The program for working with ssd kingston. Kingston KC400 and HyperX Savage SSD firmware. Preparing for firmware
Hello dear readers, once I wrote an article about, I continue this topic, only this time the topic about new SSD drives... Namely, I will show free programwhich can be free download and read the instructions for it.
Program for ssd disks
The program is very easy to use, you just need to know what to press.
Download the program for free SSD Mini Tweaker :
The archive contains two versions of the program for 32 and 64 bit systems. To see what kind of system you have, select a computer property.
We start and see this window:

After installing the checkboxes, click apply changes.
Now more about checkboxes in the program for managing SSD hard drives.
- Enable Trim - better leave, as this function is responsible for clearing unused blocks. If you disable this option, a mountain of garbage can accumulate, which will affect.
- Disable Superfetch - a function for caching frequently used files. Since the response is small for SSDs, the option can be disabled.
- Disable Prefetcher - an option to speed up the launch of the operating system and programs. Because SSD driveshave excellent speed, the option can be disabled to free up system memory.
- Leave the system core at memory - usually the system kernel is dumped into the paging file. To keep the kernel, you need to check the box. Thus, you can reduce the number of disk accesses and speed up the system. But at least 2GB of RAM is required!
- Increase the size of the filesystem cache —
also requires 2 GB of RAM. Reduces physical memory space for services and applications, but improves performance by reducing data writes to disk, hence it has a good effect on the file subsystem.
- Remove the limit from NTFS in terms of memory usage -again, a sufficient amount of RAM is required. The number of updated data in memory is increasing for writing and reading files. After this function, the launch of several applications at the same time should improve.
Disable defragmentation of system files at boot - defragmentation at boot, although a useful thing, but not with an SSD. With startup defragmentation enabled, the SSD can even be damaged!
Disable Windows Indexing System - the service is disconnected Windows Search, which indexes folders and files on a disk. In SSD Windows Search will hardly improve performance, so disable it.
You can also speed up the performance, manually disabling file content indexing.

- Disable swap file cleaning - for an SSD disk, it is recommended to disable cleaning the paging file when the system is turned off. Due to unnecessary disk access. Disable.
Disable hibernation - by disabling the mode hibernation, you can free up memory on the SSD disk if it is small. In kration hibernation is needed to dump data to a file hiberfil.sys, and when enabled, restore the information back to memory. Read more about this in the article.
Disable protection function systems - you can also disable system restore, which frees up RAM and hard drive. But System Restore will not be available. Disconnect if not in use. It is always disabled for me, I don't like it.
Disable defragmentation service - they say that defragmentation is not necessary for an SSD disk. But I advised you to disable and do defragmentation according to my article, called defragmentation for 5 points.
That's all, now you have program for optimizing SSD drives=)
The requirements of corporate users to systems for storing and processing data information differ significantly from a simple end user. For a corporate user, it is not so much the speed of writing and reading data that is important, but rather the reliability of storage and constant 24-hour access to them during the entire operation period. That is why companies develop separate series of products for this, which often exceed prices for seemingly similar models, but intended for the consumer market. Therefore, Kingston has launched a dedicated series of data center SSDs optimized primarily for read-intensive workloads.
The ease of installation, weight, and dimensions do not yet guarantee that SSDs can be used in corporate environments. The cost of making the wrong choice can often negate all the savings, as cheap SSDs running in the DataCenter can fail prematurely due to excessive writes and their write speeds drop significantly over their expected lifespan. All this ultimately leads to significant costs as a result of premature replacement.
Modern SSDs are capable of delivering the blazing fast read and write speeds for both sequential and random requests required in corporate environments where large numbers of clients can access databases concurrently without significantly affecting performance. In the case of personal use of an SSD by an end user, the difference between the minimum and maximum response times of the drive can be significantly greater. Therefore, enterprise-class SSDs are optimized not only for peak performance in the first few seconds of access, but also using a large redundant area, they also guarantee increased average stable performance over the long term, which ensures consistent performance of the entire corporate array of drives used in data centers. information even during peak periods.
NAND flash memory, which is used in SSDs, has some inherent limitations: the two most important are the ultimate design life and the likelihood of natural errors. Therefore, during the production process, each crystal of the future SSD-drive is tested and characterized by the original bit error rate (BER or RBER). This metric measures the rate at which natural errors occur without any intervention from software error correction. But there are also errors that cannot be corrected by any means. Therefore, the uncorrectable bit error rate (UBER) was introduced as “a measure of data distortion equal to the number of data errors per bit read after applying a specified error correction method”. In accordance with the proposed UBER indicator for enterprise-level SSDs proposed by the international committee JEDEC, the UBER indicator for an enterprise-level SSD is expected to be no worse than the appearance of 1 non-recoverable bit error with a frequency of 1 bit error for every 10 quadrillion bits processed (~ 1.11 petabytes), but for the client level, this indicator reduced by 10 times. In other words, SSDs designed for harsh data center environments are required to be ten times more reliable than home users. To do this, Kingston uses parity and checkpoint redundancy and loopback technologies.
In addition, to improve reliability, Kingston includes additional electronics in enterprise SSDs with power outage sensing and fail-safe logic, as well as input power monitoring and temporary power supply in case of any internal or external residual write commands. ...
Another critical parameter that differentiates enterprise SSDs from those used for the end user is the lifespan. Its duration is not so critical for a home computer due to the fact that with an estimated operating time of 8 hours a day, modern solid-state drives will last much longer than the PC itself as a whole. But for operation in conditions of data processing centers that work 24 hours a day without any interruption, this parameter is critical, since it significantly affects the cost of the entire system. But we know that all types of NAND flash used in SSDs lose their ability to reliably store data over time and eventually reach a state where they cannot be used. A set of measures is used to neutralize losses and extend the service life, but the most important is still constant control of data integrity and transfer of potentially "dead" bits to a redundant memory area that is not initially available to the user. In addition, companies are using memory chips based on e-MLC technology, and in some cases SLC technology for devices with heavy loads, although the latter solution dramatically increases the cost of data storage while significantly reducing the total device capacity. Naturally, advanced S.M.A.R.T. technologies are also used, which monitor free and occupied cells. In conventional client devices, these technologies are also used, but in a more simplified form. In other words, the main methods of struggle for increasing the service life are: reliable and advanced technologies for checking memory cells for errors and reserve capacity of the drive, which is not available to either the user or the operating system and which can be used as a temporary write buffer to improve performance, but mostly designed to replace defective cells during the expected life of the SSD.
The new Kingston DC400 series of SSDs offer superior performance than custom SSDs and are designed to last longer in tougher environments. However, it is worth noting that the Kingston DC400 is an entry-level enterprise SSD and is therefore primarily intended to be read rather than write. One of the important features of the new models is the overprovisioning capability. According to Kingston's website, enterprise SSDs reserve up to 28% of the storage capacity, while the DC400 series has only 7% reserved by default, just like consumer SSDs. If necessary, using the proprietary Kingston Manager application, the user can change the capacity of the backup area, thereby increasing the service life of the SSD and to some extent increasing the recording speed.
The Kingston DC400 SSD, like most of the company's products, comes in a plastic blister. On its front side, in addition to the brand name and an indication of the device series, only the storage capacity and the fact that the warranty period is 5 years are indicated.


On the flip side, everything looks also modest. The main thing that is present on it is a sticker where the product number is indicated and where it was produced. But the user will see important words about the guarantee only if he buys a drive and takes it out of the package. No installation instructions are included, since the SSD is targeted at the corporate market segment and it is assumed in advance that it will be installed by someone who is well versed in this.


This drive has the most common form factor - 2.5 inches and a thickness of about 7 mm, that is, it allows you to install this SSD in any modern device, up to ultrabooks.
The main characteristics of the Kingston DC400 480 GB model, according to the manufacturer:
- connection interface - SATA 3.0 (6 Gb / s), backward compatible with SATA 2.0 (3 Gb / s);
- sequential read / write speed: 555/535 MB / s;
- maximum read / write speed of random 4 KB blocks: 99000/90000 IOPS;
- read / write speed of 4KB blocks at constant loads: 85000/11000 IOPS;
- quality of service (latency) - read / write: hot plug function;
- static and dynamic wear leveling;
- enterprise-grade SMART tools: reliability tracking, collection of information on usage intensity, life assessment, wear leveling, temperature monitoring;
- service life: 257 TB (estimated as the total number of bytes written, without significant performance loss);
- power consumption: idle / average / max. while reading / max. when recording (W): 1.56 / 1.6 / 1.8 / 4.86;
- operating temperature: 0 to 70 ° C;
- mean time between failures: 2 million hours;
- size 69.9 × 100 × 7 mm;
- model weight - 92.34 g.
Kingston SSD Manager

To update SSD firmware, Kingston offers a free Kingston SSD Manager utility that can be downloaded from the official website. Using it, the user can view SMART data, SSD status, its temperature and various events related to the operation of the drive (connection / disconnection, identification numbers, etc.).

However, the most important feature of this program is the ability to change the backup area of \u200b\u200bthe drive. It is important to understand that these actions can only be performed without formatted partitions on the disk. In addition, after changing the size of the spare area, you should restart the OS for the new settings to be applied correctly. It should be noted that a minimum spare area of \u200b\u200b7% always remains while the user is working with the remaining SSD space.
Testing
To test the SSD, we used the bench with the following configuration:
- processor - Intel Core i7-4770K;
- motherboard - Intel DZ87KLT-75K;
- motherboard chipset - Intel Z87 Express;
- memory capacity - 16 GB (two GEIL DDR3-1600 modules, 8 GB each);
- memory operation mode - two-channel;
- system disk - Intel SSD 520 Series (240 GB);
- operating system - Windows 7 Ultimate 64 bit.
Additionally, the Intel RST driver was installed, and the tested SSD was connected to the SATA 6 Gb / s port, which was implemented through the controller integrated into the chipset. Another SATA port was connected to an Intel SSD 520 Series, on which the operating system and all the applications necessary for testing were installed. All SATA ports were set to AHCI mode.
For testing, we used the IOmeter utility version 2008.06.18, which is a very powerful tool for analyzing the performance of drives (both HDDs and SSDs) and is actually an industry standard for measuring drive performance.
In order not to tie the test results to a specific file system, we tested the SSD drive using the IOmeter utility without creating a logical partition on it.
During testing, the dependence of the speed of sequential and random read operations, as well as sequential and random writes, on the size of the data block was investigated.
In addition, we analyzed the dependence of the drive performance in random read and write operations for 4 KB blocks. The block size of 4 KB for random read and write operations was chosen because it is typical of the Windows operating system and blocks of this size are most common in random read and write operations. In this regard, the block size of 4 KB for random read and write operations when measuring IOPS is a kind of de facto standard.
We also tested SSD drives for the aging effect, that is, we found out how the performance of a drive in random write operations changes over time.
Data blocks of the following sizes were used to determine the speed of sequential read, random read and sequential write: 512 bytes, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512 KB, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 MB. In these tests, the IOmeter settings set the number of concurrent I / O requests (# of Outstanding I / Os) to 4, which is typical for user applications. The analysis of the dependence of the drive performance in random read and write operations on the depth of the task queue was carried out using 4 KB blocks, and the number of concurrent I / O requests was set equal to 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256. Note that the results of this test are especially important if the drive is used in a server, RAID array or NAS system. In addition, the FlashTest 4.0 utility developed in our laboratory was used to assess the read and write speed that a user can expect in real-life conditions. It uses calls to functions from the WinAPI library and copies data in the same way as it is done with standard Windows 7 and 8 tools, including displaying a standard window with a progress indicator on the screen.
The well-known utility CrystalDiskMark 5.1.0 was used as a synthetic test, which is often used to measure the performance of various drives.
Test results

The test for the "aging" of an SSD drive was based on a special preset that worked for 10 hours. Naturally, like all modern SSD drives, this model has this unpleasant property, that is, the random write speed decreases as the drive fills up ... The write speed has decreased by about 5 times, but it can be seen that the controller has advanced regeneration algorithms. If we compare its results with a regular consumer SSD, then the write speed is much higher even in such a difficult situation. This allows us to say that Kingston DC400 is more suitable for work in data centers than anyone else.

The graph shows three dependences of the data transfer rate on the block size in the main operations: sequential read, sequential write and random read. Sequential operations, both read and write, are very good for this model. At their peak, they are more than 530 MB / s, which is in line with the declared values. But in random read operations, saturation does not occur so quickly, however, peak speeds are also reached at the maximum block size.

On the random write graph, you can see the speed differences between the "new" and artificially "aged" states of the drive. The degradation of the random write speed is clearly noticeable when the buffer on the "new" drive is full. However, the speed drops are not as severe as some budget consumer SSDs have. The write speed under the constant stress test goes up to 60 Mbps at the maximum block size, which is a good indicator for SSDs. The real average data transfer rate for random writes in blocks from 512 bytes to 1 MB is presented by the graph of the "aged" drive, which is based on the results obtained after the "aging" process.
Real-world data transfer test FlashTest 4.0 shows that the write speed of the Kingston DC400 matches the results obtained in the IOMeter benchmark. In addition, it can be seen that compared to a conventional SSD, the new model is significantly faster in write speed.

CrystalMark synthetic tests show higher results, which, however, is not surprising.
conclusions
Kingston has made a strong statement with the launch of its new series of SSDs for enterprise use to get corporate IT services seriously considering a planned move to solid-state storage. And ordinary users who store large amounts of critical information at home, on home computers, will be interested in a new device and, if funds allow, they will transfer their databases to modern and reliable media from Kingston. The new Kingston DC400 delivers superior performance for its class. The SSDs in this series are designed for read-preferential loads, but can handle short-term heavy write loads if necessary. According to our data, increasing the spare area up to 30% of the SSD capacity allows for higher write speeds, so this option is likely to be in demand in the corporate sector. As of this writing, the price of this SSD is still unknown.
Kingston regularly pleases with its new products. Let's remember something from the latter, for example, the excellent HyperX Cloud headset, but what about the release of one of the fastest SSDs - the Predator. Finally, even a HyperX Savage flash drive is interesting for its high speeds, for which you need to have not only a USB 3.0 port, but also an SSD. In a word, this manufacturer has presented enough new products over the past year to please its users. Most of the devices that were presented belonged to the productive segments, but this time we will consider a budget product - the new SSD Kingston uv300, which will be reviewed in this article.
Kingston uv300 - theory and positioning
So, Kingston uv300 is a new budget line of the manufacturer, which now occupies the lowest line among all models of solid state drives. It is worth noting that it is, nevertheless, not far from the legendary v300 series, which captivated users with its combination of price and efficiency. Let's start by comparing the general specs of consumer storage drives.
There are six lines in total, three of which are conditionally budgetary, and all of them, in one form or another, have numerical indices 300-310. The mid-range segment is represented by the HyperX Fury line, and the older Savage. The Predator models stand apart, made in the form of an HHHL expansion card and giving tremendous operating speeds. What can boast of the new UV300?

For budget V300 drives, Kingston used memory with MLC cells, and although the memory itself could be very different (which also affected performance), the drives were at least reasonably reliable. TLC class memory is used, today, only in models of the lower series. Because, a priori, the TLC memory has a smaller rewriting resource, and sometimes the speed of work. However, there is no need to be afraid of this, there is SanDisk Ultra II, there is OCZ Trion 100 and other disks (from the old models you can recall the Samsung 840), which live and work for the benefit of the user. Disks with this class of memory cells are an objective reality, while modern controllers do everything to make their resource, in fact, indistinguishable from any other budget-class disks (given the standard user load). It is also worth noting that the series has a 3-year warranty. Now is the time to turn to the price of the solution.

As we can see, uv300 drives are among the cheapest among many other models. Of course, if you think so, the usual V300 series is not much more expensive. But we remember the lottery with different memory, and we should also take into account the peculiarities of the SandForce 2281 controller, which does not work so quickly with incompressible data. And finally, we note that the new series has just appeared on the market and therefore many sellers expose it to an increased price tag, which spoils the "average" value from this graph.
Appearance and features of Kingston UV300 120 GB
We are testing a 120GB drive, which is the youngest member of the range. It got to the tests in an antistatic bag, but in retail, of course, it will be sold in packaging. Visual inspection shows that the disc is completely traditional Kingston style, from the type of case to the label.

Appearance of Kingston UV300 120 GB
The new SSD is made in a 2.5 ”case with 7mm thickness. It comes in options from 120 GB and up to 480 GB, the declared characteristics reach up to 550 MB / s read and up to 510 MB / s write. For this modification (120 GB), the figures are up to 350 MB / s. The speeds for random access and small blocks will be limited to 64,000 read IOPS and only 12,000 write IOPS. Therefore, we do not expect to see any special agility in the tests.
As for the filling, the disk is represented by Toshiba 19 nm TLC memory, as well as a buffer memory chip and, finally, a Phison PS3110-S10 controller. This interesting controller can be found in drives of various directions, from budget solutions to quite expensive series. In general, this balanced solution should show good results, but of course, you need to watch it in action.
Kingston SSD Manager Software
You can also download a proprietary utility called "Kingston SSD Manager" from the official website of the company and, by tradition, we will consider this program.

As such, the utility does not have a main menu, there are several different tabs, the first of which is called "Firmware". Accordingly, it displays the name of the drive, serial number, firmware version, and if available, it is proposed to download it from a remote server. The left window of the program displays all connected Kingston drives, in the lower part a list of a number of indicators. For example, SSD temperature, conditional display of "vital signs" and more.

The SMART tab gives the user access to monitoring metrics.

The next tab demonstrates active data protection systems, and also allows you to perform Secure Erase, a useful option in some situations that completely wipes out the drive.

Finally, the last tab demonstrates, in fact, a kind of program log. The general functionality is not rich, but some useful options are still there. At the very least, the user will always be able to track the status of the disk and update the firmware.
Kingston uv300 120 GB review - benchmarks


Kingston uv300 - CrystalDiskMark
The very first test in CrystalDiskMark shows that, in fact, everything is in order with the disk speeds. Even though this is only a 120GB model, we see 380MB / s linear write speeds as well as over 540MB / s sequential reads. In the 4K column, the drive received a little less than 30 MB / s, which is also quite acceptable for a small budget model.

It can be seen how the disk can walk great while working with recording tasks, since the graph is constantly jumping, the speed either increases or decreases, giving the same values \u200b\u200bthat we could see earlier on the "hospital average". As for reading, let me remind you, the main indicator of the speed of the SSD, everything is fine and the schedule is perfectly flat.

Efficiency Kingston UV300 120GB

IOPS Results Kingston UV300 120GB
As for the arbitrary speeds on small blocks, everything is in line with the specifications. You can see it all with your own eyes, we got up to 86,000 IOPS in reading, which, in general, is even slightly higher than the performance of budget drives. At the same time, up to 22,000 IOPS writes, typical of low-speed drives. Nevertheless, the developer did not declare more in his specifications, but rather less, so there are no discrepancies with expectations and reality.

Many drives tested in the PC Mark 8 with a capacity of 120 GB had a much higher positioning, in particular, we are talking about the same SSD Apacer or different Plextor series. And yet, the device showed 144 MB / s.

Game OS launch speed
The system startup speed is slightly lower than on a number of more famous SSDs, but even here the difference is only a few seconds. Thus, the drive is fast enough to run applications, OS and programs.

Ryse Son of Rome level loading times

Diablo 3 level loading times
Gaming tests showed that the drive also coped well with games, thus securing good read rates and showing that it is quite suitable for various user tasks.
conclusions
In this article, we tested a rather interesting budget drive Kingston UV300, with a capacity of 120 GB. The device is inexpensive, but it offers enough efficiency to perform any user task, such as launching applications, games, and consistently responsiveness in Windows. The use of TLC cells did not lead to a drop in performance, and the 3-year warranty suggests that the SSD is quite reliable. The write speeds suffer a little, but again, they are much higher than those of hard drives.
The new Kingston UV300 solid state drive wins the Cost Effective award because it truly is a recommendation to all users looking to save money and get decent performance. At the same time, the device will cope with most tasks perfectly, unless you expect more from it than the developer himself claims.
Thanks to Kingston for submitting this SSD.
The advent of solid-state hard drives or SSD for short can certainly be considered a breakthrough in the development of technologies for creating devices for recording and storing digital information. The first SSDs that entered the market, with the exception of the high speed of access to arbitrary blocks of information, were in many ways inferior to traditional HDD disks. Not only could their volumes, without exaggeration, be called more than modest, they also had low fault tolerance and cost a lot of money.
What's wrong with an SSD?
The high speed, noiselessness and low power consumption of solid-state drives served as good drivers for their development. Modern SSD drives are lightweight, very fast and mechanically reliable devices used in tablets, ultrabooks and other compact devices. The price of SSDs has also dropped significantly. But still they cannot be called perfect. All SSDs have a significant drawback - the limited number of rewriting cycles.
The flash memory of most SSDs is of the MLC type and can write data from about 3 to 10 thousand times, while ordinary USBs exhaust their resource in 1000 or less rewriting cycles. There are also SSDs, for example, with the SLC memory type, which can withstand several hundred thousand rewriting cycles. There are many nuances, so it is not surprising that just this feature of SSD drives raises a lot of questions from ordinary users regarding their operation, and most importantly, extending their service life. Is SSD optimization needed in Windows 7/10 or is it just another myth created by the manufacturers and developers of commercial software themselves?
Basic training
Yes, you can leave everything as it is on a PC with an SSD and you might be right, but if you really care about your drive and want it to last as long as possible, you should consider setting it up. Let's start with whether you bought a computer with an integrated SSD or just the drive itself that you want to replace the HDD with by transferring Windows from it. In the first case, you can limit yourself to setting up the system. If you install the SSD yourself, be sure to check if the AHCI connection mode for the SATA controller is enabled in the BIOS.
There are two points here: after enabling AHCI and transferring Windows to an SSD, the system may not boot, since it will not have the appropriate drivers. So either install the drivers ahead of time, or reinstall Windows from scratch. Second. Older PCs BIOS may not have AHCI mode. In this case, the BIOS will have to be updated. Now for the firmware of the SSD controller. Solid-state drive owners often ask if the drive will run faster with the latest firmware. Yes, it will, but if you decide to update it, and in general, if the need arises, it is better to contact the service for help.
System settings. Disable defragmentation
Defragmentation is useful for HDDs, but on the contrary, it can damage SSD disks, so Windows usually automatically disables it. However, it's worth checking to see if it is actually disabled. Run with command dfrgui disk optimization utility and click "Change settings".

Make sure the "Run on schedule" checkbox is unchecked. If it is there, be sure to remove it.

Enabling TRIM
The TRIM engine optimizes the SSD by clearing unnecessary data from memory cells when it is removed from the disk. The use of TRIM ensures uniform wear of the disc cells and increases the speed of its operation. To check if TRIM is active on your system, run the command in the command line running as administrator fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify.

If the value of the returned parameter DisableDeleteNotify will be 0, then everything is in order and the trim function is enabled, if 1 means it is disabled and it should be enabled with the command fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0.
This SSD setting only applies to Windows 7/10, while Vista and XP do not support it. There are two options: either install a newer system, or look for an SSD with hardware TRIM. Please also note that some older SSD models do not support TRIM at all, although the chances are that they are still sold in digital stores.
During the process, a significant amount of data, comparable to the amount of RAM, can be written to the hiberfil.sys file on the system disk. To extend the service life of the SSD, we need to reduce the number of write cycles, so it is advisable to disable hibernation. The downside of this SSD setup is that you can no longer keep files and programs open when you turn off your computer. To disable hibernation, run the command while running with administrator privileges powercfg -h off.

Restart your computer and make sure the hidden system file hiberfil.sys is removed from the C drive.

Disable search and file indexing
What else can you do to properly configure your SSD drive for Windows 7/10? The answer is to turn off indexing of the contents of the disk, because the SSD is already fast enough. Open the properties of the disk and uncheck the box "Allow indexing of file contents ...".


But here's the thing. If you have an HDD in addition to an SSD, then you will hardly want to disable indexing on it. What will come of it? By default, the index file is located on drive C and data from drive D will still be written to the solid-state drive.
If you don't want to disable indexing on the custom volume, you will need to move the index file from the system SSD drive to the custom HDD. Open with command control / name Microsoft.IndexingOptions indexing options.

Now click "Advanced" and specify your index location, having previously created a folder on the user's drive.


If your PC only has an SSD, you can completely disable indexing and searching by opening the services.msc command in the service management snap-in and stopping the Windows Search service.

Disabling system protection
A controversial point. By disabling the creation of system shadow copies, on the one hand, you will reduce the number of write cycles, on the other hand, you will increase the risk of getting a non-working system in the event of some unexpected failure. Using rollbacks is one of the most effective and simple ways to get Windows back into working state, for this reason we would not recommend disabling this feature, especially since dots are created infrequently and take up not so much space.
Intel does not recommend disabling system protection for its SSDs, Microsoft is of the same opinion. However, it's up to you. If you are using other backup tools such as Acronis True Image, you can turn off system protection. To do this, go to the system properties, on the "System protection" tab, select the SSD drive and click "Configure". Next, in the recovery options, activate the "Disable system protection" radio button, move the slider to zero and click the "Delete" button.

Disable paging file or not?
An even more controversial solution is to disable the paging file. Someone advises transferring it to the HDD, someone completely disconnecting it, but not everything is so simple. The paging file is necessary to optimize the performance of the system and programs that require significant resources of RAM. Disabling paging can indeed reduce disk usage, but the effect will be very minor. In addition, disabling this can significantly reduce the performance of your computer.
There is no particular point in transferring the paging file to a hard HDD disk either, since it is many times slower than an SSD, and the system's constant access to it will slow down its work. Disabling, or even better, reducing the paging file is permissible only in one case - if your computer has more than 10 GB of RAM, and at the same time you do not use resource-intensive applications. And, of course, it is better to leave everything by default. You can perform all manipulations with the paging file in the performance parameters window, called in the Run window by the command systempropertiesperformance (hereinafter Additional - Change).

Prefetch and Superfetch
In theory, everything here is also better left by default. The function does not affect the longevity of the solid state drives in any way, as it does not make any recordings. Moreover, when installing Windows on an SSD, the system automatically turns it off. Want to make sure it's disabled? Go to the registry editor at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Control / Session Manager / Memory Management / PrefetchParameters and see the parameter value EnableSuperfetch... It should be set to 0. You can also disable it through the service management snap-in.

As far as Prefetch is concerned, the writes it makes to disk is so insignificant that it can be ignored. However, you can turn it off, nothing bad will happen. To do this, in the same registry key, set the parameter value EnablePrefetcher 0.

The same can be said about disabling the additional Prefetch ReadyBoot feature that logs the application loading process. The amount of entries it makes to the folder C: / Windows / Prefetch / ReadyBoot is negligible, but if you want to disable them too, set the Start parameter to 0 in the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE / SYSTEM / CurrentControlSet / Control / WMI / Autologger / ReadyBoot.

SSD optimization software
Almost everything that was shown in the examples above can be done using special utilities. How to set up an SSD under Windows 7/10 using third-party software? Very simple. Most of them have an intuitive interface, represented by a set of options that you can enable or disable. There are many SSD optimizers, but we will focus only on the most popular ones.
SSD Mini Tweaker
The most convenient portable SSD optimization software. The utility supports defragmentation, hibernation and system protection, Trim, Superfetch and Prefetcher, paging file and Layout.ini management, indexing, file system cache and some other settings.

SSD Mini Tweaker interface is represented by a window with a list of functions available for control. After applying the new settings, it may be necessary to restart the PC.
Shareware utility to optimize and tune SSD performance. There is no Russian language in Tweak-SSD, but there is a convenient step-by-step wizard that offers optimal settings. Features of this program include disabling file indexing, program compatibility assistant, hibernation, paging file, defragmentation, recording the time of the last access to a file, working with TRIM, increasing the file system cache, removing the NTFS memory limit, and taking the kernel out of memory instead of unloading parts of modules to disk.

SSD Fresh Plus
Another SSD optimizer. Unlike analogs, it supports working with S.M.A.R.T. data. With Abelssoft SSD Fresh Plus, you can disable defragmentation, use of abbreviated names for folders and files, timestamps, Windows log, prefetch services.

In total, the utility supports nine different settings to optimize SSD performance. Additional features of the program include viewing detailed information about the disc. It is distributed in paid and free editions.
Conclusion
On this, perhaps, everything. There are other guidelines for optimizing SSDs as well, but these are mostly either questionable or harmful. In particular, it is not recommended to disable write caching for the SSD drive and the USN journal of the NTFS file system. You should also not transfer programs and temporary Temp folders, browser cache, etc. from the SSD, because then what's the point in buying an SSD drive? We need to speed up the work of programs, transferring them to the HDD, you will only slow down the system.
And finally, here's some good advice. Don't bother especially with SSD optimization. Even a budget 128GB solid-state drive will take at least a decade to run out, unless you write down and delete terabytes of data every day. And during this time, not only the disk model, but also the computer itself will become hopelessly outdated.
Among the well-known and large suppliers of solid-state drives, there is Kingston, known mainly for its RAM modules and USB-Flash devices. The firm entered the ranks of SSD manufacturers early and has a rich history of its lineup. Nevertheless, Kingston products are somehow based on Sandforce controllers and represent the ssdnow line (a wide profile from the series for ordinary users to the corporate level) and HyperX. The HyperX line gets its name from the high-performance RAM modules produced under this brand.
All solid state drives need a firmware update. Some developers release them faster and more often than others, but, ultimately, it is advisable to carry out this procedure at least once in some long period of time. Recall that SSD firmware helps the drive to work faster, and most importantly, more reliable, they very often optimize the operation of the internal controller. This time, we are learning how to flash Kingston's SSD ssdnow and HyperX series.
To do this, first of all, make sure that the update is really required by finding out the firmware number. You can see it in a huge number of programs and utilities. Then find and download the archive of the flasher program from the official website for your device model. When ready, run the program as an administrator.
The utility window will open, after which it will automatically try to find your Kingston SSD, while the drive should already be detected and visible to the system. It is desirable to connect it to the native SATA ports and set the controller mode in the BIOS options to AHCI.

[click on the picture to enlarge]
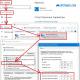
In about a minute, all Kingston drives will be found and listed. In addition, the utility will show the serial number of devices and, of course, the firmware number and their volume. In order to reflash the SSD, it is enough to mark the required drives and press the "Update Firmware" button. Actually, the program does not have any other functions, all that can be done is to rescan the computer for an SSD, find out the version of the utility and exit.
 [click on the picture to enlarge]
[click on the picture to enlarge]
The program will ask you to find the file to update and will start searching for it from its folder. This is the right decision, since it should have been inside the archive downloaded with the utility.

[click on the picture to enlarge]
Kingston Field Updater will warn you about the possible data loss of all unsaved documents and that you need to make a backup. When you're ready click "Proceed".