
Most online services for checking indexing provide an opportunity to check a small number of pages - from 10 to 100. But what if you need to check for indexing a large online store or a portal of 100,000 or several million pages? For tasks of this scale, Rush Analytics launched a module for checking indexation in Yandex and Google.
Checking site indexing
The main advantages and capabilities of this module:
- Convenient batch loading of pages for indexing check in three ways:
a) Using a list of URLs
b) With the help of a file, xls, xlsx, xml formats are supported
c) Using the Sitemap.xml file - just specify the path to the sitemap, we will parse it ourselves, get the URL from there and push them for indexing!
- Unlimited number of URLs to check - you can check for indexing from one at a time, up to several million pages!
- Indexation check is available both in Yandex and in Google: you can send your pages for checking only in one search engine or in both at once, just check one checkbox
- Convenient export to Excel. You can view the data both in the web version of the service and quickly upload it as a file
Rush Analytics' Indexing Checker is currently the only one on the market that allows you to massively check pages for indexing to this extent. If you have a large site, this solution is definitely for you.
We have provided special conditions for large sites and portals. If you have a need for a one-time or permanent check for indexing in Yandex and Google from 200,000 pages, write to us in support at [email protected] and we will find something to offer you!

For the promoted pages to be displayed in search, they must be in the index of search engines. Let's figure out how to check which website pages are in the index of Yandex or Google, find out the number of documents in the search engine database. What tools exist to track page indexing. But first, a little educational program.
What is a Search Engine Index?
Search engine index Is a database that contains information about all documents (pages from sites, files) that can participate in the search.
Not all pages are included in the index. For example, if a page on your site is considered low quality by a search engine spider, it may not be included in the index and may not participate in searches. A similar fate often awaits duplicate pages or documents containing texts copied from other sites.
Google has a main index and a supplemental index.
The secondary index includes documents that are of lower quality than documents from the main index. They do not participate in the main search, they are rarely visited by the Google robot, they practically do not bring traffic to the site.
The Google supplemental index usually includes:
- pages with non-unique content,
- pages with virtually no content and pages with text less than 500 characters,
- duplicates,
- sometimes low weight pages may be included in the secondary index.
Why is it important to check the number of pages in the index?
It is very important to track the indexing of pages, because traffic from search engines depends on it. If the page is not indexed, it will not be able to appear in the search results for any request.
The speed of site indexing is also important. If it is low, the index will contain outdated versions of pages, and new documents will find themselves in search with a long delay. To solve this problem, see the article on how to speed up site indexing.
How to find out how many pages are in the Yandex or Google index?
There are several ways to check the number of pages in the search engine index:
1. Enter in the search box the query: site: site.com (where site.com is the URL or the address of the main page of the site), as in the screenshot below:

Below the search bar, you will see the approximate number of pages in the search engine index. The example above shows the number of pages in the Google index. This method allows you to find out the number of pages in the search engine base for any site, including a competitor.
2. You can check the number of pages in the Google index in the Google webmaster service. A similar service in Yandex is Yandex.Webmaster. It shows the number of pages in the index of a given search engine. To view the data, you will need to confirm the rights to the site in the services. Therefore, this method is not suitable for analyzing competitors' sites.
If you have access to Yandex.Webmaster, go to the Indexing -\u003e Pages in Search tab and select the History display above the graph.
Site indexing in Yandex
Here you can see not only the number of pages in the index, but also the indexing history of the site.
3. With the help of online services, for example, many free services for auditing sites display information about the number of pages in the index.
How to check a page in the Yandex or Google index?
Often a webmaster needs to find out whether a specific page of a site is in the index or not. The easiest way to find out is to enter a search term consisting of the page address. If you see the page you are looking for in the search results, then it is in the index:

Yandex.Webmaster has a function that allows you not only to check whether a page is in the index or not, but also to make sure that important pages do not fall out of search. To add a page to the tracked list, go to the "Indexing" -\u003e "Important pages" section and add the required pages in the form that opens:

You can set up tracking up to 100 pages, which is enough for many projects. If you need to track more documents on the site, then you can use the Topvisor service. It allows you to check whether a site page is indexed or not, without limiting the number of documents. In addition to checking the indexing of the site, the service allows you to remove positions by queries, group queries and much more.
How do I return or add a page to the index?
In the panels for webmasters there are special services that allow you to send a page for reindexing or add a new page from the site to the search engine:
The second way to send a page for reindexing is to add links to the page in social networks, news resources and other Internet resources that search engine robots often visit.
If you sent a page for indexing, but it did not appear in the search, most likely, the robot found the document of little use. The page needs to be improved to be indexed.
How to speed up website indexing?
Site indexing can be accelerated at different stages of site promotion:
- Add your website to your webmaster panel. This will speed up the entry of the new site into the index.
- Update your content often. Then search robots will visit the site more often and new pages will be added to the index faster.
- Monitor the quality of your content. Robots may visit sites with low quality content less often or completely stop indexing such projects.
- Periodically conduct a technical audit of the site to exclude technical reasons for missing pages from the index. For example, sometimes when editing a robots.txt file, webmasters mistakenly close some documents from indexing.
- If you applied to remove a page from the index through the webmaster panels, but then changed your mind and decided to include the page in search again, then there may be problems with its indexing. It will not be added to the index no matter what you do. Sometimes only contacting the search engine support service helps to solve the problem.
- If the pages began to fly out of the index, check the site for filters, uniqueness of texts and the technical side of the site.
- If the site is too large, you can reach the limit on the number of documents in the search engine index (there is such a limit for each site). In this case, you can close secondary pages from indexing so that the main ones are present in the search.
In this article, we looked at how to check the index of a site in Yandex or Google, find out the number of pages in the search engine base, set up automatic tracking of project indexing. If you still have questions, add them in the comments below the article.

When I was first entrusted with filling the "News" section on the site, there was a lot of enthusiasm. All the knowledge that I managed to learn from SEO textbooks was used: keywords, linking, catchy lead. But two weeks and 15 articles later, Google Analytics did not show visits to the cherished page. Do search engines “see” them? Then I was worried about how to check the indexing of the site.
Site indexing in Yandex and google - what is it?
Before a page appears in the results of Google and Yandex, the search engine must know what user requests it should be shown to, what is the value of the content and whether the site violates basic rules. For this, the so-called indexing of the site is carried out in Yandex and Google: search robots enter the site, analyze the content and general content of the page, and enter it into the database.
Check the number of indexed pages
How to check the number of indexed pages? I used 3 methods.
Method 1. By hands
- Go to Google (remember that the search engine results are geo-dependent);
- In the search box, enter site: site_address, for example site: coffee.ru and click "Search in Google". The number of pages in the SERP is equal to the number of indexed pages. If you have a very fresh site and the number of pages does not exceed 30, you can see a list of specific pages right in the search results. Or
- We enter in the search bar site: address of the page of interest. Did the page you want appear in the search results? Great, so it has been indexed.
Attention! Do not put a space between the operator and the site address.
- We go to ya.ru and, by analogy with Google, enter the search bar site: site_address. The number of pages in the SERP is the number of indexed pages.
- Need to check the indexing of a specific page? Enter in the search bar url: address_interest_page and click "Find".
Method 2.Using a service for webmasters
We are urgently registering in the tools for webmasters: they provide tremendous opportunities for site analysis and development of improvement measures.
Yandex.Webmaster.
Primary Menu
We go in and register on Yandex Webmaster. In the section "Indexing sites" there is data on the number of indexed pages, with specific URLs.
Google Webmaster Tools. Registering your website in Webmaster Tools. Go to the "Google Index" tab and then "Indexing Status". Here you can see the number of indexed pages, as well as the dynamics. A handy tool when you need to check the "loss" of a part of pages from the index.
Method 3. Using third-party services
There will be no problems with finding a third-party indexing checker service - there are many of them. Here is a list of those that I regularly use.
- Seogadget
- PR-CY
They will provide the necessary information under different filters, and Seogadget will also send an email when the indexing of the site changes. But at the first stage, I advise you not to rely on one tool: use all three methods in parallel to make sure the data is correct. Are you convinced? Now you can choose the simplest and most informative one.
If the number of pages in the index significantly exceeds their real number (for example, there are only 58 pages on the site, but there are 72 in the index), these are copies of pages, affectionately called "snot" by webmasters. The best solution is to remove them to avoid falling prey to filters.
What pages of the site are visible in Google and Yandex?
The site pages are indexed, but there is still no traffic to them. There is only one explanation left - they are not visible in the search results. After all, even an indexed page can “fly away” far beyond the TOP-50, where even 1% of users do not reach. How to find out which website pages are visible in Google and Yandex? The tools for webmasters and third-party applications mentioned in the previous section will help you with this. They have the option "visibility in search" - it will tell you about the history of keywords, your site's positions on them and suggest new directions of optimization.
How to include a site in Yandex and Google
If you've started SEO optimization and want to try different approaches to content formation and promotion, waiting for indexing for 10 days is not permissible. How to make site pages in Google and Yandex appear earlier?
- We create and upload a sitemap (Sitemap);
- Signing up with Google Analytics and Webmaster Tools;
- We invite search engines to visit using Add Url (for Google and Yandex).
Website promotion yourself | Site indexing
If you consistently read my manual, then in the last article you learned how you can speed up the indexing of your site. Now we need to control this process. Those. keep track of which pages are indexed and which are not. To implement site indexing check not difficult. There are two solutions for this: a manual method and a special seo-software.
First of all, you can use the SeoPult automatic promotion system. The system is of course paid, BUT a lot of information on your site can be viewed for free! In particular, which pages are indexed, see relevant queries, tips on page optimization, and a lot of other useful information. I advise you to look there more often.
Also, you can use the free Site-Auditor program from Ashmanov. As I said, it is free, periodically updated and copes with this task quite well.
How to find out if the site pages are indexed in Yandex?
To check the indexing of the site through the Site-Auditor program, download it from the official site. We launch the software and in the "express analysis" menu we drive in our url, click "check".
The program gives us the number of pages in the Yandex and Google indexes. By clicking on these numbers, we will get to the search engine results, where our indexed pages will be. The same check can be done if you have the Yazzle program, which we used to evaluate competitors.
But there are times when such an analysis is not entirely convenient or impossible to do. For example, the PS has updated something and the software stopped working (until it is updated), and you need to urgently check it. Or, more often, you need to check the indexing of a specific page, but it is not always convenient to search in the general list. This is where the second (manual) method will help.
Checking site indexing in Yandex
You can check the indexation of your site in Yandex in the webmaster's panel webmaster.yandex.ru/. But to do this, you will have to add the site to this panel and confirm the rights to the site. Without registration, alas, it will not show all indexing data. Here is a section with indexing data in the webmaster's panel.
There you can see the indexing of pages for the last week, for 2 weeks and for all time.
Indexing a separate page in Yandex is easiest in the search itself. We stupidly drive the page into the search bar and click find. If it is in the index, Yandex will show its snippet. If it is not there, it will not show accordingly.
In the same place, if we click the green arrow next to the url of the page, we can see the saved copy of the document. This is the version of the page that is currently stored in the Yandex cache. The cache contains very important information - the date when the robot last visited your site. You can always look in the cache whether Yandex or Google took into account your last changes on the page or not.
Checking site indexing in Google
To check how your site is indexed by Google, just enter a special command in the search bar
site: site_name.domain
Google will show you how many pages are in the index. And by the green arrow (as in Yandex), you can see the saved copy of the page (the contents of the cache). Where you will see the current version of the page in the Google database. A separate page can also be viewed by simply typing it into the search bar.
Checking site indexing in Rambler
Indexing in Rambler at the moment can be checked in only one way - to drive the url into the search bar. You can also see what is in the cache there. To do this, click "copy".
I advise you to periodically check the indexing of your site. Then you will be able to spot troubles in time, for example, pages are dropped from the index. And take action in a timely manner.
But not all pages on the site need to be indexed, there are also those that need to be closed from the PS. Therefore, further we will analyze the question - how to prohibit the indexing of the site.
Search Engine Index is a database that stores information about web documents. The purpose of this "storage" is obvious - using a database, a search engine can quickly and accurately calculate the values \u200b\u200bof ranking factors, the numerical value of the relevance of a URL to a user's request, and generate search results.
For SEO specialists and site owners, this means one thing - how many pages are indexed, how many documents can be found in the search results for targeted queries, and the same number of URLs can attract traffic.
How to quickly check indexing in Yandex and Google?
There are a lot of ways and services for checking page indexing, and we have three tools that show the number of documents in the index by domain:
Just specify the domain in any of them. The tool will help you check the site for indexing and tell you how many documents are in the Google and Yandex databases, with or without subdomains:
Search Operators for Checking Indexing
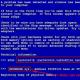
You can find out the indexing of a site using search operators. For Yandex, these are the operators "site:", "host:" and "url:".
![]()
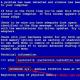
For Google - "site:", "inurl:" and "info:".
![]()
Both search engines provide approximate results, but you can use additional parameters to find out how many pages were indexed, for example, in a week:
![]()
In order to check the indexing of a specific page of the site, use the "url:" operator for Yandex and "info:" for Google.
![]()
Webmaster and Search Console
In the Webmaster, go to the "indexing" tab - "pages in search". Here you can find statistics on documents added and removed from the search. You can also view the history of changes for the entire site for a certain date interval:
![]()
You can check the indexing of a site on Google using the Search Console. In the new version of the console, go to the tab "status" - "indexing of submitted URLs" and get a picture of changes, errors, excluded pages and a schedule of impressions:
![]()
Possible indexing control
It is important to understand that crawling or crawling a page on a site does not mean it will be indexed. Sometimes it is necessary to prohibit indexing of pages that are not needed in the search, for example: URLs with technical GET parameters, service or user documents (shopping cart, personal account, etc.), documents with UTM tags. Therefore, it is desirable for each site to have:
Using the Disallow command, you can prevent the indexing of specific URLs or sections of the site.
Crawl delay - sets the minimum time for a robot to contact the server to avoid loads on the site.
Clean param - allows you to specify CGI parameters that are not important for indexing in URLs, that is, various user IDs, sessions, and so on. Used only in Yandex.
Sitemap.xml - a file that helps search robots to crawl the site, taking into account the set priorities.
Robots.txt - a file that defines the rules and parameters for crawling for all search engine robots or individually for each:
Open pages should be in search, only then can you think about ranking. Do not forget to check the site for indexing, track changes and successful positions in the search results!
Ask a question or leave a comment