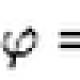The figure shows a harmonic schedule. Harmonic oscillations. If the oscillation is described by the law of sinus
Figure 1. Depicted velocity vectors and accelerates the ball. What direction shown in fig. 2, has a vector of automatic all forces attached to the ball? B) 2.
On the picture The probability detection is given by the particle detection at different distances from the walls of the pit. What does the probability density meaning at point A () indicate? C) a particle cannot be detected in the middle of a potential pit
On the picture are given graphs of the dependence of the radiative ability of an absolutely black body from the wavelength for different temperatures. Which curves corresponds to the smallest temperature? E) 5.
On the picture The wave profile is depicted at a certain point in time. What is its wavelength? B) 0,4m
Figure shows the power lines of the electrostatic field. The field strength is the largest at the point: E) 1
On the picture shown A graph of the oscillations of the material point, the equation of which is :. What is the initial phase? B)
On the picture The cross section of the conductor with current I is shown. The electric current in the conductor is directed perpendicular to the plane of the pattern from us. Which of the directions specified in the figure at point A corresponds to the direction of the magnetic induction vector? C) 3.
How much will change X-ray wavelength length with compaton scattering at an angle 90 0? Take the wavelength of componton 2.4 pm.) Will not change
How much will change X-ray wavelength length with scattering computers 60 0? Take the wavelength of componton 2.4 PM.B) 1.2 PM
At all change optical The length of the way, if on the path of the light beam, going in vacuo, to put a glass plate with a thickness of 2.5 μm? The refractive index of glass is 1.5.A) 1.25 microns
At all change periodoscillations of a mathematical pendulum with an increase in its length 4 times? A) increases by 2 times
At all Change the period of fluctuations in the physical pendulum with an increase in its mass 4 times? Will not change
How much will change Phase during one complete oscillation?
At all different Charge oscillation phases on capacitor and current streams in oscillatory circuit? a) P / 2 Rad
On the collecting lens Falls a bundle of parallel rays, as shown in the picture. What number in the figure indicates the focus of the lenses? D) 4
On a glass plate, the refractive index of which 1.5 drops a beam of light. Find the angle of falling the beam if the reflection angle is 30 0 .c) 45 0
On a 10 cm long rod is charged 1 μKl. What is the linear charge density on the rod? E) 10 -5 kl / m
A constant torque acts on the body. Which of the listed values \u200b\u200bchange over time according to the linear law? B) Corner speed
On the body weighing 1kg power 10N. Find the acceleration of the body: e) 10m / s 2
On the body Weighing 1kg is the force of F \u003d 3H for 2 seconds. Find the kinetic energy of the body after the action of power. V 0 \u003d 0m / s. 18J.
On the thin lens Falls ray light. Select the course of the beam after the refraction of its lens.a) 1
A monochromatic light with a wavelength of 220 nm is dropped on a zinc plate. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons is equal to: (the operation of the output A \u003d 6.4 · 10 -19 J, M ∈ \u003d 9.1 · 10 -31 kg.) C) 2.63 · 10-19 J.
For what Cost of photon energy with external photoeffect? \u200b\u200bD) to work the electron output and the message to it kinetic energy
On the gap falls Normally monochromatic light. The second dark diffraction strip is observed at an angle \u003d 0.01. How many wavelengths of the incident light is equal to the width of the gap? B) 200
On the gap The width is falling normally parallel bunch of monochromatic light with a wavelength. At what angle will be the third diffraction minimum of light? D) 30 0
A parallel beam of light from a monochromatic source with a length of 0.6 microns is performed on a 0.1 mm wide width of 0.1 mm. The width of the central maximum in the diffraction pattern is projected by the lens located directly behind the slit on the screen, the lens at the distance L \u003d 1M, is equal to: c) 1.2 cm
On a 0.1 mm wide width, a normal monochromatic light with a wavelength of 0.6 μm is dropped. Determine the sine of the angle corresponding to the second maximum. D) 0,012
On the slot 2 μm wide, a normally parallel bunch of monochromatic light with a wavelength of 500 nm is dropped. What an angle will be observed the second diffraction minimum of light? A) 30 0
On a width gap A \u003d 0.005 mm is dropped normally monochromatic light. The angle of deviation of the rays corresponding to the fifth dark diffraction line, J \u003d 300. Determine the wavelength of the falling light. C) 0.5 μm
On a width gap a \u003d.2 μm drops normally parallel bunch of monochromatic light (\u003d 500 nm). What angle will be the diffraction minimum of the second order light? C) 30 0
On a width gap The normally parallel bunch of monochromatic light with a wavelength drops. At what angle will be the third diffraction minimum of light? D) 30 0
On the screen An interference pattern was obtained from two coherent sources emitting light with a wavelength of 0.65 μm. The distance between the fourth and fifth interference maxima on the screen is 1 cm. What is the distance from the sources to the screen, if the distance between the sources is 0.13 mm? A) 2 m
the observer drove a car with a lilac included. When the car approaches the observer, the observer heard a higher sound tone, and when removing a lower sound tone. What effect will be observed if the siren is fixed, and the observer will turn past it?D) when approaching the tone will increase, when removing it drops
Name Thermodynamic parameters. B) Temperature, pressure, volume
Find the body speed at time t \u003d 1c.c) 4 m / s
The simplest view of the oscillations are harmonic oscillations - oscillations, in which the displacement of the oscillating point from the equilibrium position changes over time according to the law of sine or cosine.
So, with a uniform rotation of the ball around the circumference, its projection (shadow in parallel rays of light) performs on a vertical screen (Fig. 1) Harmonic oscillatory movement.
The displacement of the equilibrium position in harmonic oscillations is described by the equation (it is called the kinematic law of harmonic movement) of the form:
where x - mixing is the value characterizing the position of the oscillating point at time t relative to the equilibrium position and the distance measured from the equilibrium position until the point position at the specified point in time; A - amplitude of oscillations - the maximum bias offset from the equilibrium position; T - period of oscillations - the time of the commission of one complete fluctuation; those. The smallest period of time, after which the values \u200b\u200bof the physical quantities characterizing the oscillation are repeated; - the initial phase;
![]()
Phase oscillation at time t. The oscillation phase is an argument of a periodic function, which, with a given amplitude of oscillation, determines the state of the oscillating system (offset, speed, acceleration) of the body at any time.
If at the initial moment of time the oscillating point is maximally shifted from the equilibrium position, then the point offset from the equilibrium position changes by law
![]()
If the oscillating point is in the position of a stable equilibrium, then the point offset from the equilibrium position changes by law
![]()
The value of V, the reverse period and equal to the number of complete oscillations performed in 1 ° C are called the frequency of oscillations:
If during the time t body makes n full oscillations, then
![]()
Magnitude ![]() showing how much oscillations makes the body for C, called cyclic (circular) frequency.
showing how much oscillations makes the body for C, called cyclic (circular) frequency.
The kinematic law of harmonic movement can be written as:
A graphically dependence of the displacement of the oscillating point from time to time is depicted by a cosinoisoid (or sinusoid).
Figure 2, and presents a graph of dependence on the time of displacement of the oscillating point from the equilibrium position for the case.

Throw out how the speed of the oscillating point changes with time. To do this, find a derivative of time from this expression:
where is the amplitude of the projection of the speed on the x axis.
This formula shows that with harmonic oscillations, the projection of the body velocity on the axis x changes also by harmonic law with the same frequency, with another amplitude and ahead of the mixture on phase (Fig. 2, b).
To determine the dependence of the acceleration, we will find a time derivative from the projection of speed:
where is the amplitude of the projection of acceleration on the x axis.
With harmonic oscillations, the acceleration projection is ahead of the shift in phase on K (Fig. 2, B).
BUT. 1 s. B. 2 s. AT. 3 s. G. 4 s. D.
2. q.= 10-2COS 20. t. (CL). What is the amplitude of the charge fluctuations?
BUT. 10-2 cl. B. COS 20. t. CL. AT. 20t. CL. G. 20 cl. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
3. The period of oscillations of the mathematical pendulum is 0.5 s. What is the cyclic frequency of pendulum oscillations?
BUT. 0.5 Hz. B. 2 Hz. AT. 4 π C-1. G. π C-1. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
4. Oh x.\u003d 0.4 SIN 2 t.
BUT. 0.4 m / s2. B. 0.2 m / s2. AT. 0.1 m / s2. G. 0.8 m / s2. D. 1.6 m / s2.
5. Cargo mass m.suspended on the spring, makes harmonic oscillations with cyclic frequency ω ω 2 cargo oscillations mass m.2=4m.1 on the same spring?
A.. ω 2= ω l / 4. B. ω 2 = ω 1/2. AT. ω 2= ω 1. G. ω 2=2 ω 1. D. ω 2=4 ω 1.
6. How will the frequency of oscillations of a mathematical pendulum change if it is 4 times zoomed?
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. I. = 0.
8. Which of the above graphs (Fig. 4) expresses the dependence of the active resistance in the variable current circuit from the frequency?
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
9. The active resistance of 10 ohms is included in the alternating current circuit with a frequency of 50 Hz. What is the amplitude of the fluctuations of the strength of the current with the amplitude of the voltage oscillations at the outskirts of the active resistance of 50 V?
BUT. 5 A. B. 0.2 A. AT. 250 A. G. 0.1 A. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
10. How will the amplitude of the fluctuations of the current flow flowing through the capacitor, if with a constant voltage fluctuations amplitude frequency of voltage fluctuations increased by 2 times?
 BUT. Will increase by 2 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times. AT. Will increase 4 times.
BUT. Will increase by 2 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times. AT. Will increase 4 times.
G. It will decrease by 4 times. D. Will not change.
11. The active value of the voltage on the variable current circuit section is 220 V. What is equal to the amplitude of the voltage fluctuation on this section of the chain?
BUT. 220 V. B. 440 V. AT. 220 / https: //pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image005_1.gif "width \u003d" 25 height \u003d 23 "height \u003d" 23 "\u003e B. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
12. Figure 5 shows a diagram of a lamp generator. Specify the element of the generator schema, due to the energy of which are supported by unlucky electrical oscillations.
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
13. With harmonic oscillations along the axis Oh coordinate h. Body varies by law h.\u003d 0.6 SIN 3 t. (m). What is the amplitude of the speed oscillations?
BUT. 0.6 m / s. B. 0.2 m / s. AT. 1.8 m / s. G. 5.4 m / s. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
14. With harmonic fluctuations in the body on the spring, the maximum value of kinetic energy is 20 J, the maximum value of the potential energy of the spring is 20 j. How does the full mechanical energy of the body and springs change in time?
BUT. Varies from 0 to 20 J. B. Varies from 0 to 40 J.
AT. Does not change and equal to 20 J. G. Does not change and equal to 40 J.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
15. Which of the fluctuations listed below are free: 1 - fluctuations in the mathematical pendulum, 2 - piston oscillations in the car engine cylinder, 3 - current fluctuations in the induction generator, 4 - fluctuations in the current force in the lamp generator, 5 - current fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit.
BUT. 4. B. 1, 5. AT. 3, 4. G. 2, 3. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
Mechanical and electromagnetic oscillations
Option 2.
 1.
Figure 1 shows a timetable timetable t. Speed υ
body making harmonic oscillations along straight. What is the amplitude of body speed fluctuations?
1.
Figure 1 shows a timetable timetable t. Speed υ
body making harmonic oscillations along straight. What is the amplitude of body speed fluctuations?
BUT. 10 m / s. B. 20 m / s. AT. 3 m / s. G. 6 m / s.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
2. Electric oscillations in the oscillatory circuit are given by the equation I.\u003d 2 sin 10 t. (BUT). What is the cyclic frequency of current fluctuations?
BUT. 2 C-1. B. 10t. C-1. AT. 10 C-1. G. SIN 10. t. C-1.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
3. Current fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit occur with the cyclic frequency of 4π C-1. What is the period of current fluctuations?
BUT. 0.5 s. B. 2 s. AT. 4π S. . G. 8π2 s. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
4. Ohacceleration varies by law oh\u003d 4 COS 2 t. h.body?
BUT. 16 m. B. 8 m. AT. 4 m. G. 2 m. D. 1m.
5. k.1, makes harmonic oscillations with cyclic frequency ω 1. What is the cyclic frequency ω 2 oscillations of the same cargo on the spring rigidity k.2=4k.1?
A.. ω 2=4ω l. B. ω 2 =2ω 1. AT. ω 2= ω 1/2. G. ω 2=ω 1/4. D. ω 2=ω 1.
6. How will the period of oscillations of a mathematical pendulum change, if it is long to reduce 4 times?
BUT. Will decrease by 2 times. B. It will decrease by 4 times. AT. Will not change.
G. Will increase by 2 times. D. Will increase 4 times.
7. AC generator rotor rotates in a uniform magnetic field. How will the amplitude of the EMF induction change with increasing the frequency of its rotation 2 times?
BUT. Will not change. B. Will increase by 2 times. AT. Will decrease by 2 times. G. Will increase 4 times.
 |
D. It will decrease by 4 times.
8.
 BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
9. How will the amplitude of the fluctuations of the current flow flowing through the active resistance, if with a constant amplitude of voltage fluctuations, the frequency of oscillations of the applied voltage is 2 times?
BUT. Will increase by 2 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times. AT. Will not change.
G. Will increase 4 times. D. It will decrease by 4 times.
10. How will the amplitude of the fluctuations of the current flow flowing through the coil, the active resistance of which is zero, if with a constant amplitude of the voltage fluctuations, increase the frequency of oscillations by 2 times?
BUT. Will increase by 2 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times. AT. Will increase 4 times.
G. It will decrease by 4 times. D. Will not change.

11. A voltage dependence schedule on the AC circuit section from time to time is shown in Figure 3. What is the active voltage value?
BUT. 50 V. B. 50https: //pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image005_1.gif "width \u003d" 25 height \u003d 23 "height \u003d" 23 "\u003e B. G. 0 V.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
12. Figure 4 shows a diagram of a lamp generator. Specify the element of the generator circuit in which electrical oscillations are directly occurring.
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
13. With harmonic oscillations along the axis Ohbody speed changes by law υ \u003d 6 COS 3 t. (m / s). What is the amplitude of the acceleration oscillations?
BUT. 54 m / s2. B. 18 m / s2. AT. 6 m / s2. G. 2 m / s2. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
14. With harmonic electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit, the maximum power of the electric field of the capacitor is 50 J, the maximum value of the magnetic field of the coil of 50 j. How is the total energy of the electromagnetic field of the circuit change over time?
BUT. Varies from 0 to 50 J. B. Varies from 0 to 100 J. AT. Does not change and equal to 100 J.
G. Does not change and equal to 50 J. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
15. Which of the following fluctuations are forced: 1 - fluctuations in a mathematical pendulum; 2 - piston oscillations in a car engine cylinder; 3 - fluctuations in current force in the induction generator; 4 - fluctuations in current force in the lamp generator; 5 - current fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit.
BUT. 4. B. 1, 5. AT. 3, 4. G. 2, 3. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
Mechanical and electromagnetic oscillations
Option 3.
 1.
Figure 1 shows a chart of depending on the time of the charge of the capacitor with harmonic oscillations in the oscillatory circuit. What is the frequency of charge fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit?
1.
Figure 1 shows a chart of depending on the time of the charge of the capacitor with harmonic oscillations in the oscillatory circuit. What is the frequency of charge fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit?
BUT. 10 Hz. B. 5 Hz. AT. 3.3 Hz. G. 2.5 Hz.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
2. Cargo oscillations along the axis Ohthey are given by the equation https://pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image012_0.gif "width \u003d" 45 "height \u003d" 41 "\u003e. AT. 2t.. G. https://pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image014_0.jpg "align \u003d" left "width \u003d" 158 height \u003d 165 "height \u003d" 165 "\u003e 4. With harmonic oscillations along the axis Ohbody coordinate varies by law x.=0,9 sin.3t. (m). What is the amplitude of the acceleration oscillations?
BUT. 0.1 m / s2. B. 0.3 m / s2. AT. 0.9 m / s2. G. 2.7 m / s2. D. 8.1 m / s2.
5. Cargo mass t.1, suspended on the spring, makes harmonic oscillations with a period T.1. What is equal to the period T.2 cargo oscillations mass m.2 = 4m.1 on the same spring?
BUT. T.2\u003d T.1/4. B. T.2\u003d T.1/2. AT. T.2\u003d T.1. G. T.2 = 2T.1. D. T.2 = 4T.1.
6. How will the period of free electrical oscillations change in the oscillatory circuit, if inductance L. Covers increase 4 times?
BUT. Will increase 4 times. B. Will increase by 2 times. AT. Will not change.
 |
G. Will decrease by 2 times. D. It will decrease by 4 times.
7. The wire rectangular frame rotates at a constant speed in a homogeneous magnetic field (Fig. 2). Which of the graphs given in Figure 3 corresponds to the dependence of the EMF induction in the frame of time?
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. I.=0.
8. Which of the above graphs (Fig. 4) expresses the dependence of the inductive resistance in the AC circuit from the frequency?
 |
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
9. The active resistance of 10 ohms is included in the alternating current circuit with a frequency of 50 Hz. What is the amplitude of the voltage fluctuations on the active resistance of 10 ohms with the amplitude of the current fluctuations in the circuit 5 e?
BUT. 0.5 V. B. 50 V. AT. 1 V. G. 250 V. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
10. How will the amplitude of the voltage fluctuations on the condenser change, if with a constant amplitude of the current fluctuations, the frequency of change of current to reduce 2 times?
BUT. Will not change. B. Will increase by 2 times. AT. Will increase 4 times.
G. Will decrease by 2 times. D. It will decrease by 4 times.
11. The active value of the current value in the AC circuit is 1 A. What is the amplitude of the current fluctuations in this chain?
BUT. 1 A. B. https://pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image017_0.gif "width \u003d" 33 "height \u003d" 23 "\u003e A. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
12. Figure 5 shows a diagram of a lamp generator. Specify the generator schema element by which feedback is performed.
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
13. With electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit, the capacitor charge changes by law q.=0,01 sin.10t. (CL). What is the amplitude of the current fluctuations?
BUT. 0.01 A. B. 1 A. AT. 0.1 A. G. 10-4 A. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.

14. With harmonic fluctuations in the body on the spring, the maximum value of its kinetic energy is 30 J. What is the maximum value of the potential energy of a compressed spring?
BUT. 0 J. B. 15 J. AT. 30 J. G. 60 J.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
15. Which of the fluctuations listed below are auto-oscillations: 1 - oscillations of the mathematical pendulum, 2 - piston oscillations in the car engine cylinder, 3 - fluctuations in the current in the induction generator, 4 - fluctuations in the current in the lamp generator, 5 - fluctuations in the current strength in the oscillatory circuit?
BUT. 4. B. 1, 5. AT. 3, 4. G. 2, 3. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
Mechanical and electromagnetic oscillations
Option 4.
1. Figure 1 shows a graph of the time of the current strength through the coil of the oscillating circuit. What is the period of current fluctuations?
BUT. 0.4 s. B. 0.3 s. AT. 0.2 s. G. 0.1 s. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.

2.
The speed of the fluctuations is set by the equation ![]() (m / s). What is the initial phase of speed oscillations?
(m / s). What is the initial phase of speed oscillations?
BUT. 5. B. 3 t.+ π /3. AT. 3t.. G. π / 3.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
3. Charge fluctuations on the capacitor plates in the oscillatory circuit occurs with the cyclic frequency of 4π C-1. What is the period of charge fluctuations on the capacitor plates?
BUT. 0.5 s. B. 2 s. AT. 2π2 s. G. π s. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
4. With harmonic body fluctuations along the axis Ohacceleration varies by law AX \u003d 9 COS 3 t. (m / s2). What is the amplitude of the coordinate changes h.body?
 |
BUT. 1m. B. 3m. AT. 9 m. G. 27 m. D. 81 m.
5. Cargo suspended on a spring rigidity k.1, makes harmonic oscillations with a period T.1. What is equal to the period T.2 oscillations of the same body on the spring rigidity k.2=4k.1?
 BUT. T2.= 4T.1. B. T2 \u003d.2T.1. AT. T2 \u003d T.1.
G. T2 \u003d T.1/
2.
D. T.2 =
T.1/4.
BUT. T2.= 4T.1. B. T2 \u003d.2T.1. AT. T2 \u003d T.1.
G. T2 \u003d T.1/
2.
D. T.2 =
T.1/4.
6. How will the period of free electrical oscillations change in the oscillatory circuit, if the container WITHcondenser increase 4 times?
BUT. It will decrease by 4 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times.
AT. Will increase 4 times. G. Will increase by 2 times. D. Will not change.
7. AC generator rotor rotates with a constant frequency in a uniform magnetic field. How will EMF induction change with an increase in the magnetic field induction?
BUT. Will increase 4 times. B. Will increase by 2 times.
AT. Will decrease by 2 times. G. It will decrease by 4 times. D. Will not change.
8. Which of the above graphs (Fig. 2) expresses the dependence of capacitive resistance in the circuit of the AC from the frequency?
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
9. How will the amplitude of the fluctuations of the current flow flowing through the active resistance, if with a constant voltage fluctuations in the amplitude of the applied voltage amplitude of the applied voltage 2 times?
BUT. Will increase by 2 times. B. Will decrease by 2 times. AT. Will not change.
G. Will increase 4 times. D. It will decrease by 4 times.
 10.
How will the amplitude of the voltage fluctuations on the coil change, the active resistance of which is zero, if with a constant amplitude of the current force, the change rate of the current will decrease by 2 times?
10.
How will the amplitude of the voltage fluctuations on the coil change, the active resistance of which is zero, if with a constant amplitude of the current force, the change rate of the current will decrease by 2 times?
BUT. Will not change. B. Will increase by 2 times. AT. Will increase 4 times.
G. Will decrease by 2 times. D. It will decrease by 4 times.
11. The chart of the current force in the AC circuit from time to time is shown in Figure 3. What is the active value of the current for the current?
BUT. 0 A. B. https://pandia.ru/text/79/060/images/image025_1.gif "width \u003d" 32 "height \u003d" 23 "\u003e A.
D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
12. Figure 4 shows a diagram of a lamp generator. Specify the elements of the generator schema, with which the energy flow is adjusted from the constant voltage source.
BUT. 1. B. 2. AT. 3. G. 4. D. 5.
13. With electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit, the current of the current in the coil with an inductance of 1 GG varies by law I.=2 cos.100t. (BUT). What is the amplitude of the oscillations of EMS self-induction?
BUT. 0.02 V. B. 2 V. AT. 200 V. G. 2 · 104 V. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
14. With harmonic electrical oscillations in the oscillatory circuit, the maximum power of the electric field energy is 10 J. What is the maximum energy of the magnetic field of the coil?
BUT. 0 J. B. 5 J. AT. 10 J. G. 20 J. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
15. Which of the fluctuations listed below are forced: 1 - cargo oscillations suspended on the spring, 2 - piston oscillations in the car engine cylinder, 3 - fluctuations in the current power in the induction generator, 4 - oscillations of the pendulum in the clock, 5 - current fluctuations in the oscillatory circuit ?
BUT. 2, 3. B. 1, 5. AT. 4. G. 2, 4. D. Among the answers A-g is not correct.
Depending on the number of correct answers, an estimate is set on a five-point scale. Based on the experimental verification of the proposed tasks, the following scale of the translation of knowledge test results is recommended using tasks with a response choice in the ratings on a five-point system:
Number of correct answers: Evaluation
Periodic oscillations are called harmonic If the oscillating value changes over time by the law of cosine or sinus:
Here  - cyclic frequency of oscillations, A. - maximum deviation of the oscillating value from the equilibrium position ( oscillation amplitude
),
φ( t.)
= ω t.+
φ 0
– phase oscillations
,
φ 0
– primary phase
.
- cyclic frequency of oscillations, A. - maximum deviation of the oscillating value from the equilibrium position ( oscillation amplitude
),
φ( t.)
= ω t.+
φ 0
– phase oscillations
,
φ 0
– primary phase
.
The chart of harmonic oscillations is shown in Figure 1.

Picture 1 - chart of harmonic oscillations
With harmonic oscillations, the total energy of the system over time does not change. It can be shown that the total energy of the mechanical oscillatory system in harmonic oscillations is equal to:
 .
.
Harmonically fluctuating the amount s.(t.) obeys a differential equation:
 ,
(1)
,
(1)
which is called differential equation of harmonic oscillations.
A mathematical pendulum is a material point suspended on an unpretentious weightless thread, which performs an oscillatory movement in one vertical plane under the action of gravity.

Period of codebanis
Physical pendulum.
A physical pendulum is a solid, fixed on a fixed horizontal OCI (suspension axis), not passing through the center of gravity, and performing oscillations with respect to this axis under the action of gravity. Unlike a mathematical pendulum, a mass of such a body cannot be considered point.

For small angles of deviation α (Fig. 7.4), the physical pendulum also makes harmonic oscillations. We assume that the weight of the physical pendulum is attached to its center of gravity at the point of C. Power, which returns the pendulum to the equilibrium position, in this case there will be a strength of gravity - the power of F.
To bring the law of movement of mathematical and physical pendulums, we use the basic equation of the dynamics of rotational motion
Moment of force: it is impossible to determine explicitly. Taking into account all the values \u200b\u200bincluded in the initial differential equation of fluctuations in the physical pendulum, it has the form:
|
|
|
|
Solution of this equation 
We define the length L of a mathematical pendulum, at which the period of its oscillations is equal to the period of oscillations of the physical pendulum, i.e. or
![]() . From this ratio determine
. From this ratio determine
This formula defines the length of the physical pendulum, i.e. The length of such a mathematical pendulum, the period of oscillations of which is equal to the period of oscillations of this physical pendulum.
Spring pendulum
This cargo attached to the spring whose mass can be neglected.
While the spring is not deformed, the force of elasticity is not valid. In the spring pendulum, the oscillations are performed under the action of elasticity.



Question 36 Energy of harmonic oscillations
With harmonic oscillations, the total energy of the system over time does not change. It can be shown that the total energy of the mechanical oscillatory system with harmonic oscillations is equal.
Test in physics Harmonic oscillations for students of grade 9 with answers. The test includes 10 tasks with a response choice.
1. Select the correct statement (s).
A. oscillations are called harmonic if they occur by the law of sinus
B. oscillations are called harmonic if they occur under the law of cosine
1) only a
2) only b
3) and a, and b
4) neither, nor b
2. The figure shows the dependence of the coordinate center of the ball suspended on the spring, from time to time. The amplitude of oscillations is equal
1) 10 cm
2) 20 cm
3) -10 cm
4) -20 cm
3. The figure shows a chart of oscillations of one of the points of the string. According to the schedule, the amplitude of oscillations is equal

1) 1 · 10 -3 m
2) 2 · 10 -3 m
3) 3 · 10 -3 m
4) 4 · 10 -3 m
4. The figure shows the dependence of the coordinate center of the ball suspended on the spring, from time to time. The period of oscillations is equal

1) 2 with
2) 4 with
3) 6 with
4) 10 s
5. The figure shows a chart of oscillations of one of the points of the string. According to the schedule, the period of these oscillations is equal

1) 1 · 10 -3 with
2) 2 · 10 -3 with
3) 3 · 10 -3 with
4) 4 · 10 -3 with
6. The figure shows the dependence of the coordinate center of the ball suspended on the spring, from time to time. The frequency of oscillations is equal

1) 0.25 Hz
2) 0.5 Hz
3) 2 Hz
4) 4 Hz
7. Figure shows a schedule h.SM oscillations of one of the points of the string. According to the graph, the frequency of these oscillations is equal

1) 1000 Hz
2) 750 Hz
3) 500 Hz
4) 250 Hz
8. The figure shows the dependence of the coordinate center of the ball suspended on the spring, from time to time. What path will take place for two full fluctuations?

1) 10 cm
2) 20 cm
3) 40 cm
4) 80 cm
9. The figure shows the dependence of the coordinate center of the ball suspended on the spring, from time to time. This dependence is