Windows XP virtual machine. Create a Windows XP Virtual Machine
Today, there is a small circle of users of computer systems who prefer to use not two operating systems installed in parallel on one computer, but the so-called virtual machines in their work. Today we will find out what it is, and at the same time give readers recommendations on how to set up a Windows XP virtual machine. We note right away that there should not be any difficulties here, so you should not be afraid.
What is a Windows XP virtual machine and why is it needed?
Let's start, perhaps, with the most burning question of what this seemingly tricky concept actually represents.
If we do not consider the technical side of the functioning of such a system, the simplest explanation will be the fact that, in fact, such a program in operation is a complete analogue of a real computer, but only in a virtual version. In the operating system, which is provided as a guest, you can work in the same way as in a regular "OS" installed on the user terminal.
It goes without saying that programs are easily installed in such a system, settings are changed, etc. In other words, in the virtual Windows, you can see how this or that program will work, even if infected with a virus, without affecting the main OS.
And Windows XP as a guest system was not chosen by chance. The fact is that, starting from the version of Vista, some applications designed exclusively for the “expansion” simply stop working, and you have to run them in Well, you won’t install two “OSes”, and even so that they do not conflict between yourself? Firstly, this is a rather laborious process, and secondly, if we proceed from the integrity of a law-abiding user, then additional costs for acquiring a license are inevitable.
In this sense, the creation of Windows XP has quite a lot of advantages. In addition, the process itself does not take so much time. The only thing you have to pay attention to is some nuances when choosing parameters. But first things first.
Boot disk
Now let's consider the initial conditions and determine what we need in order to create a Windows XP virtual machine on Windows 8, for example, although for any other "OS", starting from the "seven" and above, the process will be the same.

Naturally, one cannot do without a boot disk or an image created from the original Windows XP installation disk, preferably with a full third service pack (SP3).
To do this, you can use your own tools of the system already on your computer, but it is better to give preference to programs like UltraISO, DAEMON Tools and the like. The process is quite simple, so it does not make sense to dwell on it in detail.
Creating a virtual machine: choosing a program and basic requirements
Further, for example, when a Windows XP virtual machine is created on Windows 8.1, you need to decide on the software (software). It goes without saying that when choosing a particular program, you should pay attention to the criterion of its compatibility with the installed "OS".
As for the programs themselves, there are quite a lot of them today. The most common and most popular are VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, Microsoft Virtual PC, QEMU and many others. However, in view of, so to speak, practicality and ease of use, in this example we will use VirtualBox, a program often called a “sandbox”.
Installing Oracle VirtualBox
So, a Windows XP virtual machine on Windows 10, for example, can only be created after installing the main software product in an existing environment (“OS”).
As expected, the main installation file of the program is launched first. Immediately make a reservation that the launch should be done on behalf of the Administrator, otherwise errors may occur. Further, as in all standard procedures, we select the place where the software product will be installed, check the boxes next to the lines for creating an icon on the desktop (if necessary), in general, follow the instructions of the "Installation Wizard".
During the installation process, warning windows may appear that the program has not been tested for compatibility. There is no need to panic. Just press the continue buttons. Yes, by the way, if the Internet connection suddenly disappears during the installation process, there is nothing wrong with that either - it should be so. We are waiting for the end of the process.
So the installation is complete. After pressing the confirmation button (by the way, this is exactly what this program is good for), the application will start automatically, and with an interface in the language that is installed in the existing “OS” by default.
Additional requirements
During the installation process, you should pay attention to the fact that the program may request the installation of all drivers. If such a situation arises, in all dialog boxes we simply agree with the proposals.
And further. If, nevertheless, after the installation is completed, you need to run the program in compatibility mode, you need to right-click on the “executable” and select launch in the appropriate mode with Administrator rights in the context menu. But, as practice shows, this is not required in most cases.
Windows XP virtual machine on Windows 7 and higher: first steps to create
After the first start of the program, you need to create a new virtual machine. To do this, use the corresponding button on the top panel or the command to add a machine to the menu. Let's make a reservation right away: depending on the version of the application itself, the names of buttons, menu lines or appearance may differ. But, as is already clear, the essence of this does not change.
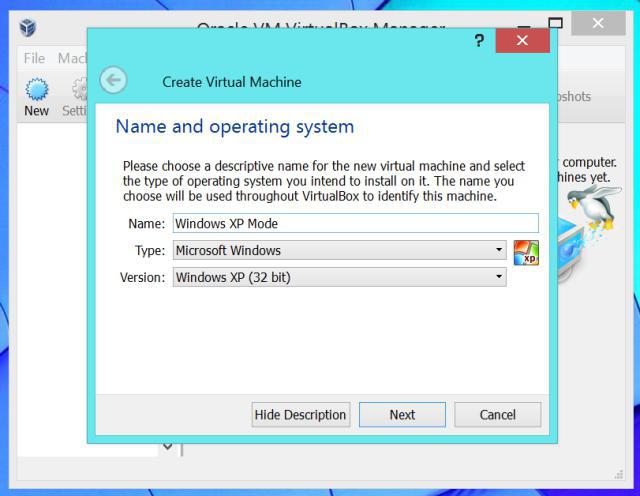
At the first stage, the Windows XP virtual machine is supposed to enter its name, after which the category of the operating system is selected, which, presumably, will be installed later (in our case, this is "explosion").
Criteria for choosing the amount of RAM
In the next step, you will need to specify the amount of RAM required for work. Here you need to be careful. For example, if you need to test one or two not too resource-intensive programs, you can put at least 192 MB.
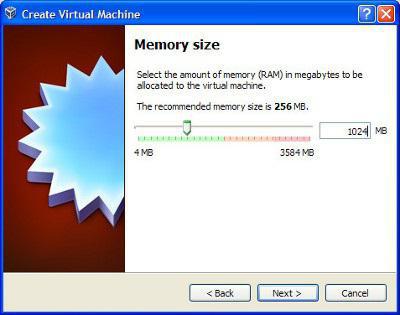
If the user wants to avoid "slowing down", it is better to use either 512 MB or 1024 MB. True, you should take into account the capabilities of your system, so it is not recommended to particularly raise the bar, otherwise, when the virtual machine is turned on, the main system will start to slow down.
The nuances of creating a virtual hard disk
Next, you should select a place on the hard drive where the image of the Windows XP virtual machine with the system installed in the future will be stored. In this case, the "Virtual Hard Disk Creation Wizard" is launched.
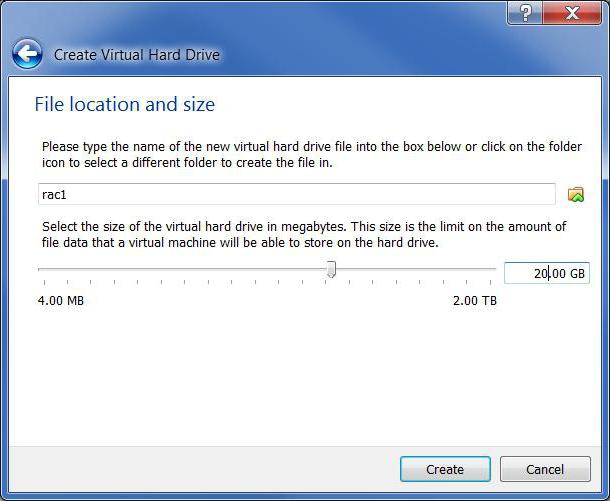
The user will be prompted to choose whether to create a dynamic or static partition. See for yourself. A dynamic section can automatically increase in size as it fills up, while a static section has fixed volumes. Regardless of which type is chosen, it is desirable to specify at least 10 GB (more is possible, but here, again, it all depends on the physical capacity of the existing hard drive, including all its logical partitions).
Along the way, the location of information storage is also selected. Note that you do not need to manually create a new partition on an existing system. In the program, you can select the desired location in the form of a folder (by default, this is Win_XP_SP3 in the specified location). Please note: it is desirable to place it on a logical partition, and not on the one where the main system is installed. For example, if Windows 7 is on drive C, for Windows XP, it's better to choose partition D.
When you continue the settings, all the parameters of the created machine will be displayed on the screen. If everything is correct, click on the finish button. The first part of the journey has been completed.
Installing Windows XP
Now we move on to the process of installing the guest system. To do this, use either the created installation disk or an image.
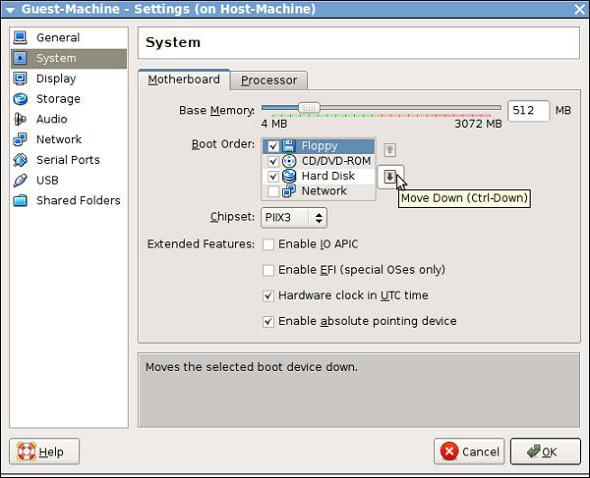
But first, in the virtual machine, you need to go to the properties menu, where you will need to configure some settings, for example, enable 3D acceleration in the "Display" section. Most importantly, in the motherboard settings menu, you need to set the boot order in such a way that the CD-ROM is in the first place for installing the "express" (you can simply drag it to the first position with the mouse).
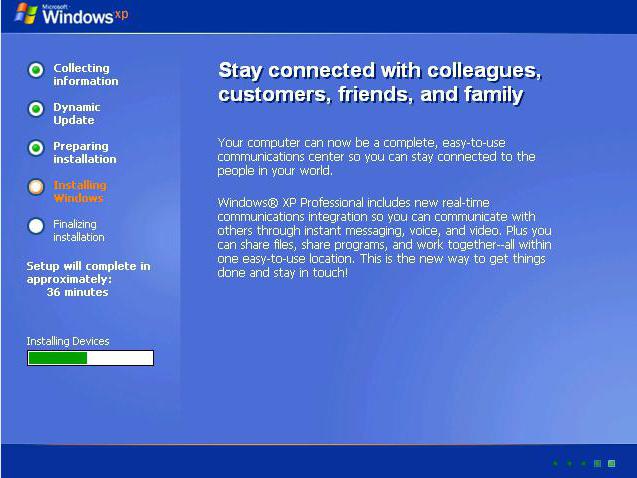
To install Windows XP, use the "Start" button. The installation itself is absolutely no different from how it would be if this “OS” was installed on the hard drive in normal mode.
Shared folders and add-ons
But that's not all. The Windows XP virtual machine needs to interact with the existing system somehow. To do this, it is desirable to create at least one shared folder, although you can also use removable media in the form of ordinary flash drives.
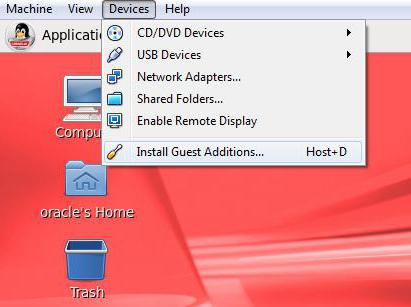
In addition, the user must be able to switch between the main and guest OS, for example, using a standard mouse. To do this, start the guest operating system, and then in the "Devices" item, select the command to install additions to it. Now that's all. We have a finished Windows XP virtual machine, fully functional and ready to use.
In the “expiry” itself, you can perform all standard actions, for example, adding new devices, working with programs and documents, etc. In general, such a Windows XP virtual machine looks absolutely identical to a real computer. In addition, if the machine is in autoload, at the start of the main system it will be possible to choose which OS to start. Although in fairness it should be noted that this is never particularly required.
Instead of a conclusion
So, here is a brief summary of the main issues related to creating and configuring a Windows XP virtual machine. Finally, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that the option was considered exclusively for Windows systems at a level higher than the “expiration”. However, the creation of such a machine can be done in almost exactly the same way in other operating systems, for example, in Linux Ubuntu or any other, while the process of its creation and functioning is absolutely no different from everything that was described above. By the way, for all those who work with systems other than Windows, this is a rather serious plus, but for the most part, those involved in software development will be satisfied.