Micro usb input. Usb pinout on the motherboard. Micro USB connectors. Types of USB connectors, their features
- in order to use the USB-inputs installed on the front of the system case, they must first be connected to the system board of the personal computer. This publication will discuss how to properly organize and perform such a connection.
Modern motherboards are now mostly available with four, six or eight USB connectors. But they are installed directly into the motherboard, as a rule, there are only two or four connectors on the rear side. Due to this, in most cases we have a couple of USB ports remaining on the motherboard. These connectors are usually made in a nine or ten pin connector.
USB pinout on the motherboard
One of the most significant problems is that global manufacturers do not use a common motherboard standard in their manufacture. Therefore, the purpose of each pin in connectors from different board manufacturers may differ in functionality from motherboards from another brand. For this reason, personal connectors are used for any wire of the USB connector on the front panel of the system case.
Wiring the USB 2.0 connector on the motherboard
Each connector housing has special designations of this kind: + 5V, D +, D- and GND (body), but the values \u200b\u200bmay be indicated slightly differently, although the essence is the same.
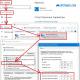
| Pin number | Wire color | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | 5V, VCC, Power | Nutrition |
| 2 | Red | 5V, VCC, Power | Nutrition |
| 3 | White | D- | Data- |
| 4 | White | D- | Data- |
| 5 | Green | D + | Data + |
| 6 | Green | D + | Data + |
| 7 | The black | GND | Earth |
| 8 | The black | GND | Earth |
| 9 | — | Key (No pin) | Key |
| 10 | Grey | GND | Earth |
All you need to do is install each of the wires (+ 5V, D +, D- and GND) in the correct locations as shown above.
Wiring the USB 3.0 connector on the motherboard
| Pin number | Name | Description | Pin number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IntA_P2_D + | Data + | 2 | ID | Identifier |
| 3 | IntA_P2_D- | Data- | 4 | IntA_P1_D + | Data + |
| 5 | GND | Earth | 6 | IntA_P1_D- | Data- |
| 7 | IntA_P2_SSTX + | Data + | 8 | GND | Earth |
| 9 | IntA_P2_SSTX- | Data- | 10 | IntA_P1_SSTX + | Data + |
| 11 | GND | Earth | 12 | IntA_P1_SSTX- | Data- |
| 13 | IntA_P2_SSRX + | Data + | 14 | GND | Earth |
| 15 | IntA_P2_SSRX- | Data- | 16 | IntA_P1_SSRX + | Data + |
| 17 | Vbus | Nutrition | 18 | IntA_P1_SSRX- | Data- |
| 19 | Key (No pin) | Key | 20 | Vbus | Nutrition |
How to connect the front panel to the motherboard
Content:
In our age of computer technology, smartphones and gadgets, it is difficult to find such a person who does not know what USB connectors are. Also, almost everyone understands words such as mini- and micro-USB connectors. After all, we use such things almost daily, which is natural. Similar connectors are found on the charger and on all computer peripherals.
But what if the wiring has moved away at the base, and there is no way even to understand what color and on what contact was soldered? This is where knowledge should be applied, and what, now let's try to figure it out.
The pinout of such a plug, or, in other words, the pinout of the USB wire, in its essence, does not carry anything super complicated. Once you figure out the sequence and colors, anyone who can hold a soldering iron can do this job.
But first you need to understand what a USB plug is.
What is a USB connector?
At its core, it is a connector with many possibilities, ranging from USB power to the transfer of complex information data. A similar cable replaced the previously used options for connecting to a computer (PS / 2 ports, etc.). It is used today for all devices connected to a personal computer, be it a mouse, flash drive, printer, camera or modem, joystick or keyboard - USB cables have become truly universal.
There are three types of such connectors:
- 1.1 - its purpose - outdated already peripheral devices with the ability to transfer information only one and a half megabits per second. Of course, after a slight modification by the manufacturer, the transmission speed rose to 12 Mbit / s, but with higher-speed options, it still could not stand the competition. Of course, when Apple already had a connector supporting 400 Mbps. Now such types also exist, but there are very few of them, since faster USB cables, mini USB, and in general, the speed of USB occupies a special place in human life long ago. Everyone is in a hurry somewhere, in a hurry to live, there are people who practically do not sleep, and therefore, the faster information is downloaded, the more preferable the connector is, right?
- 2.0. At the end of the last century, the second generation of such connectors was released. Here the manufacturer has already tried - the transmission speed has grown to almost 500 Mbit / s. And it was intended mainly for sophisticated gadgets, such as a digital video camera.
- 3.0 is really high technology. The limiting data transfer rate of 5 Gbps ensured the demand for this USB connector, which practically nullified the first and second versions. In the third series, the number of wires has been increased to nine versus four. However, the connector itself has not been modified, and therefore you can still use the types of the first and second series with it.
Pinout designations
Considering the pinout diagram, you must understand all the designations that are present on it. Usually indicated:

- Connector type - it can be active (A) and passive (B). Passive is the connection of a printer, scanner, etc. In general, a connector that only works for receiving information. Through active it is possible to receive and transmit data.
- The shape of the connector is female for female (F) and male for male (M).
- Connector sizes are regular, mini and micro.
For example USB AM, that is, an active USB plug.
The wires should be arranged by color as follows (from left to right):
- Red wire - positive, constant voltage 5V. with a maximum current of 500 milliamperes.
- White wire - data-
- Green wire - data +
- Black wire - this wire is common, "ground", "minus". There is no tension on it.
But the mini and micro connectors include 5 wires with the following arrangement:
- Red, white and green wires are located similarly to the first option.
- ID - this wire in the B connectors is free. In "A" it must be shorted to a black wire.

Sometimes a separate wire without insulation may be present in the connector - this is the so-called "mass", which is soldered to the case.
According to the presented diagrams, the outer side is visible here. In order to solder the plug on your own, you need to take a mirror image of the picture, and as you probably realized, microUSB pinout is not at all more complicated than that of conventional USB connectors.
By the way, if the damaged parts of the cable are supposed to be used only for charging mobile phones, it will be more convenient, after looking at the colors of the wires, to solder only black and red. This connector is quite enough for a phone, it will charge it. What to do with the rest of the wires? You don't need to do anything with them.
The USB connector has been around since 1997. Then it was installed in computer motherboards. Now it has received widespread implementation: it is used in smartphones and players, printers and a bunch of other devices. More and more improved versions of USB are released. The article will tell you how they differ from each other, as well as about the features of their pinout.
Types of USB connectors
Before proceeding to the story about USB pinout by color, you first need to understand the types of such an interface. First, they differ in size. Now the standard is in use, for example, for a computer, and micro - is in mobile phones and peripheral devices. Mini is also found, but this type of connector is already becoming obsolete.
Also, USB is divided into 2 types:
- A - connects to the "mother" socket on the computer or;
- B - connects to the male socket - on the peripheral device.
Now let's talk about the types and their differences.
1. v1 is a modified version of version 1.0, the use of which was decided to be discontinued due to numerous errors in the data transfer protocol. It had a low throughput rate compared to modern representatives.
Main settings:
- Two modes, differing in the speed with which information is transferred: 12 and 1.5 Mb / s.
- A maximum length of three meters is for slow communication and 5 meters for fast.
- The bus voltage is 5V (nominal), which made it possible to use plugs for charging smartphones, and the permissible load of devices connected to the connector is 0.5 A.

USB pinout by color
The pinouts are color-coded - these are generally accepted standards that simplify repair tasks. In general, the color scheme makes it easier to understand which cable is responsible for what.
The first and second versions of the USB interface have identical designations and locations. Generation III has differences associated with design and speed features. More details in the following sections.
USB 2.0 pinout
The following table shows schematically what the color pinouts for this generation of ports look like.

It should be noted that types A and B have the same circuits. The only difference is that in A the arrangement is linear, while B differs in the location above and below, as in the table:
USB 3.0
In the 3rd branch (this cable belongs to this) there are 9 connectors, sometimes 10. It all depends on the presence or absence of a shielding braid. Naturally, the number of contacts has also increased, but they are placed in a checkerboard pattern. This is for compatibility with older versions.

|
Pinout YUSB 3.0 by color |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Output | Name | Wire color | Description |
| 1 | VCC | Red | + 5V |
| 2 | D- | White | Data - |
| 3 | D + | Green | Data + |
| 4 | GND | The black | Earth |
| 5 | SS TX | Blue | super Speed \u200b\u200bcommunication connectors |
| 6 | SS TX + | Yellow | |
| 7 | Ground or GND | - | additional ground for signal wires |
| 8 | SS RX- | Violet | |
| 9 | SS RX + | Orange | for USB3 data reception (StdA_SSRX) |
USB (Universal Serial Bus - "universal serial bus") - serial data interface for medium-speed and low-speed peripheral devices. A 4-wire cable is used for connection, with two wires used for receiving and transmitting data, and 2 wires for powering a peripheral device. With built-in uSB power lines allows you to connect peripherals without their own power supply.
USB basics
USB cable consists of 4 copper conductors - 2 power conductors and 2 data conductors in twisted pair, and a grounded braid (shield).USB cables have physically different tips "to the device" and "to the host". It is possible to implement a USB device without a cable, with a tip “to the host” built into the case. One-piece integration of the cable into the device is also possible(e.g. USB keyboard, Webcam, USB mouse)although the standard prohibits this for full and high speed devices.
USB bus is strictly oriented, that is, it has the concept of a "master device" (a host, also known as a USB controller, is usually built into the south bridge chip on the motherboard) and "peripheral devices".
Devices can be powered by +5 V from the bus, but they can also require an external power supply. The standby mode for devices and splitters is also supported by a command from the bus, with the main power being removed while maintaining the standby power and turning on by a command from the bus.
USB supportsHot plugging and unplugging of devices... This is possible due to the increase in the length of the conductor of the grounding contact in relation to the signal. When connected uSB connector the first to close grounding contacts, the potentials of the cases of the two devices become equal, and further connection of the signal conductors does not lead to overvoltages, even if the devices are powered from different phases of the three-phase power network.
At the logical level, a USB device supports data transmission and reception transactions. Each package of each transaction contains a number endpoint on the device. When a device is connected, drivers in the OS kernel read a list of endpoints from the device and create control data structures to communicate with each device endpoint. The collection of endpoint and data structures in the OS kernel is called pipe.
Endpoints, and hence channels, belong to one of 4 classes:
- in-line (bulk),
- manager (control),
- isochronous (isoch),
- interrupt
Low speed devices such as a mouse may not have isochronous and streaming channels.
Control channel is intended for exchange with the device in short “question-answer” packets. Any device has control channel 0, which allows the OS software to read brief information about the device, including the manufacturer and model codes used to select the driver, and a list of other endpoints.
Interrupt channel allows you to deliver short packets in both directions, without receiving a response / confirmation, but with a delivery time guarantee - the packet will be delivered no later than N milliseconds. For example, it is used in input devices (keyboards, mice, or joysticks).
Isochronous channel allows you to deliver packages without a delivery guarantee and without answers / confirmations, but with a guaranteed delivery speed of N packets for one bus period (1 KHz for low and full speed, 8 KHz for high speed). Used to transmit audio and video information.
Streaming channel provides a guarantee of delivery of each packet, supports automatic suspension of data transmission if the device does not want it (buffer overflow or underflow), but does not guarantee the speed and delay of delivery. Used, for example, in printers and scanners.
Bus time divided into periods, at the beginning of the period the controller transmits the “start of period” packet to the entire bus. Further, during the period, interrupt packets are transmitted, then isochronous in the required amount, in the remaining time in the period, control packets are transmitted, and last of all streaming ones.
Active side of the bus there is always a controller, the transfer of a data packet from a device to a controller is implemented as a short question of the controller and a long, containing data, response of the device. The packet movement schedule for each bus period is created by a joint effort of the controller hardware and driver software, for this many controllers use DMA Direct Memory Access (Direct Memory Access) - the mode of data exchange between devices or between the device and the main memory, without the participation of the Central Processor (CPU). As a result, the transfer rate increases as no data is sent to and from the CPU.
The packet size for an endpoint is a constant hardwired into the device's endpoint table and cannot be changed. It is selected by the device developer from among those supported by the USB standard.
USB Specifications
Features, advantages and disadvantages of USB:
- High speed of exchange (full-speed signaling bit rate) - 12 Mb / s;
- Maximum cable length for high speed exchange - 5 m;
- Low exchange rate (low-speed signaling bit rate) - 1.5 Mb / s;
- Maximum cable length for low baud rate - 3 m;
- Maximum connected devices (including multipliers) - 127;
- Connection of devices with different exchange rates is possible;
- There is no need to install additional elements such as terminators;
- Supply voltage for peripheral devices - 5 V;
- The maximum current consumption per device is 500 mA.
USB signals are transmitted over two wires of a shielded 4-wire cable.
Pinout of USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 connectors
| Type A | Type B | ||
| Fork (on cable) | Power socket (on the computer) | Fork (on cable) | Power socket (on the peripheral device) |
 |
|||
USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 Pin Names and Functions
Disadvantages of USB 2.0
Although the maximum uSB 2.0 baud rate is 480 Mbit / s (60 MB / s), in real life it is unrealistic to achieve such speeds (~ 33.5 MB / s in practice). This is due to the large delays of the USB bus between the request for data transfer and the actual start of the transfer. For example, the FireWire bus, although it has a lower peak bandwidth of 400 Mbps, which is 80 Mbps (10 Mbps) less than USB 2.0, in reality allows you to provide more bandwidth for data exchange with hard drives and other storage devices. In this regard, a variety of mobile drives have long been "running into" the insufficient practical bandwidth of USB 2.0.
UBS connectors are the most common types of connectors that are used to connect various types of digital electronic devices together.
We are sure that everyone in the house has a lot of cables with such connectors, because they are used to connect peripheral devices to a computer: mice, joysticks, printers, scanners, external hard drives and much more.
In contact with
Also, when buying a mobile phone, you get connectors for connecting the gadget to a computer and a charger.
Pinout concept
Sometimes it happens that due to a broken connector or a cable break, it stops working charger device for phone or anything connected to your computer. For a person who does not know how to work with a soldering iron, this is an unpleasant surprise and problem.
But, for a person who is familiar with the basics of electronics and knows how to solder, the problem is solved simply - a new connector is soldered or an old one is re-soldered, and our favorite devices function again.
However, before proceeding with the repair, you need to know pinout of usb connector - the location of the wires by color in relation to the connector contacts. Wrong wiring will lead to failure of the connected gadgets.
General information about USB connectors
 USB (Universal Serial Bus) - a data transmission standard that was developed in 1994 to organize an interface between a computer and peripheral devices.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) - a data transmission standard that was developed in 1994 to organize an interface between a computer and peripheral devices.
Now it is used both for transferring data between digital devices and for charging the batteries of a passive device from an active, so-called "host". An example would be charging your phone from a computer.
Connectors are classified into three types:
The first type is usb 1.1
It was developed one of the first to expand the functionality of a computer and made it possible to connect additional devices to a computer, including mobile phones for digital voice transmission.
Due to the fact that the data transfer rate was low, it was replaced by usb 2.0. Currently, usb 1.1 is considered obsolete and practically not used.
The second type is usb 2.0
The most common and widely used at the moment. Most electronic devices sold in electronics stores have usb 2.0 connectors, even though they no longer quite meet modern transfer rates. In particular, hard drives can read information at a speed 3-4 times higher than the speed that this type of device provides. However, they remain widespread due to the fact that this speed is quite suitable for the operation of mice, keyboards and other devices.
The third type is usb 3.0
It is a new generation of devices, the transfer rate of which satisfies the fastest hard drives and provides a speed reserve for the future. Connectors of this type are specially marked in blue.
All connectors of the considered types have structural differences, which can be identified by the designation:

The letters F and M in the usb marking connectors mean:
- F (female) - female connector;
- М (male) - connector type "plug" (male).
To connect to portable and mobile devices, mini - usb was developed, and later - micro - usb.
Mini-AB and micro-AB connectors serve as transitional connectors for connecting mini A and mini B, micro-A and micro-B to each other.
Pinout of connectors
The pinout of the usb 2.0 connector is as follows:
- Red wire soldered to pin 1 of the connector: + 5V power is supplied;
- White wire - to contact 2: informational (D -);
- Green wire - to contact 3: informational (D +);
- Black wire - to pin 4: common.
Mini and micro usb cables have five wires of different colors and a five-pin connector. The difference between the desoldering of such micro connectors from the desoldering of the usb 2.0 connector is as follows:
- wiring the first three contacts - similar to usb 2.0;
- the purple wire goes to pin 4 - this is the ID; in connectors A - not used, in connectors B - connected to the case;
- the black wire goes to pin 5 - common.
Wiring usb 3.0 connector is done as follows:
- the wiring of the first 4 pins is identical to the wiring of the usb 2.0 connector;
- blue wire goes to pin 5 - information transfer with a plus sign;
- yellow wire - to pin 6 - information transfer with a minus sign;
- additional housing to pin 7;
- purple wire - to pin 8 - information transfer with a minus sign;
- orange wire - to pin 9 - information transfer with a plus sign.
Micro and mini usb for mobile phones
 All modern mobile phones are charged via mini and micro connectors from own charger... We discussed the pinout of mini and micro connectors above.
All modern mobile phones are charged via mini and micro connectors from own charger... We discussed the pinout of mini and micro connectors above.
Now let's talk about why it happens that the charger seems to fit in its parameters (voltage and charging current), and the connector from your phone fits well to it, but the charger is not "native" - \u200b\u200band charging does not work. Why?
The point is in some differences in the pinout of mini and micro connectors of phones inserted into the charger.
For example, such gadgets as HTC, Philips, Samsung, as well as Nokia and LG recognize the charger as their own, if 2 and 3 contacts in the connector are shorted... By connecting these contacts in the AF connector of the charger, it is quite possible to use it to charge these types of phones.
Motorola devices "require" the installation of a resistor of 200 kiloohm between 4 and 5 pins. Without him the device is charging very slowly.
Summarizing what has been said, we can conclude that when repairing cables to your favorite gadgets, it is important to know the pinout of the connectors in order to properly unsolder the cable wires, and then your electronic "friends" will serve you for a long time.