Adaptive or mobile version. Which one to choose: mobile versus responsive design? There is also a mobile version
The Age of Global Mobilization. Smartphones have made it possible to go online anytime, anywhere. Sometimes it is even more convenient from a phone than from a computer to browse sites, social networks, look for information or a place on the map. Computer operating systems are trying to approach mobile operating systems in terms of interface. The border between computer and mobile platforms is becoming thinner: mobile devices are made powerful and lay almost the functionality of a full-fledged computer, and computer interfaces are brought closer to mobile ones using, for example, common icons, a similar arrangement of elements, similar gestures.
This trend cannot but affect the creation of sites. Managers recommend "mobile" sites, clients want it, designers draw, layout designers, oddly enough, make up, and programmers come up with solutions.
It is easier, of course, right after creating a site, to determine how it will behave on a mobile device, but there are old clients and their old and not so sites for which such a solution was not provided. Although someone thinks that "mobile" sites should not be created.
Understanding that the amount of mobile traffic is growing by leaps and bounds leads to the need to come up with solutions for the correct display and usability of the site on smartphones and tablets. I see two real solutions indicated, in fact, in the title of the article. There is a third option - a mobile application, but we discard this option. Why? Well, for example, if I need to make a one-time or infrequent purchase, I won't install an application on my smartphone, it's easier to find another site. Creating an application makes sense for a large project, or for a project frequently used by clients, which will be more convenient to open through a separate application than through a mobile browser. Now, whoever you take, everyone has their own application, but, in fact, most simply do not need them.
There are two options left: responsive layout or mobile version. First, let's define what is the difference between these two methods.
Adaptive layout.
The content does not change on the site. It adjusts to the width and height of the screen. Certain parts of the content can be stretched or narrowed, arranged in a different way (they were in 3 columns - they became one), scaled, hide (but not disappear) under the button (the most common thing that is hidden under the button is the menu).
Mobile version.
It is done on a subdomain. The most common options are m..site, pda..ru / mobile /.
It is determined that the user came from a mobile device and is redirected to the mobile version with the option to switch to the full version. At the same time, the content of the site, appearance and functionality can be radically different. As a rule, this difference consists in simplifying, cutting down the site, first of all, for fast loading on mobile devices.
What is better mobile or responsive layout?
To understand this issue, consider the pros and cons of each option.
There are general pros:
correct display on mobile devices;
imprisonment for mobile devices.
Mobile version:
the ability to "cut" unnecessary functionality
Redesign the site so that the designer does not recognize his mother. This is important if the elements are located in completely different places on the mobile version than on the full version.
On the server side, use a different or slightly modified logic, which allows you to flexibly manage the functionality of the mobile version and increase its download speed
A separate domain, which will make SEOs cry, because for search engines it will be two different sites.
The need, in which case, go to the full version. For example, to get full functionality. Also, if, for example, there is a link to the mobile version on another site, then those who logged in from a computer will have to do an extra action (click “full version”) or use a version that is inconvenient for a computer.
Adaptive layout:
The site always adjusts to the current resolution. When the browser window is reduced on a computer or when the orientation is changed on a mobile device.
As a rule, with this method, all the elements are in the same places as in the full version, and for a user who knows the full version, it will not be difficult to deal with the mobile one.
The same domain, the same addresses. No redirects, no problems with sitemaps and robots. The planners are smiling.
A complex, highly loaded project will take a long time to open on a mobile device. Whether 4G or 24G, mobile internet is mobile internet.
Lack of flexibility in the choice of functionality. Everything that was on the computer will be on the mobile phone. All elements are in the same (or almost the same) places, which is not always good. To remove something, you need to hide it in css, which removes unnecessary functionality, but does not increase the loading speed. And if, on the contrary, something should be only a mobile phone, it will also always load and only hide at high resolutions.
Low resolution is not always a mobile device. Maybe just a browser window that is not open to full screen. At first glance, "so what?" But there are things that need to be displayed only on mobile devices, and in this case they will appear on the computer.
So, what should you choose a responsive layout or a mobile version?
As we can see, despite the fact that these are rather close concepts, there are differences.
In favor of what to make a choice.
If this is a highly loaded online store, or some kind of large project, then, obviously, for high performance you need to make a mobile version.
If the site is not very “heavy” or completely simple, then a responsive layout will be the best, elegant and beautiful solution.
I vote for the third option. This is still an adaptive layout, but optimized from the start, that is, initially fast loading. This is good not only for mobile users, but also for computer users.
A fast site is a good site.
It is necessary at the stage of development of technical specifications and design, to determine how the site will look on small screens. And even be ready to give up some unnecessary functionality for the sake of speed and versatility. And developers who create a website should ask themselves the question of optimizing database queries and, accordingly, reducing their number, optimizing the code on the server and client sides.
Responsive layout is the best option. And it is better to think about this even at the stage of forming the technical task. Postponed for later such a problem can come back to haunt:
- for SEO optimizers, a decrease in mobile search results and, consequently, a decrease in the number of visits from mobile devices (and this is a huge constantly increasing number of people);
- for programmers the time spent on making the site “somehow” look on smartphones, and later on adaptive re-layout or creating a mobile version
- site owners lost clients, which will go to competitors whose website on the phone performs its functions and looks correct.
The share of mobile users is growing at a steady pace: at the end of 2014, their number on the Web for the first time exceeded the number of desktop computer users. More than 10 million people access the Internet on mobile devices ONLY. And all this is happening in Russia right now.
Do you still have doubts about whether you need a mobile site? Then let's get down to business.
The purpose of this article is to introduce you to the basic terminology in the field of developing responsive websites and mobile applications and help you figure out which of the methods is right for you.
So, here are the main ways to make your services more accessible to a mobile audience.
Responsive design (eng.Adaptive / Responsive)
Many copies of the Internet have been broken on the topic of the differences between the concepts of "adaptive" and "responsive", and it is possible to write not one article, but a whole collection of essays about this. In general, the essence is this: both concepts imply the ability of the site adjust to the screens of various devices and display equally well on wide monitors as well as on tablets or mobile phones. but the concept of "responsive design" is somewhat broader and includes responsive design. Therefore, below we will call such sites adaptive.
Responsiveness is achieved with the following tools:
An example of adaptability can be found on our website site. Start shrinking the browser window and you will see how the top menu first shrinks, adjusting to the size of the window, and then completely hides in the so-called hamburger icon. You will see a similar display if you visit our site from a mobile device.


So, using responsive design, we get a website that is equally comfortable to use from any device. Of course, this is ideal, because if the site has complex functionality, it is difficult to fit it into the frame of a small mobile screen.
Despite the fact that a stripped-down version of the main site may be displayed to the user of a mobile device, the browser will load the page completely: all texts, images and scripts, so the loading time can be quite long, which is a disadvantage of responsive sites.
Separate mobile site
You don't have to make your site rubber-responsive, but create a separate version for mobile devices. You have seen examples of using this method dozens of times. It looks like this - on the main site there is a link "Go to the mobile version of the site".
This link opens a separate site with a different URL, for example, m.vk.com for Vkontakte. Also, usually the main site is configured to automatically redirect all mobile users to the mobile site.

The peculiarity of such a site is that it is maximally adapted for the convenience of working on mobile devices: the page weight is compressed, all unnecessary elements are removed. It will be much more convenient for your mobile users to get the necessary information about you and place an order.
Please note that you do not need to study programming for several months to make yourself a mobile site. Now there are many services that allow you to create a mobile version of the site in half an hour. If, for example, you want to make your business card site convenient for mobile users, then most likely such a website builder for the mobile version of the site is all you need. Also, the service of the constructor of the mobile version of the site is provided by many hosters, for detailed information you can contact the support of your hosting.
The disadvantage of a mobile site may be that you have to maintain two sites in fact and make all the important changes twice. However, you can make it so that both sites are connected from the same database, and all transformations of the main one are carried out in the mobile version, so when developing a mobile version or buying a builder, it is better to clarify this point.
Mobile app
A mobile application is not a website, but a program that is installed on a user's mobile device. This explains the main pros and cons of this approach.
The program is installed directly on the phone / tablet of your user, which means that he will be able to enter the application even without access to the Internet, as well as use the familiar interface and all the functions of his device.
At the same time, this is also a minus, since not every user wants to install an application in order to perform any minute action. Or, immediately after receiving the necessary information, the client can delete it.
Development of a mobile application is a very laborious and costly process. Websites are cross-platform, and mobile applications will have to be created separately for each platform (iOS, Android, Windows Phone).
Of course, there are special tools that simplify the creation of applications and allow you to port it to all major platforms at once, for example, Phonegap, Ionic, jQuery Mobile. But in any case, you will have to contact specialists to develop and update the application.
When do you need a mobile application? Most likely when you can offer the user something that will be useful and will interest him for a long time. For example, if you are a psychologist, you may well create an application called "Your Pocket Psychologist", which will contain articles, tests, answers to questions, and in which the user will spend some time productively.
The question is, what result do you want to get from the application. In the case of a psychologist, it will rather be an increase in customer loyalty and an easier translation of potential buyers into real ones; if they like the app, they are likely to have more confidence in the psychologist and come to him for a consultation.
If the project involves live communication between users, then both a mobile version and a mobile application would be a good option, but this will be a difficult and financially costly project.
If the project is informational, for example, a blog or a news portal, then the usual adaptive layout is more suitable for it.

To make an informed decision about whether your site needs mobility, and which option to choose, you should at least look at the web analytics data and find out how many percent of your users usually visit your site using mobile devices.
In 95% of cases, there is enough adaptability or a mobile version of the site. When creating a new site, it is worth choosing adaptability; when mobilizing an existing one, it is often faster and easier to develop an alternative mobile version.
It is impossible to cover such a serious topic in one article, but we tried to tell the main information. Feel free to ask questions in the comments, we will answer them in detail.
If you have already made a decision that your site needs to be "mobilized", write to our Support Service, and we will tell you which option is best for you, and how much it will cost.
P.S. Those who are interested in the topic of working with mobile users, on July 16, we invite you to the master class “
In order to determine which is better - a responsive design or a mobile version of the site, you first need to understand why all this is needed.
According to comscore.com, the percentage of users browsing sites from mobile devices is increasing every year:
Active subscriber base of mobile data transmission, world, million people, 2007–2015
In this regard, new algorithms for search engines were developed, and additional ranking factors were introduced: now the search results take into account how mobile-friendly the site is (convenient for viewing on mobile devices). In Google, the Mobile friendly algorithm was launched on April 21, 2015, in Yandex - “Vladivostok” on February 2, 2016.

Desktop version of the site and adapted version for mobile devices
How search engines determine if a website page is mobile-friendly:
- pages must contain content that does not require horizontal scrolling or scaling to view;
- the site should not contain elements that do not work on many mobile devices - Flash, Java applets and Silverlight plugins;
- texts on pages should be readable without scaling;
- links should be spaced enough to be easy to click on.
Most importantly, search engines rank websites unequivocally - either mobile-friendly or not.
Using the Google PageSpeed \u200b\u200bInsights tool (https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/), you can determine how fast your site's pages load, as well as their usability. PageSpeed \u200b\u200bscores can range from 0 to 100 for Page Speed \u200b\u200band User Experience, for example:
Results of 85 points and above are considered good.
If the page of the site does not meet the requirements of the service, a report is issued in the form of recommendations for eliminating problems, for example:


This service can be used for initial diagnostics and identification of problems on the website.
When is it necessary to develop a mobile or responsive version for websites?
To understand whether it is worth adapting a site for a “mobile” audience, you need to analyze it in web analytics systems (Yandex.Metrica or Google Analytics) by traffic in the context of the devices from which users visit the site. If more than 15% of the audience uses smartphones or tablets, it is recommended to develop a responsive layout or mobile version. It is important to consider the site traffic here as well. For example, for sites with a large number of visitors (from 1,000,000 and more), this bar is reduced, since such a large segment of the site's traffic cannot be neglected.
Mobile version of the site
mobile version - a separate version or a separate template adapted for display on mobile devices. It may not display all the blocks that are on the main version of the site.
A "special feature" of the mobile version: when switching to it, the URL changes in the address bar of the browser - the prefix "m." Is added to it, for example: m.example.ru.


View on a computer monitor and on a mobile device: the mobile version is different from the main one
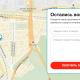
An example of a website with an adapted mobile version: http://www.lamoda.ru/ (m.lamoda.ru).
The main advantages of the mobile version of the site
- Light weight and, as a result, high download speed. This is essential for users who have low Internet access speed (GPRS or weak 3G).
- The user's choice of which version to view (mobile or main).
- Compliance with the requirements of search engines for the convenience of viewing the site on mobile devices.
Disadvantages of the mobile version
- If it is necessary to make changes to the site, they will have to be made both on the regular version of the site and on the mobile one, i.e. the volume of work doubles.
- When developing it, you often have to discard some of the content.
- Since the mobile version and the main version of the site are on different domains, it does not improve the behavioral factors of the main domain, that is, it will be a disadvantage for SEO optimization.
This is a special design of web pages in which the elements of the site change their size and position at different display resolutions. The site automatically adapts to the size of the device on which it is open, be it a PC monitor, smartphone or tablet. Thanks to this type of layout, the site will be conveniently and clearly displayed on various devices. With the use of adaptive design technologies, the functionality of the site does not suffer at all.


View on a computer monitor and on a mobile device - the adaptive version is different from the main one
An example of a site with an adaptive version: http://www.mvideo.ru/.
Benefits of responsive design for mobile
- One URL for all content.
- Flexible interface - you can customize the comfortable display of the site for any screen width.
- Responsive design meets the requirements of search engines for the convenience of viewing the site on mobile devices.
- If the site has a responsive version, then the behavioral factors become better on mobile devices, and from this the overall site performance improves. This will be a big plus for ranking in search results.
Disadvantages of responsive design for mobile devices
- The need to create separate layouts of site pages for each display resolution.
- The adaptive version, unlike the mobile one, cannot be switched to normal mode. That is, the user does not have the choice of displaying the site. The disadvantage is relevant if there are errors in the adaptive version - for example, elements are displayed incorrectly.
- The complexity of adding a new page template, because they will need to be configured to display correctly on the responsive version. If you add information to existing page templates, then there will be no display problems.
Which is better: a responsive layout for mobile devices or a mobile version of the site?
The best solution for a website is to use a responsive layout for mobile devices. Despite a number of shortcomings, a site with a responsive layout is more functional. Also, the presence of page templates implies the ease of adding content to the site, in contrast to the mobile version, in which the work on adding content is duplicated, since there are actually two different sites. A big plus is the fact that the responsive version improves the behavioral factors of the main site. This is useful in terms of promotion and usability. Based on this, we recommend making your choice in favor of a responsive layout.
This is an additional simplified version of the site, usually located on a subdomain with the prefix "m" (for example, m. Site).
As you can see from the picture, the version for phones also opens on the tablets and it is irritated and stretches in width, because the tablet is practically a very, very wide smartphone 🙂
Externally and stylistically, of course, it can be made as the main site (so that there is no feeling that you are on some other people's page): the same colors, fonts, elements. But the structure can be drastically different, and most often it is. It is unlikely that someone will choose an apartment or pick up a car for themselves via the phone, or apply for a bank loan. After all, it is inconvenient, the screen is small (compared to a laptop or computer). But finding the nearest ATMs or the address of a pizzeria is the opposite. Therefore, mobile versions are greatly simplified, without any complex calculators, huge comparison tables for two or more similar products. They remove all the most difficult and simplify access to contacts, working hours, and so on.
Benefits
- Since this is an additional version of the site, it is loaded separately (i.e. the main site is not loaded). And I repeat once again: as a rule, it is greatly simplified. Therefore, it loads quickly relatively adaptive.
- Maintaining the mobile version is quite simple: changes and improvements do not affect computers.
disadvantages
- As a designer, I will immediately express my "fairy" about tablets: the version for smartphones, stretched in width, looks terrible on them. No, well, of course, you can use it. But adaptive in this regard has run very far away.
- All this is extremely inconvenient for SEO optimization. Two addresses - the main site and the mobile version - means the content will be duplicated.