How to make full use of RAM. The memory is reserved by a video card or other equipment. Reset BIOS settings
After upgrading to Windows 10, many users started complaining about the problem of using an incomplete amount of RAM. For example, let's take a case from the Microsoft forum. Installing 6GB of RAM in Windows 10 32 only showed 3.92GB. The entire amount of RAM was inaccessible, or rather, the system simply did not see it. In some cases, reinstalling the RAM strips in places and cleaning the contacts helped to solve this problem. However, in a number of cases, it was not possible to solve this problem.
Ways to customize the display of all RAM on Windows 10
If you are faced with a situation where not all RAM is available on Windows 10 and you have not swapped the modules, you should follow these steps:
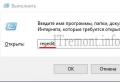
- Press "Win + R" and enter "msconfig".
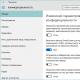
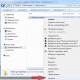
- The System Configuration window will open. Go to the "Download" tab. Click on the "Advanced options" button.

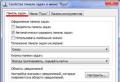
- A small window will open. Here you need to uncheck "Maximum memory".

- After saving the changes, you need to restart your computer and see how much memory is used.
If Windows 10 does not see the full amount of RAM, you should remove the strips from the slots and swap them. We also recommend cleaning the contacts of the RAM modules. To do this, you should take a rubber band and carefully wipe the dirt off the contacts.

If you insert the modules incorrectly, the post will pass when the PC boots. You will need to return the modules to their places and restart the computer. After windows boot 10 32 bit, you need to download the MemTest86 program and check the operability of the RAM.
If everything is in order with the modules, but Windows does not see all rAMmaybe you have used old version motherboard firmware and you need to update the BIOS, as well as check some of its parameters.
- The first bIOS parameter, which is responsible for the stable operation of RAM, is memory reallocation. AT different versions firmware, this section may be called differently (Memory Hole Remapping, H / W DRAM Over 4GB Remapping, Hardware Memory Hole). Therefore, it is worthwhile to study in detail the instructions for the board or find a description for the version of the BIOS used.
The memory reallocation function transfers the address blocks used by expansion cards to the address space beyond 4 GB. Thus, it is possible to increase the amount of RAM (otherwise Windows 10 will see 3-3.5 GB). To fully support such a volume, you need to use 64 bit processors and 64th bit versions OS (or server versions of 32-bit operating systems that allow PAE physical address expansion). If the amount of RAM is less, be sure to turn off this option (Disabled), as RAM problems may occur. Enabling memory reallocation - the Enabled value.

- Memory options for AGP video aperture are the amount of memory that the system shares with the video adapter. It is needed to display textures and render images. This amount of memory may not be used by the system if it is blocked by the video adapter. There is only one way to enable it: boot into BIOS, select AGP Aperture size. The default values \u200b\u200bare 32 MB, 64 MB, 128 MB, and Auto. We look at how much memory the video card has and set the desired value by value. This is often 128 MB. However, you can try each parameter to see which one gives the best result.

After making all changes to bIOS settings you need to boot into Windows and check if the entire amount of RAM is visible. If the system still does not see the RAM, it is worth trying to insert other modules into the slot. Perhaps the old RAM strips are out of order or have defects.
For information on why the system does not see all the RAM and how to fix it, see the video:
Updated: 13.04.2019 Published: 15.06.2018
Description
The system detects less RAM than is installed in the computer.
Or not all memory is available to the system:
Also, not all of its volume can be determined in the BIOS (more often, only half).
Cause
- Part of the memory is taken up by the built-in video card.
- Edition or bitness limit of the operating system.
- Software limitation.
- System memory reservation.
- Defective RAM.
- Processor limitation.
- BIOS error or the need to update it.
- The maximum volume limit that the motherboard supports.
- The motherboard does not support one of the memory modules.
Decision
1. Using the built-in video card
This problem is characterized by insignificant memory allocation for the video adapter. In this case, we will observe a slight decrease available memory, eg:
If we want the built-in video card to consume less memory, go to BIOS / UEFI and find one of the parameters:
- Share Memory Size
- Onboard VGA Frame Buffer
- Display Cache Window Size
- On-Chip Video Window Size
- Onboard Video Memory Size
- Internal Graphic Mode Select
- Integrated Graphics Share Memory
* in different versions of BIOS, they can be called differently. It is also possible that other parameters can be used - in this case, you need to study the documentation for motherboard or use a search engine.
After we change the amount of memory reserved for the video systems needed:
2. Operating system limits
Different editions windows systems have a limit on the maximum used memory space.
a) All 32-bit versions can use a maximum of 3.25 GB of RAM. This architectural limitation is the limit that a 32-bit system is capable of. The picture will be something like this:
To use more than 3 GB of memory, you need to reinstall the system to the 64-bit version.
b) Windows editions also have limitations. For example, Windows 10 Home 64 bits will allow you to use 128 GB, and Windows 10 Pro x64 - 512 GB. With Windows 7, the situation is worse - the home basic edition will only allow you to use 8 GB, and the initial one, only 2 GB.
More details in the tables:
| OS | Limit, GB | |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit | 64-bit | |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 | 128 |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 | 512 |
| Windows 8 | 4 | 128 |
| Windows 8 Enterprise | 2 | 512 |
| Windows 8 Professional | 4 | 512 |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 | 2 |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 | 8 |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 | 16 |
| Windows 7 Professional | 4 | 192 |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 4 | 192 |
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 4 | 192 |
If our problem is related to the revision limit, we need to update the system or reinstall it.
3. Software limitation
The limitation can be set in the system. To remove it, open the command line and enter the command msconfig - the "System Configuration" window will open (you can also use windows search by window name).
In the window that opens, go to the tab and click on Extra options:

We check that the box is not checked Maximum memory:
4. Setting up the basic I / O system
In order for the computer to use all the memory, in some cases, it may be necessary to configure the BIOS / UEFI:
5. The maximum volume that the motherboard supports
It is necessary to check what the maximum volume can be seen by the motherboard itself. To do this, you should use the instructions - it comes in the kit, and you can also download it on the manufacturer's website. Also, similar information can be found on some online stores:

6. Defective memory module
In the event of a memory failure, the system and the BIOS will not display all of its volume (usually only half). For example, if 16 GB is inserted into the computer (2 strips of 8 GB each), we will see only 8.
In this case, you can try to pull out and reinsert the memory sticks (you can blow them a little from dust). Also, the planks can be swapped. You can also try cleaning the contacts (a regular eraser will do). Some laptops or all-in-ones have a separate plug, opening which you can get to the memory modules, otherwise you need to disassemble the computer completely.
If this does not help, we perform a memory test. In the case when the test also shows part of the memory, we try to pull out both strips and insert them one by one - if the computer does not turn on with one of them, this faulty strip must be replaced, if the computer starts up with all the strips, perhaps we are dealing with a problem BIOS (step below).
7. Processor limitations
Each processor has its own limit to support the maximum amount of RAM. You need to go to the developer's official website and check the maximum volume supported by our processor.

8. Installing the driver for the chipset
Updating or reinstalling the driver may also help resolve the issue. To do this, we determine the manufacturer and model of the motherboard, go to the manufacturer's website, find the page specific model and download the driver for the chipset. Install the downloaded driver and restart your computer.
Also, the driver can be installed in a semi-automatic mode using the DriverHub program.
9. Problem with BIOS / UEFI
Since BIOS / UEFI is responsible for collecting information about the computer, the problem may occur at the initial stage of turning on the PC.
First, let's try to reset the settings. To do this, disconnect the computer from the power source and take out the battery for 20 minutes (you can try it for the first time, seconds, for 10). If this does not help, update the BIOS.
10. Support for the module from the motherboard
If the memory was purchased in addition, and it differs from the second strip, you need to make sure that the motherboard supports the new module.
This can be done on the official website of the motherboard manufacturer - go to the support section and find the compatibility sheet. Find the purchased memory among the list of equipment.
11. Windows license limitation
The systems that come with computers use a strict licensing policy that restricts hardware replacement. This can lead to a situation where when adding memory, it will not be recognized as a whole.
In this case, you need to reinstall the system. In this case, a simple reinstallation over the existing system will not help - only full formatting system partition with the installation of a new Windows.
12. Rearranging memory modules
Sometimes, rearranging memory modules by sisters helps. We just disassemble the computer, take out the modules and swap them.
13. Cleaning modules with an eraser
If the problem appeared by itself, you can try to remove the memory modules from the motherboard and clean their contacts with an eraser. Then we blow through the connectors on the motherboard and insert the memory into place.
In this article we will figure out how to remove the 4 GB memory limitation on 32 bit versions of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, and use all the RAM available on the computer.
Most windows users convinced that 32 bit Microsoft OS does not support more than 4GB of RAM... Thus, the maximum memory available in Windows 8 / 8.1 x86 is 4 GB. And taking into account the fact that Windows reserves a part of the memory for its own needs and requirements peripherals) most often for a video card), end user usually about 3-3.5 GB of memory are available for use.
At first glance, everything is logical - the addressing limit for a 32-bit address bus is the same 4 GB. In all official microsoft documents specifies exactly this maximum memory size supported in all client versions of the x86 system. Although Microsoft is actually a little misleading.
What is PAE and why is it needed
PAE (Physical Address Extension - extension of physical addressing) - this option x86 processor, allowing it to access to more than 4 GB of physical memory... We will not go deep into the technical details of PAE technology, just note that this technology has been supported by all processors and directly in Windows OS for quite some time.
So for example the 32 bit version Windows Serverrunning on an x86 processor can use PAE to access the entire system RAM (up to 64GB or up to 128GB depending on processor generation).
Moreover, support for PAE mode in the Windows kernel has been available since Windows XP. It's just that by default PAE is available only in server operating systems, and in client Windows operating systems, although this mode is available, it is disabled.
Note... PAE can only be used on 32-bit versions of Windows running on x86-compatible processors.
Limitations of PAE Mode
- PAE does not expand the virtual address space of each process. Each process running on a 32 bit system is still limited to 4 GB of address space.
Advice... PAE will not help increase the amount of memory available for a resource-intensive application (such as a graphics or video editor). If there is such a need, it is better to upgrade to a 64-bit OS.
- When using PAE, a slight decrease in system performance should be noted due to a decrease in the speed of access to memory, caused by the overhead of switching mapped pages in memory
- Some device drivers may not work correctly in a 36-bit address space.
So, we can conclude that the upper limit of available physical memory in 32-bit versions of Windows is programmatically limited at the OS kernel level. And if there is software restriction, that means it can be bypassed! How to enable PAE mode in 32 bit Windows 8.1 and use all available RAM.
Patch enabling PAE to use all RAM on Windows 8 / 8.1 x86
Enable PAE Mode in Windows 8 (Windows 8.1) regular means will not work (for this you have to manually edit the kernel file ntoskrnl.exe and re-sign it in a HEX editor). The easiest way is to use a ready-made patch PatchPae2which is written by the enthusiast Wen Jia Liu. You can download the patch PatchPae2. (the archive contains the patcher itself - PatchPae2.exe, its source codes and necessary instructions).
The patch is a small utility command line, which allows you to modify the kernel files of 32-bit versions of Windows in order to activate PAE mode, which allows you to use more than 4 GB of RAM (up to 128 GB of memory).
PatchPae2 will work with the following operating systems:
- Windows Vista SP2
- Windows 7 / Windows 7 SP1
- Windows 8 / Windows 8.1
Note... Before installing a patch, it is recommended to disable optimizers and RAM drivers in order to prevent conflicts. They can be activated after applying the patch and booting the system in PAE mode.
Installing PAE - patch in Windows 8 / 8.1
Attention. This instruction can only be used for 32-bit versions of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, for previous Microsoft OS the procedure is slightly different! Be careful!

Note. At any time, the user, after rebooting, can switch from PAE mode to normal mode in the boot menu, or vice versa.
Important! After installing the patch, you need to be especially careful when installing updates windows security... Because some windows updates sometimes they also contain updates for the kernel, after installing them, the PAE kernel must also be updated: PatchPae2.exe -type kernel -o ntoskrnx.exe ntoskrnl.exe
In addition, the problems described and may occur.
Removing the PAE patch
To remove the PAE patch from the system, you must:
- Remove matching entry from boot menu (the easiest way to do this is with msconfig)
- Delete files ntoskrnx.exe and winloadp.exe in the catalog % Windir% \\ System32.
The patch does not make any other changes to the system.
Greetings, dear readers! To our great joy, the prices for components are steadily creeping downward, and today 8 GB of RAM on a home computer is not something out of the ordinary, but a “minimum program” for an advanced gamer.
However, the user can expect an unpleasant surprise: regardless of the amount of RAM installed and the number of brackets on the computer, the operating system does not see all the RAM.
Today we will figure out why all the RAM is not used and how you can deal with it.
32-bit OS
To understand the essence of the problem, one should recall a little the history of the development of computer technology. I will not go into too much detail and will try to give a brief summary. On a PC created back in 1981, the commands to peripheral devices and access to RAM were combined. The ratio of the address space allocated for RAM and BIOS was 5: 3.
With the introduction of the 80386 processor in 1985, the address separation remained unchanged for compatibility with predecessor computers. Devices using the address space have been allocated a whole fourth gigabyte. At that time, such a value seemed like an exorbitant figure: Bill Gates himself, the creator of Windows, said that 640 kilobytes of RAM is enough for everyone.
This 32bit architecture became the standard by which office equipment developed over the next 20 years. In 32 bit Windows, regardless of size installed memory, only 3.25 GB is available to the user - everything else is consumed by system resources. This is observed on the outdated, but in some places still used "Piggy", and on windows 7 and on windows 10.
The fact that the user can not use all the memory for his needs is eliminated on the 64bit version of Windows. You can find out the version of Windows by finding the "Computer" item in the "Start" menu by clicking on it right click mouse and selecting "Properties". 
Please note that due to the difference in architecture, an upgrade from 32-bit to 64-bit is not possible: you will need complete reinstallation operating system. You will also have to find 64-bit drivers for all devices.
Hardware problem
It may also happen that the computer simply does not see one of the two installed rails. To fix the problem, you can experiment with the slots in which these bars are installed. Often it is enough to simply swap modules or install them in different slots.
Wiping the RAM contacts with medical or industrial alcohol can also help. If this liquid is not on hand, you can wipe them with a regular rubber band. If the modules are not installed correctly, a diagnostic wizard will start. We'll have to put the RAM in the correct position.
Configuration settings
If a situation arises when the user did not shaman with the hardware, but a part of the RAM became unavailable, it is necessary to perform the following algorithm:
- Enter msconfig in the search bar and run the found file;
- In the window that opens, go to the "Download" tab and select the "Additional parameters" item;
- In the next window, uncheck the "Maximum memory" box.
With your changes saved, restart your computer and check how much memory is now in use. The method works regardless of the tasks assigned to the computer - when executing a program or in a game. Usually in modern games there are no settings for how much RAM they are allowed to use, and in fact they are the same programs.
And I once again draw your attention to the fact that when assembling a computer yourself, be guided by the DDR4 standard. You can find out how and by clicking on the link.
Clear.
I looked at the processor specification of my old computer on the intel website - it says about it:
Instruction Set 32-bit
http://ark.intel.com/products/27438/Intel-Pentium-4-Processor-2_40-GHz-512K-Cache-533-MHz-FSB
In general, I read on the internet on this topic - I came to the conclusion that in order for Windows to see and start using 4 GB of RAM, software alone is not enough. That is, even server windows versions, in which there is a full-fledged PAE (and at least install any patches there) - they will still not be able to interact with all the memory if the chipset in the motherboard does not have additional lines for interacting with the memory. Those. in order for all this to work - in addition to software support, hardware is also needed. Again, using the example of my old computer - there is a motherboard on the i945 chipset - the instructions for the motherboard state that the memory can be installed up to 4 GB. But in reality - what do not you think of, it is still impossible to use all 4 GB there completely. We can say that the chipset is 32-bit and it will not be able to perceive addresses larger than 2 ^ 32 (this is 4 GB), i.e. physically, the microcircuit does not have so many cells for recording the address or whatever, there are not so many lines on the board ... And since the entire total address space (32-bit is obtained) goes not only to the RAM, but also to all devices - video, sound there, all sorts of controllers, etc. - then a certain part of the RAM remains without addresses and the system cannot interact with them. It turns out that in order to use all 4 GB of memory on a 32-bit chipset, you need to have nothing on the board except a processor, memory and a chipset - no other equipment. But why would such a system be needed then? :-)
But, for example, already on the G31 chip (like) there are additional 4 lines for working with memory, the address space increases to 2 ^ (32 + 4) \u003d 2 ^ 36, that is, up to 64 GB (although here, too, in fact, it turns out not 64, but 64 minus the amount of address space that the equipment will occupy).
In general, in the end it turns out that in order for Windows to interact with all memory, it is necessary that
1. Chipset mat. the board physically allowed the use of an address space of more than 32 bits.
2. Chipset mat. boards knew how to do "memory mapping" - this is when memory cells with addresses that are occupied by equipment are assigned other free addresses from the space above the first 32 bits
3. operating system knew how to use this feature mate. boards (as far as I understand, the ability of the OS to use this feature of the motherboard is called PAE - Physical Address Extensions).
Well, the conclusion (why it does not work for many) is my conclusion and, perhaps, I am mistaken.
This patch, described in the article, is only the third item listed above - software. But if the board does not physically have additional lines and does not know how to redirect memory, then nothing can be earned.