Modern processors and motherboards. How to choose a motherboard for a new computer or upgrade? A universal technique. Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth

The question is very acute, given that professional electronics engineers recommend building a system unit around it.
The motherboard is the most important component of any computer. The stability of the entire computer as a whole depends on its quality and stable operation. Do not forget that all other components are attached to it in one way or another, and the motherboard coordinates their work. And if we compare the system unit with the house, then it is advisable to compare the motherboard with its foundation.
In total, there are three dozen parameters that can characterize this board, but this article will focus on the most significant of them that really affect the performance and stability of a computer device.

Component manufacturer.
Despite the fact that there are enough manufacturers of computer components in the world, only a few of them make decent motherboards. And so the question which company is better buying a motherboard is quite simple to answer. You should stop your choice on the following four manufacturers:
- Asus.
- AsRock (Subsidiary of Asus. The developments of this company are used with minor changes.).
- Gigabyte.
- MSI.
It is better not to pay attention to such exotic manufacturers as Zotac and Biostar, as they are inferior to the main companies both in quality and functionality. If you need to assemble a server or workstation, then you can take a closer look at Intel products. There is nothing superfluous in such cards and they are optimal for long-term and uninterrupted operation in 24/7 mode.
Important! By and large, there is no difference between the four major manufacturers, and at home the difference is completely invisible. For server and workstation the best choice will become the company's productsIntel.
Processor socket.
Each motherboard has a socket for installing a central processor called socket. This is the most important selection criterion, since only one type of processor can be installed in the selected socket.
How to choose the right processor for your motherboard? First of all, you should decide with the manufacturer of the processor. Only two companies in the world make decent processors: Intel and AMD. The sockets of these companies are incompatible in principle.
- Intel sockets.
Leading manufacturer of processors and chipsets. It holds about 75% of the market, and only new processors from AMD were able to improve the situation somewhat. The following Intel socket models are relevant:
- LGA 2066.
The newest and most modern socket of an American company. Supports the most productive processors and will be in demand for a long time. The only drawback of the motherboard on such a socket is the high price.
- LGA 2011-3.
Platform previous generation, but still the performance of such processors is more than enough to solve all household tasks.
- LGA 1151-v2.
The mass segment of processors, which perfectly combines an affordable price and acceptable performance. Ideal for the modern home computer. It should not be confused with the previous LGA 1151 platform, as their sockets are not compatible.
Important! If you need to build a mid-range computer for the home, then you should opt for a motherboard with a socketLGA 1151-v2. This is the best option in all respects.
- AMD sockets.
The Canadian manufacturer makes affordable, but not as powerful processors as Intel's eternal competitor. However, thanks to affordable price and broad opportunities AMD processors are quite popular for overclocking.
The most common sockets are:
- Socket TR4.
The most powerful processors of the company are built on this socket. Supports up to 16 (!!) cores and a four-channel memory controller. Perfect for both a highly productive home computer and a workstation.
- Socket AM3 +.
A socket for budget mothers. Poor performance and very low price. Suitable only for office computer.
- Socket AM1.
Mass segment of sockets from AMD company. Direct competitor to Intel's LGA 1151-v2. Has similar characteristics. Perfect for home assembly system unit.
Important! If you decide to build a computer based on processorsAMD then question as choose a processor for the motherboard the solution is very simple. An ideal choice would be a board with an AM1 socket.
Chipsets of motherboards.
A chipset is a chipset that provides the functionality of the motherboard as a whole. How much depends on him hard drives or video cards can be connected and how quickly they will work. Socket and chipset determine 80% of the final cost of the motherboard.
By and large, the chipsets differ from each other only in the type and number of supported interfaces. All existing chipsets can be classified into three broad groups:
- First level.
Motherboards based on this chipset can only be used in office computers or in extremely cheap entry-level system units. AMD 760G or NVidia 7025 can be classified as such chipsets from AMD. Intel has H110 or H170 (270) chipsets.
- Middle level.
Golden mean. Fully suitable for forming home system blocks. Allows you to connect as many hard drives and USB devices as you need. How to choose a motherboardAMDwith sufficient functionality? Just choose devices with a chipset and B350 or X370. For mothers on Intel processors, such chipsets would be Intel B350 or Intel Z350.
- High performance chipsets.
Maximum functionality for a lot of money. An almost unlimited number of hard drives, USB devices and at least 2 video cards can be connected to such a motherboard. Some models contain wi-Fi modules or bluetooth.
For mothers on Intel, such a chipset is X299. For AMD, maximum functionality can be obtained on AMD X399.
Important! For a computer that costs up to a thousand dollars (about 60,000 rubles), a chipset is more than enoughZ350 (Intel) orX370 (AMD).
Motherboard dimensions.
Modern motherboards differ from each other not only in functionality, but also in size. This is also worth considering when collecting computers. There are five standard sizes in total:
- E-ATX.
The largest items. Typically, this size is used for the most advanced mothers with flagship processors and elite chipsets. The size is 30.5 * 33 centimeters. An expensive, large enclosure is required for assembly.
- ATX.
Classic size, most motherboards have that. Dimensions 30.5 * 24.4 centimeters. The smartest choice for building a computer, as most cases are manufactured exactly for this size.
- Micro —ATX.
Reduced version of mother ATX. In most cases, it has reduced functionality and is created on simplified mid-range chipsets. Dimensions 24.4 * 24.4 centimeters. Considered a budget option.
- Mini —ATX.
Such a mother is intended for assembling compact systems with little or no video cards. The functionality of the chipset has been cut down. Most budget system units are built on mothers of this size. The physical size of the board is 17 * 17 centimeters.
- Mini —STX.
A very miniature printed circuit board measuring 14 * 14 centimeters. Designed specifically for creating multimedia centers and ultra-compact computers for video playback. They are used where the greatest compactness is required.
Important! ATX andMicro —ATX - the most suitable standard sizes of motherboards for a universal home computer.
Number of slots for random access memory.
In most cases, the motherboard has either 2 or 4 RAM slots. There is an extremely small group of elite mothers who boast 8 slots for memory sticks, but such devices are few and they are very expensive.
Important! It is most profitable to buy boards with 4 memory slots. This will make it possible to quickly add RAM without changing the entire device.
Rear panel connection interfaces.
A wide variety of connectors can be located on the rear panel, including such unusual ones as S / PDIF or an antenna for Wi-Fi. Modern boards are equipped with multiple USB ports, audio jacks, and a PS / 2 port for connecting a keyboard or mouse. RJ-45 is mandatory for Internet connection.
Important! NumberThere must be at least 6 USB ports on the rear panel, and 2 of them must beUSB 3.0. In addition, the presence of a port will not be superfluous.USB -C (all modern phones are equipped with it) andHDMI (it will be convenient to connect a TV or monitor).
Pay particular attention to the audio connectors. It is best if the motherboard will natively support 5.1 or 7.1 sound. This will eliminate the need to purchase an additional audio card.
Connecting hard drives (HDD and SSD).
Today, even budget motherboards have at least 4 SATA connectors, where you can connect any hard disks (including solid state) and DVD drives if still needed.
A mid-budget device may have 8-10 SATA connectors, which will not be superfluous if you plan to store a large amount of information.
Important! The connector will not be superfluousSATA Express required to connectSSD drives and allowing them to run at full speed.
Expansion board connectors.
The motherboard must have at least one PCI-x16 slot for connecting a modern video card. Several PCI-x1 slots will also come in handy, where you can connect additional sound cards, video capture cards, TV tuners and much more.
Important! If you plan to play a lot and actively play games, then you should think about purchasing a device with twoPCI -x16 connectors. This will allow you to connect two video cards at once.
Selection results.
Summarizing all of the above, we can summarize the following.
For an office computer, a motherboard with socket AMD AM3 + with an integrated video card, two lines of RAM and a minimum number of connectors and interfaces.
In the event that you need a universal home computer, then the best choice would be a board with an LGA 1151-v2 socket, with four lines of RAM and with all common interfaces.
If you want to play at maximum performance or deal with video processing, you should pay close attention to the LGA 2066 socket, which will provide maximum performance and functionality.
When assembling a PC on their own, few people think abouthow to choose a motherboard... This component, along with the power supply, does not directly affect system performance. Therefore, many users do not take into account the main nuances. In ready-made solutions presented by various assemblers (domestic and international), no one is in a hurry to pay attention to this module either. Wishing to attract a client at a low price, such computers are often equipped with budget "motherboards" equipped with a minimum set of interfaces.
How to choose a motherboard for your computer, in order to get the highest possible performance, leave a reserve of potential for the future, but at the same time not overpay - and our material will tell. So that the selection process does not cause difficulties even for a beginner who is "on you" with hardware, all the nuances are painted in stages.
Motherboard for a computer: how to choose
Stage 1: Form Factor
Standardization is a great boon in the modern world. Those times, when each manufacturer of computer equipment developed its own standards and interfaces, will seem to the modern user to be savage and hoary antiquity. For about 20 years, the PC market has been dominated by the ATX standard, which strictly describes the principles of the layout of computers, regulates the power supply schemes and determines the format of this technology.
Before, how to choose a motherboard, you need to decide: it is selected for a specific case, or it will be purchased after the choice of the board. In the latter case, there are no special restrictions, and this subtitle can be omitted.
Selection of the format taking into account the type of case
If you like a certain model of the case, or the motherboard is purchased to upgrade an existing PC, then the "tower" imposes some restrictions. Big Tower and Full Tower cases (such are some gaming models) support all motherboard formats for regular (non-server) computers. Midi Tower (in this format most home PCs are executed) are compatible with ATX motherboards, and usually there are no problems with them either.
Mini Tower, as well as HTPC and other compact computers, which are designed to save space on the desktop or act as a home multimedia center - require the use of compact motherboards. Which motherboard to choose for them depends on the manufacturer. Typically, Mini-ATX motherboards differ from full-size ones in height (28.4 cm versus 30.5 cm) and width (24.4 cm versus 20.8 cm).
How to choose a Micro-ATX motherboard
Micro-ATX motherboards are components suitable for a compact system unit, but special attention should be paid when selecting them. Often sellers mark with this designation two types that are completely different in size: Micro-ATX and Flex-ATX. Both have almost the same height (24.4 and 22.9 cm), but differ in width (24.4 versus 19.1 cm). Most flex boards are referred to by vendors as "micro", and square boards are often incompatible with small PCs! 
There is also an ITX format, which differs from ATX in a slightly different arrangement of external connectors and a smaller size.Which motherboard to choose (ITX or ATX) - depends on the case. When upgrading a media center, it is advisable to arm yourself with a ruler and measure the values \u200b\u200bby comparing them with the standards at the same "Wikipedia ", So as not to miscalculate.
Stage 2: processor socket
4 SATA ports are the minimum for a modern PC. One of them will be occupied by the system SSD, the other by the hard drive for storing files. Another slot may be required when installing an optical drive ( DVD discs gradually remain in the past, but they have not completely lost their relevance). It is advisable to leave the fourth connector in reserve, in case of an upgrade, if you need another HDD.
Stage 5: expansion slots
Almost all modern motherboards are equipped with a full-length PCI-E x16 slot for installing a video card. Only ultra-compact ITX boards can lack it, as they are designed to use a CPU with integrated graphics (for example, Intel Atom or AMD A-series).
If in the future it is planned to build a configuration of two video cards, the corresponding slots should also be 2. In this case, the MP chipset requires hardware support for SLI or CrossFire technology (depending on the manufacturer of the graphic card).
Read more about this: and
In addition to graphics cards, PCI-E slots (scaled down to x1 or x4) can be used for TV tuners, sound cards, high-speed SSDs with the appropriate interface, and other expansion cards. Although older PCI is becoming obsolete, devices on this bus are still found.

From left to right: PCI-E x16, PCI-E x1, PCI, PCI-E x16, 2 PCI and again PCI-E x16
If you plan to install a video card with a dual-slot cooling system (and this is the case for most gaming models), it is important to take into account that expansion slots adjacent to PCI-E x16 may not be available.
Stage 6: USB
USB interface in everyday life is the most demanded of all wired data transmission standards. It is used to connect keyboards, mice and other peripherals, removable storage, photo and video cameras, smartphones, tablets, webcams and many other devices. All motherboards for home PCs are equipped with USB ports, the only difference is in the supported generation of this protocol and the number of connectors. On the rear panel, you can find from 2 to 10 (and even 12) such slots, but most of them belong to the outdated generation 2.0. More modern USB 3s are blue or red (instead of black), and are in the minority.

4 USB 2.0 are black, USB 3.0 is blue
External USB ports are clearly visible in the photo, and it is not difficult to count them. Another thing is the internal connectors designed to bring ports to the front panel of the PC. And there can be from 2 to 12 and more (on specialized boards). If the PC case has USB3 jacks on the front, then beforehow to choose a motherboard, you need to make sure that there is an internal contact block on the board. And if, in addition to them, it is planned to use an additional panel installed in the drive slot, then there should be at least two USB3 pads on the MP.

2 USB3 pads on board
Stage 7: cooling and cooler compatibility
To improve heat removal from power circuits, the south bridge and other critical units, manufacturers use compact (and sometimes not so) radiators. Their presence is good, especially if experiments with overclocking are planned, or intensive use of the computer is expected. When choosing, preference should be given to models with refrigerated elements.
There are also cases when the benefit in the form of additional radiators turns into unpleasant nuances. If a massive tower cooler is installed on the PC, like the Noctua NH-D14, then the standard MP cooling system (in particular, its protruding elements) may interfere with the installation of the radiator. The same goes for video cards or memory sticks on tightly packed Flex-ATX boards. 
Before, how to choose a motherboard, it is worth considering the need for additional cooling. Cases equipped with lighting, transparent walls and other modding elements are often equipped with auxiliary fans. They require connection to 3-pin connectors on the board, so if fans are needed, there should be a supply of 2-4 such connectors on the MP.

On-board fan connector
Which motherboard to choose in 2016
The question is which motherboard to choose in 2016 year, cannot have a definite answer in principle. It is highly individual, and the choice is determined based on the needs of a particular user. For a gaming PC, it will be one, for an office - another, for a multimedia - the third. It can only be noted in general terms what should bemotherboard how to choose it to fit your budget and tasks, so as not to miscalculate.
- Don't chase cheapness. Saving several hundred rubles at the cost of abandoning the necessary functions is an irrational choice. It is advisable to decide on all the described parameters (socket, memory type and number of slots, list of interfaces), and only then - from the options that are suitable according to the criteria, look for an acceptable one for the budget.
- For a new PC - functionality first, and then dimensions. When assembling a new PC, you need to immediately select the optimal motherboard option, and only then look for a compatible case. Attempting to build a gaming system on the chassis of a compact media center will result in low reliability of such an assembly (due to the cramped layout and constant overheating).
- You shouldn't overpay either.Choosing a geek-friendly motherboard with Game, Ultra, Top, Super, Ultimate, etc. consoles for a multimedia or office PC is just as irrational as buying a cheap Flex -ATX MP under Intel Core i7-6700k, which is planned to be overclocked. The performance gain, if it does appear, is at the level of a couple of percent, and money will be paid for unused functionality, such as 3 PCI-E x16 slots or advanced CPU overclocking options.
Which motherboard to choose: A selection of 10 models
To make choosing a motherboard easier, we have collected for you a number of good motherboards for specific purposes:
For gaming PC you should consider full-size ATX boards equipped with full functionality. If the budget is not limited for assembling on Intel, you can choose Gigabyte GA-X99-UD4 (for processors for socket 2011) or MSI Z170A GAMING M7 (1151). If the amount is limited, the GIGABYTE GA-B150-HD3 DDR3 is suitable for an inexpensive gaming PC.
On AMD, if performance is the most important thing, you should look towards ASUS SABERTOOTH 990FX R2.0. If you want to save money without losing quality - GIGABYTE GA-970A-UD3P. Both boards are socket AM3 + and support FX series processors. But you shouldn't ignore FM2 +, the top APU models for which also claim to be gaming. For A-series processors, the best choice is the GIGABYTE GA-F2A88X-D3H.
For office PCgaming experience is not as important as accessibility, stability and silence. Therefore, Micro-ATX and Flex-ATX motherboards will become the best choice here, since the rule “the fewer nodes in the system, the higher its reliability” is also relevant here. For an Intel office computer, the best choice of motherboard is MSI H170M PRO-VDH D3. Of its "trump cards" are 4 USB3 ports on the rear panel, support for the latest core processors 6000 series, as well as 4 slots for memory and the presence of all three (VGA, DVI and HDMI) connectors for connecting a monitor. On AMD, the motherboard on the FM2 + socket ASUS A88XM-A, which has similar capabilities, will be a good choice for an office.
Multimedia PC is often used in conjunction with TV and / or home theater systems, therefore it requires a compact body. To avoid noise, you need to use energy efficient components that do not require powerful cooling. On Intel for this purpose,
How to choose the right motherboard and what to look for when buying.
Motherboard (MP) Is the biggest and most important part in a computer. Much depends on its selection. When replacing the MP, its dimensions must be taken into account.
Sometimes you need to select a video card for the MP and the processor. This requires some knowledge. This article will help you learn more about how to select a motherboard.
Elements of the motherboard
MP consists of: chipset, socket, slots, etc. Depending on the purpose of the MP, different components are used.
For different purposes, they use excellent motherboard models (for example, MP for should be much more powerful, and have a good network card and.
This level is not required for simple work. This difference determines the cost of the motherboard).
To choose the right motherboard
It is not recommended to put a powerful processor on a cheap MP (the motherboard simply cannot withstand such a load for a long time and will have to be changed). It works and vice versa - a weak processor does not need a powerful MP \u200b\u200b- this is wasted money.
MP should be chosen only after you have chosen all the components for your own (the class of the motherboard and the types of connectors for connection depend on the components).
Let's consider in more detail the elements of the MT.
Socket
This is a connector on the motherboard for connecting to the processor. It is of two types: nested or slotted.

The shape of the socket depends on the processor type. Currently, processors are produced by two companies: AMD and Intel. Current AMD sockets: FM2, FM2 +, AM3, AM3 +. Intel denotes sockets with numeric values \u200b\u200b- 1150, 1155, 2011.
Differences between AMD and Intel processors:
- Various number and type of contacts;
- Different distances for mounting coolers;
- Different sizes of socket connectors;
- availability of controllers;
- Integrated support in the graphics processor;
- Various connectors for system buses (the system bus is the total number of lines for transmission of all types of signals - addresses and control data - between the processor and other devices in your machine)
- Different types of processors
- Different number of USB ports and their types. For example, the number of ports USB0 and USB 3.0 (They differ in data transfer speed. USB 3.0 transfers information much faster)
- Differ in the amount of cache memory.
- Processors different manufacturers differ in size.
- MPs from different manufacturers support different technologies and differ in performance parameters.
The reliability of AMD and Intel is approximately the same. The products of both companies meet the requirements of the US Department of Defense: 10 years of normal operation.
There is always a defect rate, but the purchase guarantee evens out it.
Processors from different companies with the same characteristics cannot be installed on the same motherboard.
How to determine the socket type
It is important to know the manufacturer's firm. This data can be found:
1 According to the documents. When purchasing an MP, the documents contain information about the manufacturer, characteristics, safety, operation, etc. Usually a socket is denoted by the letter "S", or by the word "Socket" with information about it.
2 By number. You can find the name and number of the socket near the socket for the processor on the MP. You need to remove the side panel of the computer and the cooler. You can find the socket number on the Internet on the official website, in the catalog.
3 Compare... If no socket data is available, you can compare the processor socket and socket number.
4 With the help of the Everest program. The program scans and outputs data computer system on the screen. Its interface is similar to a conductor (it forms information like a conductor)
To find out the scan results, you need to open the program and search through and DMI. Find the folder with processors and select the one of interest. Find "socket type" in the last folder, there will be information about the socket.
The CPU-Z program on the title page recognizes the data immediately. Plus this - ease of use and speed, socket number, and processor socket.

The socket type is not difficult to determine.
Chipset
Chipset - a block of microcircuits (from the English. Chip set - a set of chips). Each MP has a built-in processor, which is responsible for managing all components connected to the MP and their well-coordinated work. This processor is called a chipset.
In older models of MP microcircuits chipsets are divided into two blocks — north and south bridge... The North Bridge provides the processor with RAM (RAM controller) and a video card (PCI-E x16 controller).
South - is responsible for communication of the processor with: hard drives, optical drives, expansion cards, etc. via controllers SATA, IDE, PCI-E x1, PCI, USB, sound.
In modern models north bridge is under the processor, and the southern one remains on an open surface. This improves productivity.

There is a difference in the performance of the processor and the chipset. The system will operate at the minimum performance of one of the devices.
For example, if the processor is weak, then its indicators will determine the parameters of the system and vice versa.
The main processor manufacturers are the same two companies: AMD and Intel.
To choose a chipset, you need to decide on its purpose. For home / office use, Intel (with an integrated graphics card) or AMD (with an integrated core) chipset is suitable.
When working in graphics editors or for gamers, choose devices with a discrete card.
Intel chipsets are marked with a number after a letter, this is a performance indicator. There are 3 types of this parameter: X (maximum), P (for those who want to upgrade their computer in the future), G (home / office version).
The new socket 1155 has changed the marking: H (for ordinary users) and Z (according to the characteristics, this is P + H).
AMD chipsets have different notation systems. If only numbers are indicated, this is a budget product. G or V are talking about the built-in video core.
X or GX indicates incomplete support for multiple video cards. FX can support multiple graphics cards.
Intel Chipsets
Current Intel chipset representatives:
- H270 / B250 - suitable for simple tasks, multifunctional and gaming computers
- Q270 - suitable for network companies
- Z270 - suitable for powerful graphics editors and gamers
- X299 / X99 - suitable for very powerful graphics editors
Most computers can be supplied with H270 and B250 motherboards. The functionality of the Q270 is excellent, with the ability to support special security options and remote control (ordinary users will not need this).
The Z270's capabilities allow you to change the processor multiplier (with the “K” index). This chipset supports memory above 2400 MHz (not available for other chipsets).
In addition, the Z270 chipset is in demand in powerful gaming PCs with support for multiple video cards due to the presence of more PCI-E lanes.
Motherboards based on X99 / X299 chipsets are required only for ultra-powerful and expensive professional computers with processors on sockets 2011-3 / 2066.
AMD Chipsets
Current AMD chipsets include:
- A320 - suitable for simple tasks, multifunctional and gaming computers
- B350 - suitable for graphics editors and gamers
- X370 is suitable for enthusiasts.
You can't overclock the processor on the A320 chipset, but the capabilities of the B350 allow it. In addition to the basic functionality, the X370 has a larger number of PCI-E lines (for mounting several video cards)
VIDEO: AMD. Choosing a motherboard for Ryzen
AMD B450. Choosing a motherboard for Ryzen
Slots
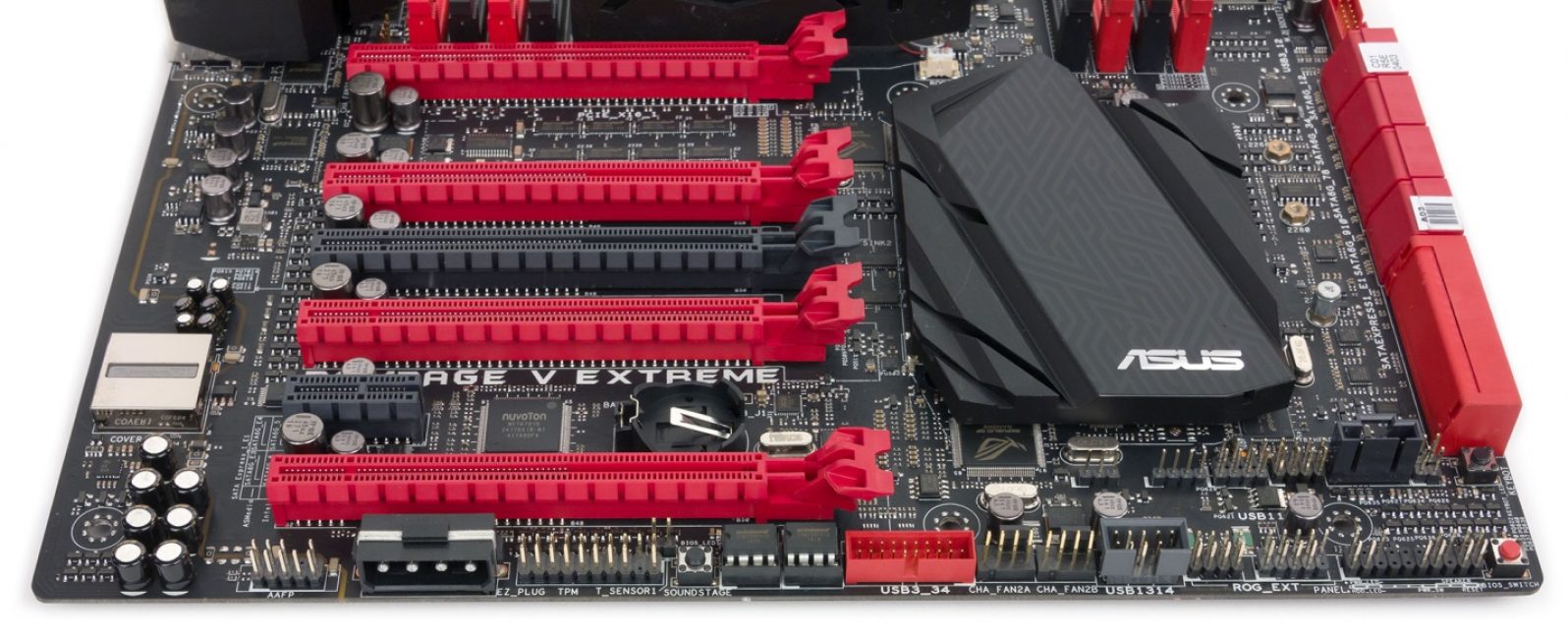
Slots are connectors on the MP. They allow connecting additional boards (expansion cards) to them. DDR5 is the most current slot (the numbers at the end indicate the production period).
There are two or more RAM slots per motherboard (but rarely more than four). To increase the RAM, one slot is replaced with another, with a higher RAM.
Video card slots are of two types (different in bandwidth): AGP and PCI Express... The most commonly used slot is PCIe x16.
Bigger slot bandwidth provides better performance. It is worth knowing that there is no difference in everyday use.
Special purpose motherboards may not have video slots. Their capabilities are limited and not suitable for home PCs.
There are different connectors for different processor slots. There are slots for mounts and other functions (for example, a slot for a motherboard expansion). There can be four slots for SATA3 hard drives.
Video connectors
The video connector is an important element in a motherboard. The possibility and convenience of connection depends on it.
To connect monitors on video cards, VGA and DVI connectors are installed. The quality of the video signal and the price of the video card depend on the type of connector.

The MP has built-in connectors for an audio system. For ordinary speakers, no load, the budget version of the ALC8xx codecs is suitable. ALC1150 connector for higher quality codec.
On expensive motherboards for games, codecs are installed with high quality sound. Three codecs are enough to connect speakers with 2.0 and 2.1 audio systems.
For multichannel acoustics, five to six audio jacks with a 5.1 and 7.1 system are suitable.
To connect a high quality audio system, you need optical output with a digital Hi-Fi system.

Modern motherboards come with a built-in network card. You also need to have a router that, if it fails, is able to protect the connection. The Rj-45 connector is shown in the figure below.

Cheap options network card indicated by the manufacturer's name Realtek. Professional referrals require Killer or Intel.
A good network card does not guarantee that there will be no network outages. Problems often occur due to poor signal quality.
Built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Some PCs are equipped with connectors for bluetooth and Wi-Fi (budget options without such details). Consider this when choosing. But they can be installed additionally.

In order not to overheat the MP, fans (coolers) are placed on the board. There are no or few coolers on cheap motherboards. Under heavy loads, the MP systems are provided with additional coolers.
An expensive motherboard does not guarantee high performance.
- 1. Interaction of the motherboard and processor
- 2. Choosing Socket "a
- 3. Bus frequency
- 4. Chipset
- 5. Manufacturers
- 6. "Gaming" or "non-gaming" board
- 7. Memory
- 8. Board Form Factor
- 9. Number of interfaces and connectors
- 10. Overclocking the processor
The motherboard is the connecting link of all other computer devices, and therefore the question of how to choose the right motherboard is far from idle. The stability of the PC and its durability depend on the choice of the motherboard, and we do not want to find ourselves in a situation of the need for frequent, expensive hardware selections and updates, right?
In this material, we will tell you what motherboards are, what parameters you should pay attention to in the first place, how to choose a motherboard so that it fits the processor, and so on. First of all, you should ask yourself the question: in which PC the motherboard will be located - office, gaming or with mixed purposes (home).
Interaction between motherboard and processor
First of all, we must decide on the architecture of our future PC, namely, decide whether we will build our entire system based on AMD or Intel.

Socket selection
Socket is a type of connector in the motherboard corresponding to the processor connector, it is he who divides all existing boards into two large categories:
- Sockets starting with AM, FM, and S support AMD processors;
- Sockets starting with LGA have support for Intel processors.
Thus, we understand that the choice of a motherboard and a processor must occur simultaneously, and if you plan to use a motherboard for more than one processor generation, you will be forced to remain true to the previous choice of the processor manufacturer. It is also worth noting that a motherboard can be equipped with more than one socket (but of the same type), but such solutions are usually preferred for creating servers, rather than PCs for personal use.
Bus frequency

In this paragraph, we are talking about the total bandwidth of the device, the higher the frequency, the higher the system performance, everything is obvious here. As a reminder, the processor bus frequency must also match the motherboard bus frequency, otherwise you will be wasting your money. Find the devices that will show the best performance when working in tandem.
Chipset
Everything is simple here, the chipset, also known as the north bridge, is a set of microcircuits contained on the motherboard and acting as a connecting link between connected devices. The most popular manufacturers include the aforementioned AMD and Intel, as well as ATI and NVIDIA, well-known for the production of video cards.

The main modern Intel chipsets include:
- B250 / H270 - for office, multimedia and gaming PCs;
- Q270 - for the corporate sector;
- Z270 - for powerful gaming and professional PCs;
- X99 / X299 - for very powerful professional PCs.
The main modern AMD chipsets include:
- A320 - for office and multimedia PCs;
- B350 - for gaming and professional PCs;
- The X370 is for the enthusiast.
These chipsets have a lot of differences, but in the end we are only interested in their intended use. If we are looking for a motherboard for a gaming computer, then we stop at the Z270 and B350, and so on. Knowing the final purpose of the computer being assembled will not be difficult even for a beginner to choose a motherboard.
Manufacturers
This point is important if you decide to choose a motherboard. The most expensive and most relevant in the high price segment are motherboards from ASUS. If we look through the prism of price / quality, especially if we are looking for a motherboard for games, then we should pay attention to the MSI brand. In a more customer-loyal segment, motherboards from Gigabyte and ASRock look good.

There are less eminent manufacturers on the motherboard market and their name is legion, but such fierce battles do not flare up around motherboards as around processors or video cards, and therefore you should not overpay solely for the name, all the more unsuccessful models are found among the headliners of the market. In any case, it is worth remembering that when asked how to choose a motherboard, the answer should not begin with the manufacturer's name - it is secondary.
"Gaming" or "non-gaming" board
In fact, the motherboard is not responsible for performance in resource-intensive applications like demanding games, so this concept is very ephemeral. If you insert four strips of RAM into an expensive board and repeat this process with a cheaper one, the result will not change.
 You have to pay for the appearance
You have to pay for the appearance The only difference is the card's potential when overclocking the processor; here you should take a careful look at the board's power supply, cooling, voltage stability during overclocking, and other secondary characteristics. In general, a few words will be said about this in the conclusion.
Memory
The number of slots depends on the form factor of the motherboard, so don't expect to fit more than two strips into a compact format motherboard. Full-size motherboards can handle four slots, and sometimes more. The current type of memory at the moment is DDR4, but they also differ in frequency. True, we do not recommend chasing beautiful numbers above 3000 MHz for now, the price growth is exponential, but the performance gain is not so great

These are not all the characteristics that distinguish good pay from weak, but there will be enough of them not to get into an unpleasant situation after the purchase.
Board Form Factor
The dimensions of the board directly affect the dimensions of your computer case, and, accordingly, the space it occupies, so there is no point in taking the largest format - it will not necessarily be the most productive, but it will certainly be the most bulky.

Let's take a closer look at the options available:
E-ATX - size 305x330 mm. These boards are designed for the LGA 2011-3 connector and, as can be seen from the dimensions, can become a headache in terms of ergonomics. They are designed for top-end processors and are equipped with the most efficient cooling and power elements. If the occupied space is not a headache for you, you can safely give them your preference.

Standard-ATX - 305x244mm. Perhaps the most widely presented format on the market, with it you will not have any problems with compatibility with other devices, but, as before, the board is rather bulky and not suitable for compact solutions.

Micro-ATX - 244x244 mm. The reduction in board height is achieved by reducing the PCI-e slots. If earlier this form factor was perceived as a budget analogue of larger motherboards, then with the development of electronics it became able to implement all the functionality of its older brothers.
Mini-iTX - 170 × 170 mm - an option for those who like to replace the standard computer case with something compact and stylized as a multimedia player.

Mini-STX - 140 × 140 mm. It already uses memory modules from external laptops and external power supplies. You can experiment with assembling a PC based on this board, but most likely you will lose in performance and overpay.
Number of interfaces and connectors
Often, buyers choose a board based on the name of the manufacturer or the mythical term “gaming”, but when they come home they find that they simply cannot connect a particular device to it. So that such an incident does not happen to you, we will try to briefly review all the external interfaces necessary for the motherboard.

First, you need to decide how many USB outputs you need on the rear panel to connect peripherals... Do not chase the number, but a reasonable 4-6 ports should be present. It is advisable that a couple of them comply with the 3.0 standard, then you will not have the hassle of connecting portable hard drives. The 3.1 format is slowly entering our life - it would be nice to look beyond the event horizon and attend to its presence.
SATA is another necessary connector, high-speed SSDs work with this interface, since this connector is an integral part of any, even the most budget motherboard. 
Advice from my own experience - be sure to consider the wi-Fi adapter... A router is already installed in almost every home and it is much easier to purchase a suitable board than to take the time-consuming process of laying a cable to your computer and spoil the appearance of the room.
If you are an audiophile and sound quality is important to you, pay attention to whether the integrated sound card supports 5.1 and 7.1 systems, or immediately ask to add a suitable discrete sound card to your motherboard.
PCI-express slots and their location are not so critical for gamers who choose one top-end card, but if you are pursuing other goals and want to use SLI / Crossfire technologies, then take a look at the number of ports and the comfort of their location - it will not be superfluous.
Overclocking the processor
If your motherboard is the basis for overclocking the processor, then you need to immediately inquire about the previous experience of the owners of this motherboard in order to achieve maximum results and increase performance as much as possible. If you are looking for an "overlocker" card, do not shy away from reviews from reputable experts. If the same card from time to time shows decent performance in this difficult matter, it is likely that it is the answer to your question of how to choose a motherboard for your computer.
I hope our article on the tricky issue of choosing a motherboard helped you, and you will never again become a victim of the cunning of sellers or your own ignorance of the issue. Patience in analyzing the saturated motherboard market and good luck with your purchase.