Php programming language description. Description of automation equipment. PHP is a server-side language
PHP programming language
PHP was invented by Rasmus Lerdorf at the end of 1994. The first version was released in 1995 under the name "Personal Home Pages Toolkit", then it was redesigned and called PHP / FI Version 2 (FI - Data Processing Module for Forms). Support for mSQL databases has also been added. From that moment on, volunteers began to take part in the development.
PHP usage statistics are approximate, but according to research by Netcraft, in early 2001, PHP was used on more than 5,300,000 sites worldwide. For comparison: at this time the number of IIS servers was about the same (5 million). The development of the PHP interpreter has taken the form of an organized command process, with the kernel being developed by Zend.com. At the same time, PHP is distributed freely: its latest version can be downloaded from the PHP.net website. PHP modules are shipped with the Apache server, in kits of Linux systems.
Initially, PHP stands for Preprocessor of Home Pages - home page preprocessor. It is the language of scripts embedded in HTML pages and executed on the server. For the most part, its syntax is borrowed from languages \u200b\u200bsuch as C, Perl, Java, and at the same time it adds a lot of features that these languages \u200b\u200black. To put it simply, PHP's syntax is a sensible alternative to both the strictness of C and the "infinity" of Perl.
PHP is endowed with almost a complete set of functionality that a web programmer could only dream of (before the advent of PHP). Its purpose is to enable the creation of dynamically generated web pages as quickly as possible. With good reason, we can say that learning and using PHP will be beneficial to both beginners and professional programmers.
Comparison of the programming language PHP with other programming languages \u200b\u200bfor Web applications
To answer the rationale for the choice of programming tools, PHP was compared with other programming languages \u200b\u200bfor Web applications. PHP's main competitors are JSP (Java Server Pages and Java Scriptlets), ASP.NET (Active Server Pages), Perl, Cold Fusion Server Pages.
1. Programming languages \u200b\u200bPHP and Perl
The Perl language was created by the programmer Larry Wall and stands for Practical Extraction and Report Language. It can be translated as "a language for practical data extraction and reporting." Perl is an interpreter and has been around much earlier than the Web. With the advent of the Internet, Perl has proven to be a convenient tool for creating dynamic Web pages. Perl gained widespread acceptance because it was available on every web server, since almost all of them ran under UNIX, and the only alternative was the more complex C language. Perl loses to PHP in finesse, while PHP offers functionality similar to Perl when much less redundancy and comparative simplicity of syntax. The redundancy of Perl is due to the fact that it was developed for a wide variety of applications, which could not but affect its syntax, while PHP was originally developed for the Internet. According to many users, who did not initially know either PHP or Perl, learning PHP is much easier.
2. Programming languages \u200b\u200bPHP and Java
Generally speaking, there is a distinction between Java and Java technology. The Java language is C-like languagewhich was designed as "improved C ++". Java technology includes the client and server parts, as well as access to databases, therefore it is most correct to compare Java technology with the Apache / PHP / MySQL bundle. Java technology was developed as a cross-platform technology for building enterprise-scale Web applications. The main advantages of this technology are cross-platform portability and an object-oriented language, which allows you to create complex and large applications. Disadvantages include slow execution, large memory consumption (fees for cross-platform portability), and the complexity of developing Web applications compared to PHP. Meanwhile, PHP is almost as good as Java in terms of flexibility and scalability of the created applications. Also, using Java for development is enough simple applications hardly justifiable, and when working on serious tasks Java is more expensive.
3. Programming languages \u200b\u200bPHP and ASP.NET
ASP (Active Server Pages) is a scripting language from Microsoft. If the ASP language was significantly inferior to PHP in many respects, first of all, in terms of script execution time, then with the advent of ASP.NET technology, the situation has changed. The main strength of ASP.NET lies in the ability to use all the power windows interface for developing web applications. This allows you to develop pages with a complex interface without worrying about storing, encrypting, and passing variables used in dynamic pages. ASP.NET is tightly integrated into Microsoft's new NET technology. Main feature Web application development with ASP.NET is the ability to use any programming language of the NET runtime. It can be either a modified version of Visual Basic - Visual Basic.NET, or a new C # language or a Java clone - J #. Moreover, several programming languages \u200b\u200bcan be used within a single Web application. All this makes it possible to combine programmers who know different programming languages \u200b\u200bwithin a single project. ASP.NET Web application code is compiled into the Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL), sometimes simply called IL. The device-independent IL code is cached in the Web server to improve performance, similar to Java bytecode. But unlike Java technology, which provides platform independence, NET provides development language independence. Running ASP.NET Web applications on non-Windows servers is nearly impossible. Moreover, if a Web application makes heavy use of NET components, viewing a dynamic page will only be possible on Windows and only with internet browser Explorer. Therefore, in terms of portability, PHP certainly differs from ASP.NET for the better. Another extremely important argument in favor of PHP is that it quickly fixes discovered errors. Theoretically, you can correct them yourself if you have sufficient qualifications. You can also write a letter to the developers, and with a high degree of probability, the error will be fixed in the next version. And PHP versions come out very often. Another benefit of PHP, especially for beginners, is that it is easier to use to build Web applications. Thus, when choosing between ASP.NET and PHP, you should start with the task at hand. If on the Intranet of a large corporation, most of the servers and client machines run under windows management, ASP.NET is more than justified. At the same time, PHP is more useful for developing a Web site on the Internet.
4. Programming languages \u200b\u200bPHP and ColdFusion
The ColdFusion package was developed by Allaire and is intended for the rapid development of both interactive and dynamic Web-documents by processing information obtained from a database. The downside of ColdFusion is its rather low portability. PHP runs on almost all platforms, while ColdFusion only runs on four: Win32, Solaris, HP / UX, and Linux. In addition, ColdFusion, like ASP, is a commercial development. ColdFusion is not widely used. Compared to PHP, it is more resource-demanding. The advantage of ColdFusion is a good integrated development environment and, as a result, simpler language constructs than in PHP and faster code writing. However, due to such a high-level language, some tasks are more difficult to solve in it.
5. Programming languages \u200b\u200bPHP 4.0 and PHP 5.0
The main differences lie in the implementation of the object-oriented model. PHP 4.0 was powered by Zend Engine 1.0. For PHP 5.0, Zend completely rewrote the engine and released Zend Engine 2.0, which, according to its creators, implements a "new object model". Compared to PHP 4.0, the fifth version of the language has the following features:
1. Introduced private and public (protected) members and methods of the class, as well as abstract classes and methods.
2. Introduced interfaces, while the class can implement an arbitrary list of interfaces.
3. PHP 5 also has advanced features for cloning objects. The copy constructor intended for this allows you not only to clone objects identically, but to change some of their properties.
4. Introduced constant members and class methods.
5. One of the most important innovations is the presence of destructors.
6. The good news is that PHP 5.0 introduces static class members. In PHP 4.0, if there was a need to use static members, it was necessary to use an artificial trick, which consisted of combining global variables with static methods. This resulted in classes that acted in the same way as static ones. This technique, to put it mildly, is not very good, since it caused problems associated with the use of global variables. Now in PHP 5.0, static methods can be declared explicitly using the static keyword.
7. PHP 5.0 introduces an exception handling mechanism that is not available in PHP 4.0. Thus, as a result of such innovations in the object model, PHP 5.0 has become a fully professional programming language, which allows it to be used to solve problems of any complexity.
"SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL №5"
Research work on the topic:
"Web Programming Language - PHP"
Completed: student
9 "A" class
Ryabov Artem
Teacher: A.K. Abdrazakova
INTRODUCTION …………………………………………………………………………….… ... 3
Chapter 1. Introduction to PHP and MySQL ……………………… .. …………… .. ……. ………… .5
1.1. What is PHP? …………………………………………………………………… 5
1.2. PHP Features …………………………………………………………………… .5
1.3. A Brief History of PHP ……….… ... ……………………. …………………… ... ………… 6
1.4. Why choose PHP ………………………………………………………7
1.5. What MySQL ……………………………………………………………………..7
1.6. MySQL Features ……………………………………………………………… 8
Chapter 2. PHP Usage Examples …………………………………………………… ... 9
2.1. Working with forms ………………………………………………………………… ..9
2.2. Working with MySQL (saving data in a database) ... ………………………… 11
2.3. Working with MySQL (retrieving data from the database). ………………………… 13
CONCLUSION …………………………………………………………………… .. ……… .15
BIBLIOGRAPHY ……………………………………………… ...… 16
APPENDICES ………………………………………………………………………… ... 17
Introduction
PHP is a programming language used on the web server side to dynamically generate HTML pages. This is evidenced by the decoding of its name: PHP - Personal HyperText Processor.
PHP is one of the few programming languages \u200b\u200bcreated specifically for developing web applications. Therefore, it includes all the functions necessary specifically for working on a web server, and at the same time is devoid of the redundancy inherent in many of its competitors.
A very nice feature of PHP is that its commands are included in ordinary HTML pages using special tags that make the PHP machine perform the necessary actions on the server. PHP programs do not need special CGI directories with special permissions. Moreover, on one page, you can freely alternate between "simple" HTML and PHP-code.
PHP is platform independent. PHP integrates perfectly into all popular web servers: Apacce and IIS, Zens and Netscape Enterprise Server, runs under Windows and OS / 2, MacOS and almost all UNIX-like systems. As a result, PHP works for almost all hosters that allow their own executable scripts.
A great feature of PHP is its integration with almost all modern Internet technologies. PHP supports most modern web protocols: IMAP, FTP, POP, XML, SNMP and others. PHP works great with databases. It is difficult to find a DBMS that is not supported by PHP. MySQL and MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL and Oracle, Sybase and Interbase ... The list of databases supported by PHP alone will probably take a whole screen.
PHP includes a huge number of built-in functions: processing strings and arrays, working with the file system and with HTTP, by email, date and time, Cyrillic and other national alphabets ... When I first started programming in PHP, I was simply amazed at the abundance of built-in functions! Thanks to them, many algorithms that require writing in most languages program code the size of several screens, are implemented in PHP with one command (more precisely, by calling one function).
Modern trends in the development of programming languages \u200b\u200bhave not spared PHP either. Object-oriented programming tools have been around since PHP3. And the PHP4 object model fully implements the classic concepts of object-oriented programming: inheritance, encapsulation and polymorphism.
All of the above allows without any stretch to call PHP the undisputed leader among web programming languages.
goal research - Explore and see examples of PHP scripts execution
An object research –Language PHP, Databases MySQL.
Subject of study - the functional meaning and relevance of the language.
Hypothesis research is that given language very simple, easily integrates into HTML, in combination PHP + MySQL + HTML is much superior simple HTML.Based on the hypothesis, the following tasks :
Tasks:
Explore features and capabilities pHP language;
Compare PHP and HTML functionality;
Get acquainted with MySQL databases;
Process the results obtained, draw conclusions.
The theoretical basis of the presented material is the historical data presented in reference books, material from the Internet.
Research methods: in the course of the research, description, analysis of literature on the topic, and study of some variables were used.
The practical significance of the study : this material can be used by teachers and students for later, in-depth study of the given language.
The structure and content of the work include:
Introductory part, which justifies the choice and relevance of the topic.
Chapter 1. Introduction to PHP and MySQL contains 6 sections. The first section explains what PHP is. The second describes its capabilities. The third section of the chapter describes the history of the PHP language. In the fourth, it says why it is worth choosing this particular programming language. The fifth and sixth sections are devoted to information about MySQL databases.
Chapter 2. PHP Usage Examples consists of 3 sections. The first section shows how PHP can easily process data from HTML forms. In the second, we will enter information into the database. In the third section, we will receive information from databases.
Conclusion contains the main conclusions on the topic, confirming the hypothesis of the research.
Chapter 1. An introduction to PHP and MySQL
1.1. What is PHP?
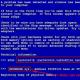
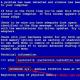
PHP is a scripting language embedded in HTML that is interpreted and executed on the server. The easiest way to show this is with an example:
|
|
After executing this script, we will receive a page in which it will be written:
Hi, I "m a PHP script! (see appendix 1)
Quite simple and useless.
The main difference from CGI scripts written in other languages, such as Perl or C, is that in CGI programs you write the output HTML code yourself, and using PHP you embed your program into the finished HTML page using the opening and closing tags (in the example).
The difference between PHP and JavaScript is that the PHP script is executed on the server, and the result of the work is transmitted to the client, while the JavaScript code is completely transferred to the client machine and only there is executed.
Internet Information Server buffs will find PHP very similar to Active Server Pages (ASP), while Java enthusiasts will say PHP is similar to Java Server Pages (JSP). All three languages \u200b\u200ballow you to place code that runs on your Web server inside HTML pages.
1.2. PHP features
In a few words - everything that can be done with CGI programs can be done in PHP. For example: process data from forms, generate dynamic pages, receive and send cookies.
In addition, PHP includes support for many databases (databases), which makes writing Web applications using a database as easy as possible.
Here is a partial list of supported databases:
| Adabas D | InterBase | Solid |
| dBase | mSQL | Sybase |
| Empress | MySQL | Velocis |
| FilePro | Oracle | Unix dbm |
| Informix | PostgreSQL |
On top of that, PHP understands the IMAP, SNMP, NNTP, POP3 and even HTTP protocols, and also has the ability to work with sockets and communicate over other protocols.
1.3. A brief history of PHP
PHP began in the fall of 1994, when Rasmus Lerdorf decided to expand the capabilities of his Home-page and write a small engine to perform simple tasks. Such an engine was ready by the beginning of 1995 and was called Personal Home Page Tools. He was not very skilled - he understood the simplest language and only a few macros.
By mid-1995, a second version appeared, called PHP / FI Version 2. The FI prefix was added from another Rasmus package that could handle forms (Form Interpritator). PHP / FI was compiled into Apache and used the standard Apache API. PHP scripts turned out to be faster than similar CGI scripts, since the server did not need to spawn a new process. PHP is close to Perl, the most popular language for writing CGI programs. Support for many well-known databases has been added (eg MySQL and Oracle). The interface to the GD - library, allowed generating images on the fly. From that moment, PHP / FI was widely used.
In late 1997, Zeev Suraski and Andi Gutmans decided to rewrite the internal engine in order to fix interpreter errors and improve the speed of script execution. Six months later, on June 6, 1998, a new version was released, which was named PHP 3. By the summer of 1999, PHP 3 was included in several commercial products. As of November 1999, according to NetCraft, PHP was used on over 1 million domains.
1.4. Why choose PHP
Web application developers need not be told that web pages are not just text and pictures. A site worthy of attention should support some level of interactivity with the user: searching for information, selling products, conferences, etc. Traditionally, all this was implemented by CGI scripts written in Perl. But CGI scripts are very poorly scalable. Each new CGI call requires the kernel to spawn a new process, which takes CPU time and wastes RAM. PHP offers another option — it runs as part of a Web server, and is thus similar to Microsoft's ASP.
I bring to your attention a quick guide to pHP language for dummies in several parts. I guarantee you will be able to write your first working PHP code after reading this series of articles (or in the process of reading). PHP is one of the easiest programming languages \u200b\u200bto learn, it is a server-side (server-side) scripting language (interpreted language).
It is used to create web projects. Can be used directly in HTML code. And although the result of the script is often displayed directly in the client's browser, PHP does not need only one browser to run. That is, you will not be able to run the index.php file directly in the browser, as you probably already did with the index.html file. PHP scripts and web pages created using PHP require a web server to run.
If you do not yet have a hosting site for your site, then I recommend experimenting with PHP scripts on a local server designed for testing projects. To organize a local server in the Windows operating system (WAMP, Windows-Apache-MySQL-PHP) packages can be useful: Denver, XAMPP, AppServ, OpenServer, etc. After installing these packages, you will receive a server already configured and ready to use, and it will be managed through the convenient menu of the program itself. Also, there are separate implementations of APACHE, MySQL and PHP for operating system Windows, but you will have to configure them yourself through the configuration files and there will be no menu with checkmarks. To start, restart and stop such a server, you can use * .bat or * .cmd batch files (batch file) with commands to start, restart or stop the APACHE and MySQL services. The third and most difficult option for a beginner is a virtual machine with the installed and configured Linux operating system (LAMP, Linux-Apache-MySQL-PHP). Ready-made images of such "virtual machines" are often found on the Internet, so you may only need to know how to configure programs like VirtualBox or VMware.
Preparing for PHP Programming for Dummies
- PHP code should be placed in the index.php file, the file itself should be placed in the root directory of the site located on the web server.

- All PHP code must be enclosed between descriptors or an abbreviated version, but the web server may not be configured to use an abbreviated version of this notation, so the first option is preferred.
- PHP code can be inserted anywhere in the HTML code.
- Commenting in PHP code is done as follows:
- To view your code, open your web browser and in address bar enter: http: //localhost/www/MyEX/index.php

Displaying data to the screen using PHP for dummies
- Outputting data to a window (client area of \u200b\u200bthe web browser) using PHP can be done using the echo statement. This operator allows you to display data different types: numbers, character strings, etc.
- Output statement syntax:
- String data is wrapped in double or single quotes... Within double quotes, the code is interpreted by PHP. Anything enclosed in single quotes is displayed without any interpretation. Example:
Example $ x code
Example $ x code

- To display more detailed information about a variable, which may be needed when debugging a program, use the var_dump () function. Its syntax is:
- One or more variable names are specified in the variable list. This function returns nothing. Example:
- Less informative than var_dump (), the function for dumping information about variables is:
- For variables of the "array" type, this function displays a list of the form index \u003d\u003e element.

PHP Variables for Dummies
- Variables are containers for storing data. The data stored in a variable is called the value of that variable.
- A variable has a name - a sequence of letters, numbers and an underscore without spaces or punctuation marks, necessarily beginning with a dollar sign ($), followed by a letter or underscore.
- The correct variable names are $ _tel, $ tmp, $ my_, $ address_234_45.
- Invalid variable names: $ 234tel, my address, $ tel: 234.
- PHP is case-sensitive with respect to variable and constant names. but keywords can be used in any case.
PHP Data Types and Data Conversions for Dummies
| Data type | Example | Description of values |
|---|---|---|
| String or character (string) | "Hi everyone" "123456" "25 rubles" |
Quoted sequence of characters |
| Integer, numeric (integer) | -234 25 0 |
A number or sequence of digits, preceded by a number sign |
| Numeric floating point (float) | 5.47 21.4 35E-3 |
A number with a fractional part (35E2 means 3500) |
| Logical (boolean) | true false |
This type has two meanings: true (true, yes), false (false, no) |
| NULL | null | This data type has one value - null |
| Array | This data type has one set of values \u200b\u200bthat can be of different types. | |
| Object | A program object defined by its properties |
- In order to find out what type of variable, you need to use the function:
- To explicitly set a type, you can use one of two ways:
PHP Constants for Dummies
- A constant is a named value that does not change during the execution of a program (script).
- Unlike variables, you cannot change the values \u200b\u200bof constants that were assigned to them when they were declared. Constants are useful for storing values \u200b\u200bthat should not change while the program is running. Constants can contain only scalar data (boolean, integer, float and string types).
- In PHP, constants are defined by the define () function. Here is its syntax:
$ name is the name of the constant.
$ value is the value of the constant.
$ case_sen - optional parameter logical type, indicating whether to case-sensitive (true) or not (false).
Define ("pi", 3.14, true); echo pi; // Prints 3.14
- You can use the defined () function to check for the existence of a constant. This function returns true if the constant is declared. Example:
Differences between constants and variables in PHP for dummies
- Constants do not have a dollar sign ($) prefix.
- Constants can only be defined using the define () function, not by assigning a value.
- Constants can be defined and accessed anywhere without regard to scope.
- Constants cannot be defined or canceled after the initial announcement.
- Constants can only have scalar values.
PHP Programming for Dummies. Part 1 was last modified: March 3rd, 2016 by Admin
This site already has articles about and is given. Now we will talk about what PHP is.
What is PHP and what can you do with it?
This easy introduction to PHP explains the basics of PHP and how you can do it. use to create rich web pages and applications... PHP is a programming language that can be used for writing web applications... A web application can be anything from a simple “contact us” form to a complete blogging system, an online store, or a forum. Yet .
PHP is a server-side language
PHP is known as server-side programming language... It means that it runs on a web server... Most web programming languages \u200b\u200bare server-side languages, but some, like JavaScript, run client-side, which means they run in a web browser.
Server-side languages \u200b\u200bgive you more flexibility because you can do things that are difficult to do with JavaScript — for example, working with files, databases, or working with images. It must be said that JavaScript has spread very quickly these days.
Server side code execution is more in a safe waythan on the client side, as JavaScript does. Because the JavaScript code is sent to the web browser, it is easy for site visitors to view and edit. Even a single page of the site is possible with ease. The server-side code remains on the web server and is not available to site visitors. PHP is a tool that resides on a web server and runs PHP scripts there.
PHP - open source software
PHP is software with open source code ... This means that anyone can access and run PHP. This helps ensure that PHP will run for a long time. PHP is free to download and use. This is the reason that many hosting providers use PHP extensively. You will find that the vast majority of web hosts support PHP.
PHP is focused on developing web applications
While many programming languages \u200b\u200bcan be used to create web applications, PHP is one of the languages \u200b\u200bspecifically designed for use on the Internet. PHP has many useful web features, such as:
- Reading and processing web forms and cookies
- Functions for creating and working with graphics
- Establishing connection with popular databases such as
- Functions for working with.
You can mix PHP code with HTML code
One of the great features of PHP is that you can include blocks of PHP code in HTML pages.
You can insulate PHP blocks with special characters... When the web server receives information about the page,
all PHP blocks are run by the PHP engine, while other parts of the page are sent "as is" to the browser.
This feature makes it easy to make regular web pages interactive. Great tool for forms with feedback and forms with similar functions.
Using PHP
You can use PHP to write almost any type of web application or script. Common PHP applications include:
After reading the article, you can consolidate your knowledge by going through a short one that is based on the material in this article. Good luck in learning PHP!
© Andrey Kukharchik
Computer newspaper
Introduction
The Internet has long been firmly entrenched in our lives. This bold statement can be proved or refuted many times, but somehow everything changes, and no one will argue with this.
Gone are the days when many users personal computers in order to save disk space, we removed the "Internet Explorer" program from all of us adored operating system, because we simply did not need it. Now even those who do not have access to the Web try not to touch this program, since the Internet formats have long since moved to other areas of our computer life. And if a modem has settled in the computer, it is simply impossible to avoid the presence of a browser, since I really want to see at least one eye, but what is there, beyond the telephone line? And when the acquaintance took place, it is no longer so easy to give up the advantages of the network. After a while, you begin to realize that you need to somehow invest yourself and your ideas and manifest yourself on the endless expanses of the Global Network. It has even become prestigious to make your own page, and even if there is little useful in it, and the counter only records your infrequent visits, what has been done can become the beginning of a serious project and change your whole life.
Traveling through the vastness global network Internet, you, of course, more than once paid attention to hyperlinks, which sometimes reach outwardly very large sizes and are simply bewildered by the presence of strange symbols. And of course, everyone paid attention to the forms that had to be filled out and received something in return. But few people think about how it all works and what it all means.
I suggest you plunge into the world of programming. This world is in many ways unlike anything, but it has its own unwritten laws and rules, its pros and cons. The world that opens before us is visible for only one more step, but this step must be mastered, and it will be much easier to go further.
PHP history
You should always start with the simplest, and now I will try to introduce you to programming in the PHP scripting language. PHP (reads pee-pee) was born in the fall of 1994, and its creator, Rasmus Lerdorf, used the language for his own purposes, in order to have an idea of \u200b\u200bthose people who visit his site and get acquainted with his resume.
According to the author, PHP was written literally in a day between business meetings. At first it was just an ordinary-looking CGI wrapper written in Perl, and it served solely for specific purposes. For reference - CGI (Common Gateway Interface) - a common gateway interface, is a standard that is designed to create HTTP server applications.
This application, called a gateway or CGI program, is launched by the server in real time. The server sends user requests to the CGI program, which processes them and returns the result of its work to the user's screen.
Thus, the visitor receives dynamic information that can change as a result of the influence of various factors. The gateway itself (CGI script) can be written in various programming languages \u200b\u200b- C / C ++, Fortran, Perl, TCL, Unix Schell, Visual Basic, Apple Script and other similar languages. But in the case of PHP, for writing it in the original version, the Perl language was chosen, as the most simple and accessible.
As a result of further exploitation, it turned out that the shell has low performance, and the author was forced to rewrite everything from scratch, but in the C language, which made it possible to increase the speed of PHP. The users of the server where the site with the first version of PHP was located asked for the same tool, and although the author did not expect that someone else would use this language, PHP quickly grew into an independent project, and at the beginning of 1995 the first known to us came out product version. The name of this first package was Personal Home Page Tools. At that time, PHP had more than modest capabilities. He had a basic code analyzer that understood several special commands, as well as various utilities for use on the home page, necessary to build useful things like a guestbook, counter, chat, statistics systems and the like. By mid-1995, the language was thoroughly revised, form processing appeared, functions for working with databases were added, and in this form the second version of the product was released.
Today PHP is a powerful cross-platform set of tools that resides on the server and is designed to handle custom code embedded in an HTML page. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to easily create dynamic sites. Files created in this way are stored and processed on the server, and when a visitor requests a document from PHP, the script is processed not by the visitor's browser, such as Java Script, but by the server, and only the results of the work are transmitted to the visitor. This is how a CGI program written in C or Perl works. But unlike CGI, PHP code can be embedded anywhere on an HTML page, which is a major advantage over CGI. And besides, the PHP language itself is very easy to learn and does not require any specific knowledge. For example, I personally had quite enough experience acquired ten years ago in computer science lessons at school, where we studied the BASIC language in the then very fashionable and expensive Yamaha. Despite such a rosy characteristic, PHP also has disadvantages. It is worth noting the rather slow (compared to CGI programs) work of PHP scripts, as well as the complexity of writing large and complex programs... One way or another, PHP remains an interpreted language, which will inevitably lead to performance degradation in the case of very large and complex programs, but, to perform simple manipulations on the site, PHP is the best choice... No wonder that by the middle of 2000 PHP was used by more than 2.5 million sites!
PHP features
Like any programming language, PHP has its own syntax. It is very similar to the syntax of C or Perl. Programmers writing in these languages \u200b\u200bwill be able to master PHP in just a few days. But even if you've never programmed before, PHP will be easy on you and provide a base to jump into more advanced languages. All commands are logical enough and the rules are simple. The syntax includes statements separated by semicolons. One of the main mistakes novice programmers make is the lack of a semicolon between statements. Fortunately, errors in PHP are displayed on the screen by default (unlike in CGI, where all errors are written to a log file), and it will not be difficult to find them with a certain care and experience. Moreover, a smart interpreter will prompt the line number where the error occurred.
For programming in PHP you need any text editorbut for convenience it should provide syntax highlighting and line numbering. I am using CuteHTML that comes with the nice FTP manager CuteFTP latest versions... The editor is very convenient, without unnecessary unnecessary functions, it is built into context menu, does not require installation and has everything you need for programming. We also need a kit for working with PHP. Typically Apache + PHP is used, although this is not required, any server is suitable, for example Microsoft's IIS. But the first option is free and has great support from documentation (including in Russian) and forums where you can find out any question.
Now let's get down to business - let's write our first script. In order for the server to know which of the files contains the PHP code, its extension (file) must be made either phtml, or php3, or php. Strictly speaking, any extension can be assigned, but I recommend that you always use phtml for compatibility reasons. Each command in PHP usually starts with ""(hereinafter, without quotes). As you remember, several commands are separated by semicolons. Anywhere in the PHP script you can put a comment, it starts with" / * ", and ends with" * / "If the comment is small and takes only one line, you can put "//" and thus easily comment out any line to its end. As usual, spaces, tabs and line feeds are simply ignored and can be used to improve the readability of PHP code.
Display and variables in PHP
PHP makes it very easy to organize the display of text on the screen. Let's look at an example script:This script can be located anywhere in the HTML document, and by itself it is not useful, as it only displays the phrase "Hello world!" But in this way we get acquainted with one of the most common PHP commands - displaying information on the user's screen. In order to give our script useful functions, let's get acquainted with variables. A variable is characterized by a name, type and value. The name can be anything and include numbers, letters of the English alphabet and allowed characters (for example, underscore or dash). By type, variables are divided into integers, floating point and symbolic. The value according to the type can be almost anything. For example, the variable a \u003d 5. This tells us that the name of the variable is a, the type is integer, the value is 5. Here are more examples of names and values:
As you can see, all variables in PHP (but not only in it) must begin with a $ character, which allows the interpreter to accurately distinguish them from PHP commands. In the first line of our script, the $ name variable is assigned the value 6, and this variable automatically becomes an integer. By the way, it is not required to describe the type of the variable in advance, as in Pascal or Visual Basic, but although the division into types is purely conditional, each variable automatically tends to use the correct type, according to the value. The second line of code sets the $ h12 variable to 4.89, which is a floating point value. The third and fourth lines of code are assigned to their variable valuesthat are character strings. Anything enclosed in quotes (including numbers) will be interpreted as a character string. If variables are not previously defined, but are used, their value is assumed to be either zero or an empty string, depending on the type.
As in any language, you can perform any arithmetic operations on variables, and this does not require the presence of a special operator, it is enough to specify the variable for the result, the equal sign and list the variables or values \u200b\u200bin natural order with the necessary arithmetic signs. Example:
The result of the script is displaying the number 4. All arithmetic operations and functions, multilevel brackets, logical operations, operations of increasing or decreasing by one, and much more are supported. In addition, it is very simple and natural to organize the comparison if - then - otherwise. To do this, PHP uses the if () () else () construction. There are various syntaxes for this operator, but this one is the main one and the most logical of all. (if) if (condition) (then) (what is in quotes is executed) (otherwise) else (what is in quotes is executed). It is not necessary to put a semicolon after the quotes, as usual between operators. But inside quotes, operators are separated from each other only through semicolons. It is allowed to nest several verification operators one into one. In this case, you need to be very careful about the number of closing quotes, since if even one is missing, the interpreter will generate a code error. Let's look at a simple example:
A true comparison uses two equal signs so that the interpreter can easily distinguish comparison from assignment. The result of the script is 95, because $ a is not equal to $ b, and the command echo $ b. $ A; (there is a dot between the variables, not an arithmetic operation sign) displays the specified variables in a row. Inequality (false) is denoted by! \u003d, All other arithmetic and logical symbols and operators are allowed (for example, or, and,\u003e,<= и т.д.).
PHP has a means of rapidly changing a variable by one in the direction of increasing or decreasing. To do this, you need to specify the name of the variable and after it, without an equal sign, two pluses or minuses in a row, respectively. For example, $ a ++; - the $ a variable will be incremented by one. Simultaneous assignment of one value to several variables is supported - $ a \u003d $ b \u003d 4 ;. Both variables will be equal to four. Here are some more examples of non-standard arithmetic operations in PHP:
File attachments in PHP
Anyone who has made at least one page on the network has encountered the problem of changing certain data on it. Of course, it is not difficult when there are several pages or one page :-), but if you have made a large site, a small addition (for example, in the menu) in hundreds of files can turn into a real nightmare! PHP solves this problem all at once by allowing you to nest one page into another. This is achieved with the REQUIRE and INCLUDE statements. These operators must be followed by the path to the file attachment in parentheses. For example INCLUDE ("text.phtml"). The difference between these operators is that REQUIRE is replaced by the contents of the specified file and can be used only once, while INCLUDE inserts and executes the contents of the specified file, which allows it to be applied multiple times, for example, in a loop. In any case, when the file is executed, the PHP interpreter (correctly speaking - parser) is in the HTML state, and to include it, the code must be enclosed in the... File attachments can only take place inside the server space available to PHP. In other words, you cannot use http: //
Quite often there are sites whose links include special characters - &,?,%. All of this could be the result of PHP's work. The fact is that if you add? Name \u003d value at the end of the link, this value will be available under the same name in the file where the link points. If multiple names need to be added, they can be separated by &. Now we can make a website that will be accessible with just one page. And this page will display all the rest of the information based on the data received from the link. The form of such a link will be something like this: http: //name.ru/index.phtml? Link \u003d 1. The unit at the end of the link is our parameter, which will be substituted in the index.phtml file. For example, like this:
... beginning of file ... ... end of file ...
Please note that the code we have written takes into account the situation when the visitor, for various reasons, specified an incorrect parameter. In this case, a pre-prepared page with an error message is displayed. If the parameter matches any of the site files, it is embedded in the code of the index.phtml file and executed. Thus, the beginning and end remain the same, and only the middle changes. And any changes do not seem as scary as they used to. After all, they need to be made only in one file, and this will be reflected on the entire site.
There is another way. Its essence lies in the fact that PHP has access to the so-called server environment variables. One of these variables is the path requested by the visitor relative to the site address. And this path becomes available to us for use. In this case, our links will look like this: http: //name.ru/index.phtml? Patch / name.phtml. The second part of the link - patch / name.phtml - will be available to us if we read the $ QUERY_STRING parameter. For example, like this: $ add \u003d $ QUERY_STRING. Now, let's change our head index.phtml file to make everything work automatically. And if the requested parameter is not specified (correctly speaking, it will be equal to an empty line), to open something, assign the $ add variable the name of the file that should be opened as the main page. Let it be the main.phtml file. Then the code will look like this:
... beginning of file ... ... end of file ...
As you can see, it's even easier. But I want to warn you right away that this method, although simpler than the first, opens the way to obtaining information about the server where the site is located with such a structure organization. An attacker or just a curious person, in the presence of certain circumstances and knowledge, can learn a lot about your server, and this opens a direct path to hacking. So be careful and don't get yourself into big trouble. You can protect yourself from such problems, but that's a completely different story.
An example of a hit counter on PHP
If you have read everything carefully, you will easily receive a start-up capital of knowledge, and it will give you the opportunity to independently study the PHP language in the future. And at the end, I suggest you get acquainted with the script code that will allow you to organize a counter of visits on any of the pages of your site. This counter will not be fully functional, since it has quite a few drawbacks, but it is quite suitable as an example of PHP application. Anywhere on your page (but only where it is needed) paste the following code:Page visitors -
In the same directory as your page, create a counter.dat file, upload it to the server and, using your FTP manager, change the attributes of this file so that it is writable. Usually you need to check the boxes on all attributes of the file. If you don't, the script will continually give an error when trying to write to a file. By the way, to prevent this from happening, it is worth putting the @ symbol in front of the command to write and open the file, it will cancel the display of the error message on the visitor's screen. When the attributes are changed, refresh your page on the server and refer to it at its address in the browser. You will see that where you inserted the PHP code, a line appears: "Page visitors -" and then the number corresponding to the number of visits. And no trace of code! It was processed on a server on the Internet, and the result of this execution was simply transmitted to the browser.
The algorithm for this script is very simple. In the first line, we assign the selected variable the name of the file where the number of visits will be stored. In the second, we open a connection to this file for reading. Then we check the success of the connection, and if the file exists and it is readable, we read a string of 10 bytes from it, which is more than enough for the counter, and close the connection to the file. We increase the counter reading by one and display its new value on the screen. At the next stage, we need to write a new counter value, and for this we reopen the connection (descriptor) with the file, but for writing, clearing the contents of the file. If it is successful, write the new counter value there and close the file descriptor. That's all.
At this point, we will consider our first acquaintance with the PHP language complete. Of course, there is still a lot of useful and interesting things left, but, unfortunately, it is impossible to cover everything at once. However, this is why smart people came up with the Network, to make the inaccessible available. There are many useful resources on the Internet on the topic of PHP, and with minimal search engine skills, you can easily find them. And I would advise you to subscribe to the PHP mailing list for everyone !, in which new articles, example scripts appear regularly once a week, there is a section of questions and answers, as well as a lot of other useful information. You can find a subscription form and subscribe at a web address.
All previous issues of the mailing list are also posted there. And at the address you can see how it all works in action. Everything that you come across on this site is made on PHP. Chat, forum, private announcements, statistics system - this is only a small part of the possibilities that PHP programming gives us.